
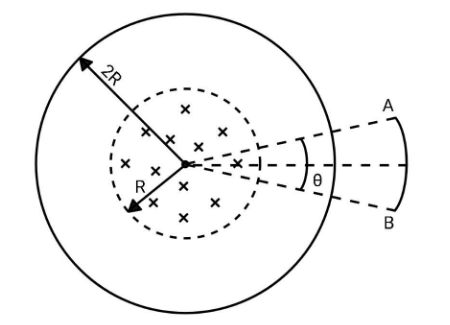
In the given figure, two concentric cylindrical regions in which time varying magnetic fields are present as shown. From the center to radius $R$ magnetic field is perpendicular into the plane varying as $\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}} = - 2{k_0}$ and in a region from $R$ to $2R$ magnetic field is perpendicular out of the plane varying as $\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}} = 4{k_0}$. Find the induced emf across an area AB of radius $3R$.
A. $6{R^2}{k_0}\theta $
B. $5{R^2}{k_0}\theta $
C. $7{R^2}{k_0}\theta $
D. None of these

Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: We are supposed to find out the emf across an area AB of radius $3R$. In order to do this, you will consider the Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction which gives the relation between the magnetic field, the area of the loop and the induced emf. Take the magnetic field in the region from centre to $R$ negative and from $R$ to $2R$ positive as they are in opposite directions.
Complete step by step answer:
The Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction is, whenever the flux of magnetic field inside a closed conducting loop changes, it creates an emf in the loop. Mathematically, the Law can be given as $\xi = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$, where $\phi $ is the flux which is given as $\phi = BA$. Here, $B$ is the magnetic field and $A$ is the area of the loop.Now, let us consider the area AB of radius $3R$. The flux through the area AB will be the flux ${\phi _1}$ and flux ${\phi _2}$ due to the magnetic fields in the cylindrical regions. Therefore, $\phi = {\phi _1} + {\phi _2}$.
Now, we have ${\phi _1} = {B_1}{A_1} = {B_1}\left( {\dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right)$
$
{A_1} + {A_2} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {2R} \right)}^2}\theta }}{2} = 2{R^2}\theta \\
\Rightarrow {A_2} = 2{R^2}\theta - \dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2} = \dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2} \\
$
Therefore, we have \[\phi = {B_1}\left( {\dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right) + {B_2}\left( {\dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right)\]
Substituting the value of flux $\phi $ in the equation of $\xi $, we get,
$
\xi = - \dfrac{d}{{dt}}\left( {{B_1}\left( {\dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right) + {B_2}\left( {\dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right)} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \xi = \dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( { - \dfrac{{d{B_1}}}{{dt}}} \right) + \dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( { - \dfrac{{d{B_2}}}{{dt}}} \right) \\ $
In the question, we are given that $\dfrac{{d{B_1}}}{{dt}} = - 2{k_0}$ and $\dfrac{{d{B_2}}}{{dt}} = 4{k_0}$
$
\Rightarrow \xi = \dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( { - \left( { - 2{k_0}} \right)} \right) + \dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( { - \left( {4{k_0}} \right)} \right) \\
\therefore\xi = \dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( {2{k_0} - 12{k_0}} \right) = - 5{R^2}{k_0}\theta $
Hence, the induced emf across an area AB of radius $3R$ is \[5{R^2}{k_0}\theta \].
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: If the rate of change of magnetic field with respect to time was not given, we would have considered the signs of the magnetic fields to be opposite to each other, that too after knowing the value or the expression of the magnetic field. Remember the Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction, whenever you see this type of question, directly apply the Faraday’s Law (keeping in mind the appropriate signs).
Complete step by step answer:
The Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction is, whenever the flux of magnetic field inside a closed conducting loop changes, it creates an emf in the loop. Mathematically, the Law can be given as $\xi = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$, where $\phi $ is the flux which is given as $\phi = BA$. Here, $B$ is the magnetic field and $A$ is the area of the loop.Now, let us consider the area AB of radius $3R$. The flux through the area AB will be the flux ${\phi _1}$ and flux ${\phi _2}$ due to the magnetic fields in the cylindrical regions. Therefore, $\phi = {\phi _1} + {\phi _2}$.
Now, we have ${\phi _1} = {B_1}{A_1} = {B_1}\left( {\dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right)$
$
{A_1} + {A_2} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {2R} \right)}^2}\theta }}{2} = 2{R^2}\theta \\
\Rightarrow {A_2} = 2{R^2}\theta - \dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2} = \dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2} \\
$
Therefore, we have \[\phi = {B_1}\left( {\dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right) + {B_2}\left( {\dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right)\]
Substituting the value of flux $\phi $ in the equation of $\xi $, we get,
$
\xi = - \dfrac{d}{{dt}}\left( {{B_1}\left( {\dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right) + {B_2}\left( {\dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2}} \right)} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \xi = \dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( { - \dfrac{{d{B_1}}}{{dt}}} \right) + \dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( { - \dfrac{{d{B_2}}}{{dt}}} \right) \\ $
In the question, we are given that $\dfrac{{d{B_1}}}{{dt}} = - 2{k_0}$ and $\dfrac{{d{B_2}}}{{dt}} = 4{k_0}$
$
\Rightarrow \xi = \dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( { - \left( { - 2{k_0}} \right)} \right) + \dfrac{{3{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( { - \left( {4{k_0}} \right)} \right) \\
\therefore\xi = \dfrac{{{R^2}\theta }}{2}\left( {2{k_0} - 12{k_0}} \right) = - 5{R^2}{k_0}\theta $
Hence, the induced emf across an area AB of radius $3R$ is \[5{R^2}{k_0}\theta \].
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: If the rate of change of magnetic field with respect to time was not given, we would have considered the signs of the magnetic fields to be opposite to each other, that too after knowing the value or the expression of the magnetic field. Remember the Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction, whenever you see this type of question, directly apply the Faraday’s Law (keeping in mind the appropriate signs).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




