
In the image given below, the total number of reflections of the light ray before it exits the system will be
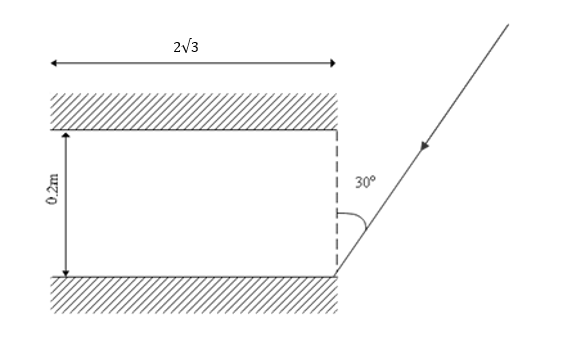
(A) 28
(B) 30
(C) 34
(D) 36

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: When light is reflected from a plane mirror, the incident angle and the reflected angle are the same. Calculate the distance covered by the light ray between two reflections and divide the total length of the plane mirrors by that distance to determine the number of reflections
Complete step by step solution:
We know that:
Length of mirror is ${\text{L}} = 2\sqrt 3 $
Distance between the mirrors is $d = 0.2$
Since the light ray is incident on a plane mirror, the ray will be reflected at the same angle with respect to the normal at which it is incident, as shown below.
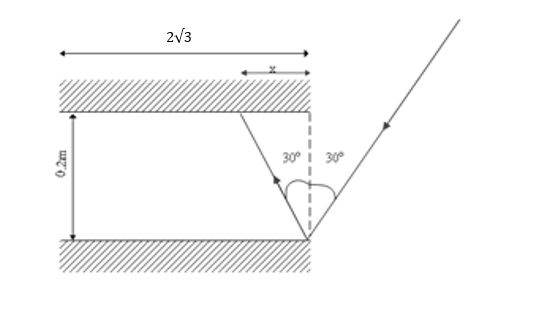
Suppose the ray covers a horizontal distance $x$ between two reflections. Further, let \[n\] be the total number of reflections the light ray undergoes before it exits the system of two mirrors.
Since we want to find out the number of reflections before the light ray exits the system, it must cover a total horizontal distance $L$ in $n$ reflections. As the ray covers distance $x$ between two reflections, to cover distance $L$, we must have $nx = L$.
And we also know that,
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{x}{d} $
$\Rightarrow x = d\tan \theta $
On substituting the value of \[x\] in $nx = L$, we get
$\Rightarrow n = \dfrac{L}{{d\tan \theta }}$
$\therefore n = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 3 }}{{0.2\tan {{30}^ \circ }}} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 3 }}{{0.2\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}}} = 30$
So, after the 30th reflection, the light ray will have covered a horizontal distance of $2\sqrt 3 \,m$ and will exit the system.
Note:
Since the light ray is reflected between two plane mirrors, it will always cover a constant amount of horizontal distance between two reflections so we don’t have to calculate the distance for each individual reflection. We must also make sure that the angle of reflection is measured with respect to the normal of the mirror plane.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that:
Length of mirror is ${\text{L}} = 2\sqrt 3 $
Distance between the mirrors is $d = 0.2$
Since the light ray is incident on a plane mirror, the ray will be reflected at the same angle with respect to the normal at which it is incident, as shown below.

Suppose the ray covers a horizontal distance $x$ between two reflections. Further, let \[n\] be the total number of reflections the light ray undergoes before it exits the system of two mirrors.
Since we want to find out the number of reflections before the light ray exits the system, it must cover a total horizontal distance $L$ in $n$ reflections. As the ray covers distance $x$ between two reflections, to cover distance $L$, we must have $nx = L$.
And we also know that,
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{x}{d} $
$\Rightarrow x = d\tan \theta $
On substituting the value of \[x\] in $nx = L$, we get
$\Rightarrow n = \dfrac{L}{{d\tan \theta }}$
$\therefore n = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 3 }}{{0.2\tan {{30}^ \circ }}} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 3 }}{{0.2\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}}} = 30$
So, after the 30th reflection, the light ray will have covered a horizontal distance of $2\sqrt 3 \,m$ and will exit the system.
Note:
Since the light ray is reflected between two plane mirrors, it will always cover a constant amount of horizontal distance between two reflections so we don’t have to calculate the distance for each individual reflection. We must also make sure that the angle of reflection is measured with respect to the normal of the mirror plane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




