
In the given figure, a fuse in one of the bulbs causes all the others to go out. Which bulb has fused?
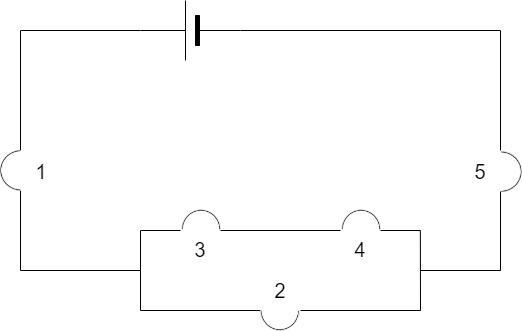
A. 1
B. 4
C. 3
D. 2

Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this problem, we have to understand the trends of the electrical properties such as voltage and current when there is a combination of two or more resistances in either series or parallel. This can help us understand the fusing of the bulb that can cause all the bulbs in the circuit to switch off.
Step by step solution:
When there are two or more resistances to be connected in the circuit, the connections can be performed in two different types: i) Series ii) Parallel
In the series, the end of one resistor is connected to the start of another resistor and all the other resistors are connected end to end, like a chain.
In the parallel, the ends of all the resistors are bundled and connected to one terminal.
The net resistance in a series circuit, is given by:
$R = {R_1} + {R_2} + .. + {R_n}$
The net resistance in the parallel circuit is given by:
$\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + .. + \dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}}$
Now, let us study the variation of the current in the series and parallel circuits.
When two or more resistors are connected in series, the current flowing through all the resistors will be the same.
When two or more resistors are connected in parallel, the main current splits into the branches and the branch current flows through the individual resistances which depends on the value of the individual resistances.
If ${R_i}$ is the resistance of a resistor in parallel and V is the voltage across the branch, the branch current is given by –
${I_i} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_i}}}$
Let us consider the following circuit:
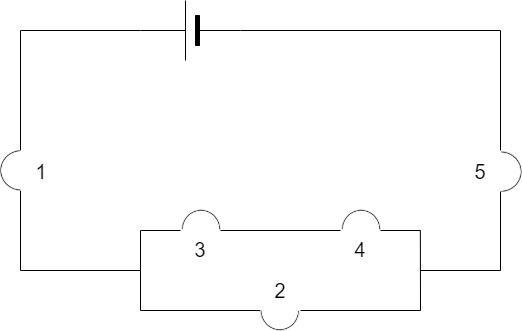
In this circuit, the bulb 1 is in series with the bulb 5 and the parallel combination of the bulbs 2, 3 and 4.
Hence, the main current will be the same through bulb 1, bulb 5 and the entire parallel combination of the bulbs 2, 3 and 4.
For all the bulbs in the series to be switched off, the bulb 1 or bulb 5 should fuse out since the fuse out of bulbs 2, 3 or 4 will not affect the current through the bulbs 1 or 5. Hence, it has to be either bulb 1 or bulb 5.
As per the given options, we can conclude that the fusing of bulb 1 will lead to switching off of all the remaining bulbs in the circuit.
Hence, the correct option is Option A.
Note:For the very same reason as explained in this problem, the appliances and devices in the domestic electric circuit are connected in parallel such that the failure of one appliance should not affect the functioning of the other bulbs.
Step by step solution:
When there are two or more resistances to be connected in the circuit, the connections can be performed in two different types: i) Series ii) Parallel
In the series, the end of one resistor is connected to the start of another resistor and all the other resistors are connected end to end, like a chain.
In the parallel, the ends of all the resistors are bundled and connected to one terminal.
The net resistance in a series circuit, is given by:
$R = {R_1} + {R_2} + .. + {R_n}$
The net resistance in the parallel circuit is given by:
$\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + .. + \dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}}$
Now, let us study the variation of the current in the series and parallel circuits.
When two or more resistors are connected in series, the current flowing through all the resistors will be the same.
When two or more resistors are connected in parallel, the main current splits into the branches and the branch current flows through the individual resistances which depends on the value of the individual resistances.
If ${R_i}$ is the resistance of a resistor in parallel and V is the voltage across the branch, the branch current is given by –
${I_i} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_i}}}$
Let us consider the following circuit:

In this circuit, the bulb 1 is in series with the bulb 5 and the parallel combination of the bulbs 2, 3 and 4.
Hence, the main current will be the same through bulb 1, bulb 5 and the entire parallel combination of the bulbs 2, 3 and 4.
For all the bulbs in the series to be switched off, the bulb 1 or bulb 5 should fuse out since the fuse out of bulbs 2, 3 or 4 will not affect the current through the bulbs 1 or 5. Hence, it has to be either bulb 1 or bulb 5.
As per the given options, we can conclude that the fusing of bulb 1 will lead to switching off of all the remaining bulbs in the circuit.
Hence, the correct option is Option A.
Note:For the very same reason as explained in this problem, the appliances and devices in the domestic electric circuit are connected in parallel such that the failure of one appliance should not affect the functioning of the other bulbs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




