
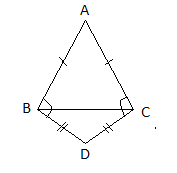
In the given figure, ABC and DBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC. Show that \[\angle ABC = \angle ACD\]

Answer
585k+ views
Hint: In an isosceles triangle, two sides are equal in length; hence its base angles are also equal.
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices, which are the basic shapes in geometry. It is a closed two-dimensional shape with three straight sides.
A triangle has three sides, and their type depends on the length of its sides and the size of its angles. There are basically three types of a triangle based on the length of the sides, namely: Scalene Triangle, Isosceles Triangle, and Equilateral Triangle.
An isosceles triangle is a triangle that has two sides of equal length. All the three angles of the isosceles triangle are acute angle, i.e., less than,\[{90^ \circ }\]whereas it’s the total sum of internal angle is \[{180^ \circ }\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given \[\vartriangle ABC\]is an isosceles triangle
Where \[AC = AB\]
Therefore \[\angle ABC = \angle ACB - - - (i)\]
[Since angle opposite to the equal sides of a triangle is equal]
Also \[\vartriangle BCD\] is an isosceles triangle
Where \[AC = AB\]
\[\angle DBC = \angle DCB - - - (ii)\]
[Since angle opposite to the equal sides of a triangle is equal]
Now add equation (i) and (ii), we get
\[\angle ACB + \angle DCB = \angle ABC + \angle DBC\]
In the figure since
\[\angle ABD = \angle ABC + \angle DBC\]
And
\[\angle ACD = \angle ACB + \angle DCB\]
Hence we conclude
\[\angle ABD = \angle ACD\]
Hence proved
Note: Another method to prove\[\angle ABD = \angle ACD\]in this question is by joining a line between the vertex A and D and proving the triangle ABD and ACD are equal and then showing\[\angle ABD = \angle ACD\] by CPCT.
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices, which are the basic shapes in geometry. It is a closed two-dimensional shape with three straight sides.
A triangle has three sides, and their type depends on the length of its sides and the size of its angles. There are basically three types of a triangle based on the length of the sides, namely: Scalene Triangle, Isosceles Triangle, and Equilateral Triangle.
An isosceles triangle is a triangle that has two sides of equal length. All the three angles of the isosceles triangle are acute angle, i.e., less than,\[{90^ \circ }\]whereas it’s the total sum of internal angle is \[{180^ \circ }\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given \[\vartriangle ABC\]is an isosceles triangle
Where \[AC = AB\]
Therefore \[\angle ABC = \angle ACB - - - (i)\]
[Since angle opposite to the equal sides of a triangle is equal]
Also \[\vartriangle BCD\] is an isosceles triangle
Where \[AC = AB\]
\[\angle DBC = \angle DCB - - - (ii)\]
[Since angle opposite to the equal sides of a triangle is equal]
Now add equation (i) and (ii), we get
\[\angle ACB + \angle DCB = \angle ABC + \angle DBC\]
In the figure since
\[\angle ABD = \angle ABC + \angle DBC\]
And
\[\angle ACD = \angle ACB + \angle DCB\]
Hence we conclude
\[\angle ABD = \angle ACD\]
Hence proved
Note: Another method to prove\[\angle ABD = \angle ACD\]in this question is by joining a line between the vertex A and D and proving the triangle ABD and ACD are equal and then showing\[\angle ABD = \angle ACD\] by CPCT.
Recently Updated Pages
Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

The coating formed on the metals such as iron silver class 12 chemistry CBSE

Metals are refined by using different methods Which class 12 chemistry CBSE

What do you understand by denaturation of proteins class 12 chemistry CBSE

Assertion Nitrobenzene is used as a solvent in FriedelCrafts class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Convert 40circ C to Fahrenheit A 104circ F B 107circ class 8 maths CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science





