
In the given diagrammatic representation of muscle contraction, identify the process marked as 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
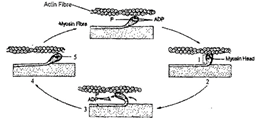
A) 1-Cross bridge, 2-Cross bridge formation, 3-Breaking of the cross bridge, 4-Sliding (rotation), 5-ATP
B) 1-Cross bridge, 2-Cross bridge formation, 3-Sliding / rotation, 4-Breaking of the cross bridge, 5-ATP
C) 1-Cross bridge, 2-Breaking of the cross bridge, 3-Sliding/rotation, 4-Cross bridge formation, 5-AMP
D) 1-Cross bridge, 2-Cross bridge formation, 3-Sliding/rotation, 4-ADP, 5-Breaking of the cross bridge.

Answer
355.5k+ views
Hint:
Skeletal muscles are contractile in nature i.e., they contract when exited. This process involves two steps 1) Neurotransmitter transmission. 2) Excitation-contraction coupling. Contraction of skeletal muscles means sliding actin and myosin fibres past each other so that the effective length of myofibril is shortened.
Complete step by step solution:
The above figure represents the sliding filament theory for skeletal muscle contraction. For the contraction to take place, actin and myosin filaments need to be located very close to each other. This Is achieved by springy titin protein that holds actin and myosin close enough to facilitate the proper functioning of sarcomere contractile machinery. This contraction cycle is explained by the sliding filament mechanism.
Myosin heads hydrolyze ATP and become reoriented and energized, after myosin heads bind to actin, forming cross-bridges then myosin heads rotate toward the centre of the sarcomere ( this is also known as power stroke) then myosin heads bind ATP and the cross-bridges detach from actin.
So 1 represents cross-bridge and 2 represents cross-bridge formation, 3 represents sliding/ rotation of myosin heads, 4 represents the breaking of cross-bridge, and 5 represents ATP to which myosin heads bind.
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note:
Neuromuscular transmission is the process by which the brain signals a muscle to contract. Its steps are: The action potential to initiate skeletal muscle contraction is delivered to the muscle where motor neuron fibers innervate the muscle fiber. This point of a nerve-muscle contract is called the neuromuscular junction or end motor plate.
Skeletal muscles are contractile in nature i.e., they contract when exited. This process involves two steps 1) Neurotransmitter transmission. 2) Excitation-contraction coupling. Contraction of skeletal muscles means sliding actin and myosin fibres past each other so that the effective length of myofibril is shortened.
Complete step by step solution:
The above figure represents the sliding filament theory for skeletal muscle contraction. For the contraction to take place, actin and myosin filaments need to be located very close to each other. This Is achieved by springy titin protein that holds actin and myosin close enough to facilitate the proper functioning of sarcomere contractile machinery. This contraction cycle is explained by the sliding filament mechanism.
Myosin heads hydrolyze ATP and become reoriented and energized, after myosin heads bind to actin, forming cross-bridges then myosin heads rotate toward the centre of the sarcomere ( this is also known as power stroke) then myosin heads bind ATP and the cross-bridges detach from actin.
So 1 represents cross-bridge and 2 represents cross-bridge formation, 3 represents sliding/ rotation of myosin heads, 4 represents the breaking of cross-bridge, and 5 represents ATP to which myosin heads bind.
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note:
Neuromuscular transmission is the process by which the brain signals a muscle to contract. Its steps are: The action potential to initiate skeletal muscle contraction is delivered to the muscle where motor neuron fibers innervate the muscle fiber. This point of a nerve-muscle contract is called the neuromuscular junction or end motor plate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE




