
In the IUPAC system, $PhC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{O_2}H$ is named as:
A. 3-phenylpropanoic acid
B. Benzylacetic acid
C. carboxyethyl benzene
D. 2-phenylpropanoic acid
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: As we know that carboxylic acid consists of carboxyl groups. A carboxyl group is a functional group consisting of carbonyl group $(C = O)$ with hydroxyl group $(O - H)$ attached to the same carbon atom. We can use carboxylic acids as precursors to produce other compounds like esters, aldehydes and ketones.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start by discussing what is carboxylic acid? Carboxylic acids are organic aids which has the form of $RCOOH$ here R can be a hydrogen atom (or) alkyl group (hydrocarbon atom).The general structure of carboxylic acid is,


Carboxylic acid consists of two polar functional groups namely the carbonyl group and the hydroxyl group. The carbonyl group and hydroxyl group are collectively called carboxyl groups.
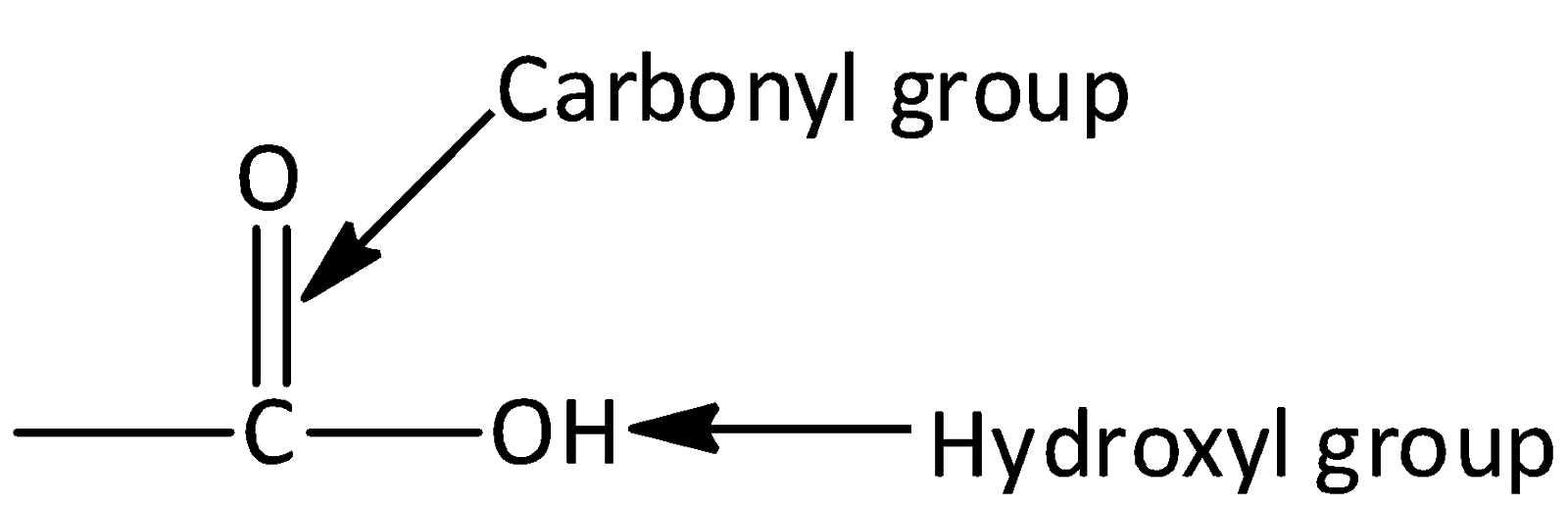
IUPAC naming of Carboxylic acids:
The longest continuous carbon chain consisting of the carboxyl group i.e. the parent compound is determined.
The carboxyl carbon is numbered as carbon-${\text{1}}$.
The –e ending of the parent alkane is replaced with suffix –oic acid. If there are two carboxyl groups,–dioic acid is used as the suffix.
The substituents are named and numbered.
The given compound is $PhC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{O_2}H$.
We can draw the structure of this compound as,
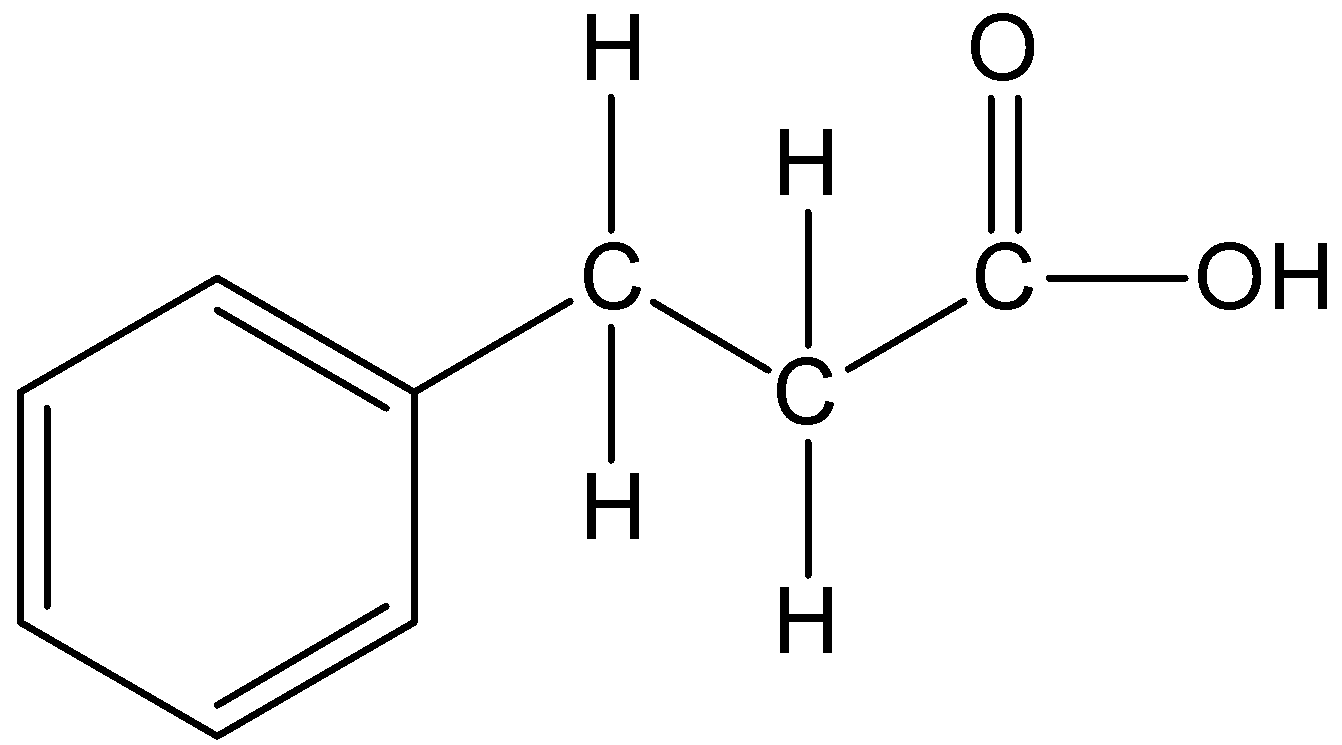
In the compound, the parent carbon chain is propane and it becomes propanoic acid. The phenyl substituent is present at the third carbon position. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is 3-phenylpropanoic acid.
So, the correct answer is Option A .
Note:
The low-molar mass carboxylic acids (one to five carbon atoms) are soluble in water. The solubility of the carboxylic acids decreases as the carbon content of the carboxylic acid increases because the molecules become more hydrocarbon like and less polar.
For example, acetic acid (the two-carbon carboxylic acid present in vinegar) is completely soluble in water, whereas hexadecanoic acid (sixteen–carbon carboxylic acid present in palm oil) is insoluble in water. The lower-mass carboxylic acids have sharp, sour tastes and unpleasant aromas. Carboxylic acid has higher boiling points than alkanes, alcohols, ethers or ketone of similar molecular weight.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start by discussing what is carboxylic acid? Carboxylic acids are organic aids which has the form of $RCOOH$ here R can be a hydrogen atom (or) alkyl group (hydrocarbon atom).The general structure of carboxylic acid is,


