
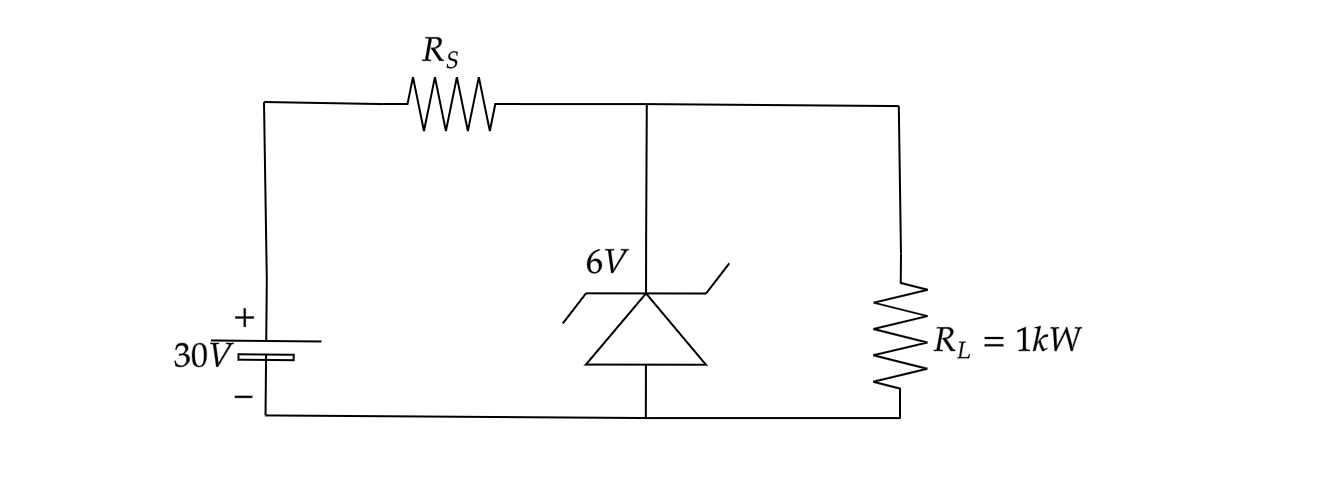
In the given circuit what is the maximum value of $ R_S $ for a zener diode to regulate voltage on load resistance?
$ \left( A \right)2k\Omega $
$ \left( B \right)5k\Omega $
$ \left( C \right)6k\Omega $
$ \left( D \right)4k\Omega $

Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint: There is a mistake in the question that the value of load resistance is given in matt it should be in ohm. If calculated by taking its power then the solution will not match with the optio. Hence we will solve by taking load resistance on kiloohm. To satisfy the given condition the voltage across the load must be equal to the enor voltage. Then using ohm’s law in the further step we can calculate the value of $ R_S $ .
Complete answer:
As per the problem we need to calculate the maximum value of $ R_S $ for a zener diode to regulate voltage on load resistance.
Now the zener diode to regulate voltage on load resistance we can write it as,
$ V_{R_L} = V_Z \ldots \ldots \left( 1 \right) $
Where,
The voltage across the load resistance is represent as $ V_{R_L} $
And the voltage across zener diode is represented as $ VZ $
Now in place of $ V_{R_L} $ we can write,
$ V_{R_L} = I_{R_L} \ldots \ldots \left( 2 \right) $
Now using ohm's law on current value we will get,
$ I = \dfrac{V}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} $
Here the load resistance and $ R_S $ are connected in series,
Hence the equivalent resistance be,
$ \operatorname{R} {\text{eq}} = R_S + R_L $
Now putting the value in the above current equation we will get,
$ I = \dfrac{V}{{R_S + R_L}} $
Putting this value in the above equation $ \left( 2 \right) $ we will get,
$ V_{R_L} = \dfrac{V}{{R_S + R_L}}R_L \ldots \ldots \left( 3 \right) $
Putting equation $ \left( 3 \right) $ in place of equation $ \left( 1 \right) $ we will get,
$ \dfrac{V}{{R_S + R_L}}R_L = V_Z $
From the figure we know,
$ V = 30V $
$ RL = 1k\Omega $
$ V_Z = 6V $
Now putting these values we will get,
$ \dfrac{{30V}}{{R_S + 1k\Omega }} \times 1k\Omega = 6V $
Cancelling the terms we will get,
$ \dfrac{{5k\Omega }}{{R_S + 1k\Omega }} = 1 $
Rearranging the above equation we will egt,
$ 5k\Omega = R_S + 1k\Omega $
Hence the value of $ R_S = 4k\Omega $ .
Therefore the correct option is $ \left( D \right) $ .
Note:
Here the zener diode is also called voltage regulator only reverse biased because it is specially made to have a reverse voltage breakdown at a specific voltage. Note that if the zener diode is biased in the forward direction it behaves like a normal signal passing the current increasing linearly with voltage, now in this case it will not act as a voltage regulator.
Complete answer:
As per the problem we need to calculate the maximum value of $ R_S $ for a zener diode to regulate voltage on load resistance.
Now the zener diode to regulate voltage on load resistance we can write it as,
$ V_{R_L} = V_Z \ldots \ldots \left( 1 \right) $
Where,
The voltage across the load resistance is represent as $ V_{R_L} $
And the voltage across zener diode is represented as $ VZ $
Now in place of $ V_{R_L} $ we can write,
$ V_{R_L} = I_{R_L} \ldots \ldots \left( 2 \right) $
Now using ohm's law on current value we will get,
$ I = \dfrac{V}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} $
Here the load resistance and $ R_S $ are connected in series,
Hence the equivalent resistance be,
$ \operatorname{R} {\text{eq}} = R_S + R_L $
Now putting the value in the above current equation we will get,
$ I = \dfrac{V}{{R_S + R_L}} $
Putting this value in the above equation $ \left( 2 \right) $ we will get,
$ V_{R_L} = \dfrac{V}{{R_S + R_L}}R_L \ldots \ldots \left( 3 \right) $
Putting equation $ \left( 3 \right) $ in place of equation $ \left( 1 \right) $ we will get,
$ \dfrac{V}{{R_S + R_L}}R_L = V_Z $
From the figure we know,
$ V = 30V $
$ RL = 1k\Omega $
$ V_Z = 6V $
Now putting these values we will get,
$ \dfrac{{30V}}{{R_S + 1k\Omega }} \times 1k\Omega = 6V $
Cancelling the terms we will get,
$ \dfrac{{5k\Omega }}{{R_S + 1k\Omega }} = 1 $
Rearranging the above equation we will egt,
$ 5k\Omega = R_S + 1k\Omega $
Hence the value of $ R_S = 4k\Omega $ .
Therefore the correct option is $ \left( D \right) $ .
Note:
Here the zener diode is also called voltage regulator only reverse biased because it is specially made to have a reverse voltage breakdown at a specific voltage. Note that if the zener diode is biased in the forward direction it behaves like a normal signal passing the current increasing linearly with voltage, now in this case it will not act as a voltage regulator.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




