
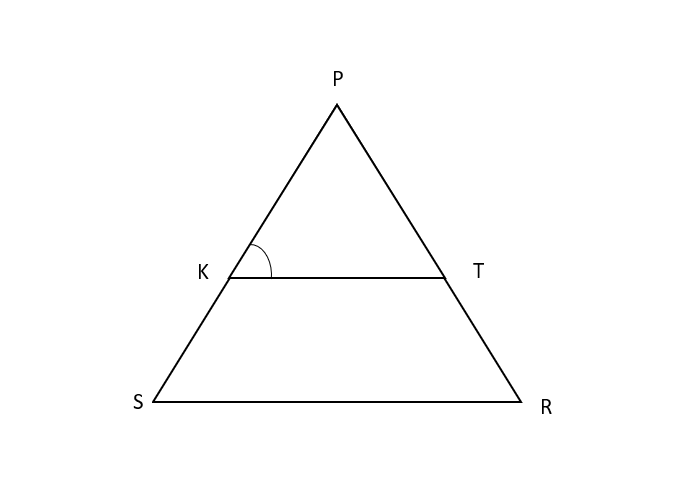
In the given figure, $\dfrac{{PK}}{{KS}} = \dfrac{{PT}}{{TR}}$ and $\angle PKT = \angle PRS$. Prove that $\Delta PSR$ is an isosceles triangle.

Answer
631.5k+ views
Hint: Try to solve using SAS congruence postulate.
Given: $\dfrac{{PK}}{{KS}} = \dfrac{{PT}}{{TR}}$ and $\angle PKT = \angle PRS$
To prove that $\Delta PSR$ is an isosceles triangle.
An isosceles triangle is a triangle with (at least) two equal sides.
Proof:
$\dfrac{{PK}}{{KS}} = \dfrac{{PT}}{{TR}}\left( {\because {\text{Given}}} \right)$
Rewriting above as:
$\dfrac{{KS}}{{KP}} = \dfrac{{RT}}{{PT}}$
Adding 1 both sides, we get
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{KS}}{{KP}} + 1 = \dfrac{{RT}}{{PT}} + 1 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{KS + KP}}{{KP}} = \dfrac{{RT + PT}}{{PT}} \\
$
Now, from the figure, we can say that \[KS + KP = PS\] and \[RT + PT = PR\].
$\therefore \dfrac{{PS}}{{KP}} = \dfrac{{PR}}{{PT}}$
Now, $\angle KPT$ is common angle to $\Delta KPT$ and $\Delta SPR$
SAS congruence postulate states that if two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then these two triangles are congruent and vice versa.
Using SAS similarity of triangles, $\Delta KPT \sim \Delta SPR$
$
\Rightarrow \angle PKT = \angle PSR \\
\Rightarrow \angle PRS = \angle PSR{\text{ }}\left( {\because \angle PKT = \angle PRS} \right) \\
$
Since, two angles of $\Delta PSR$are equal, it is an isosceles triangle.
Hence Proved.
Note: Whenever you need to prove sides as equal of a triangle, always try to prove triangles as similar. Also, we have the methods SSS (side-side-side), SAS (side-angle-side), ASA (angle-side-angle), AAS (angle-angle-side) and AAA (angle-angle-angle), to prove that two triangles are similar.
Given: $\dfrac{{PK}}{{KS}} = \dfrac{{PT}}{{TR}}$ and $\angle PKT = \angle PRS$
To prove that $\Delta PSR$ is an isosceles triangle.
An isosceles triangle is a triangle with (at least) two equal sides.
Proof:
$\dfrac{{PK}}{{KS}} = \dfrac{{PT}}{{TR}}\left( {\because {\text{Given}}} \right)$
Rewriting above as:
$\dfrac{{KS}}{{KP}} = \dfrac{{RT}}{{PT}}$
Adding 1 both sides, we get
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{KS}}{{KP}} + 1 = \dfrac{{RT}}{{PT}} + 1 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{KS + KP}}{{KP}} = \dfrac{{RT + PT}}{{PT}} \\
$
Now, from the figure, we can say that \[KS + KP = PS\] and \[RT + PT = PR\].
$\therefore \dfrac{{PS}}{{KP}} = \dfrac{{PR}}{{PT}}$
Now, $\angle KPT$ is common angle to $\Delta KPT$ and $\Delta SPR$
SAS congruence postulate states that if two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then these two triangles are congruent and vice versa.
Using SAS similarity of triangles, $\Delta KPT \sim \Delta SPR$
$
\Rightarrow \angle PKT = \angle PSR \\
\Rightarrow \angle PRS = \angle PSR{\text{ }}\left( {\because \angle PKT = \angle PRS} \right) \\
$
Since, two angles of $\Delta PSR$are equal, it is an isosceles triangle.
Hence Proved.
Note: Whenever you need to prove sides as equal of a triangle, always try to prove triangles as similar. Also, we have the methods SSS (side-side-side), SAS (side-angle-side), ASA (angle-side-angle), AAS (angle-angle-side) and AAA (angle-angle-angle), to prove that two triangles are similar.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

What were the major teachings of Baba Guru Nanak class 7 social science CBSE

What are the controls affecting the climate of Ind class 7 social science CBSE

Fill in the blanks with appropriate modals a Drivers class 7 english CBSE

In an election between two candidates one got 55 o-class-7-maths-CBSE