Carboxylic acid consists of two polar functional groups namely the carbonyl group and the hydroxyl group. The carbonyl group and hydroxyl group are collectively called carboxyl groups.

IUPAC naming of Carboxylic acids:
The longest continuous carbon chain consisting of the carboxyl group i.e. the parent compound is determined.
The carboxyl carbon is numbered as carbon-${\text{1}}$.
The –e ending of the parent alkane is replaced with suffix –oic acid. If there are two carboxyl groups,–dioic acid is used as the suffix.
The substituents are named and numbered.
The given compound is $PhC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{O_2}H$.
We can draw the structure of this compound as,

In the compound, the parent carbon chain is propane and it becomes propanoic acid. The phenyl substituent is present at the third carbon position. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is 3-phenylpropanoic acid.
So, the correct answer is Option A .
Note:
The low-molar mass carboxylic acids (one to five carbon atoms) are soluble in water. The solubility of the carboxylic acids decreases as the carbon content of the carboxylic acid increases because the molecules become more hydrocarbon like and less polar.
For example, acetic acid (the two-carbon carboxylic acid present in vinegar) is completely soluble in water, whereas hexadecanoic acid (sixteen–carbon carboxylic acid present in palm oil) is insoluble in water. The lower-mass carboxylic acids have sharp, sour tastes and unpleasant aromas. Carboxylic acid has higher boiling points than alkanes, alcohols, ethers or ketone of similar molecular weight.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




