
In the given circuit, the potential difference across $3\mu F$ capacitor will be:
A) 16 V
B) 10 V
C) 6 V
D) 4 V
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Kirchhoff’s first law states the total current entering a junction or a node is equal to the charge leaving the node as no charge is lost. In order to find the solution of the given question apply Kirchhoff’s first law along the given circuit.
Formula used:
$\Sigma I = 0$
Complete answer:
Kirchhoff’s first law also known as the current law is given as the sum of the current entering in a junction is equal to the sum of the current leaving the junction.
Mathematically, it is given as
$\Sigma I = 0$ ; where I is denoted as the current in the circuit.
The second law of Kirchhoff’s states that the algebraic sum of all the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is equal to zero for a closed loop series path.
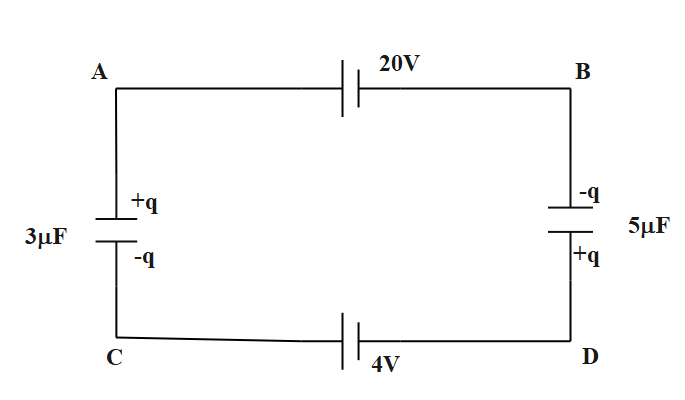
Using Kirchhoff’s voltage law in the loop ABCDA,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{q}{3} + 4 + \dfrac{q}{5} - 20 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{q}{3} + \dfrac{q}{5} = 20 - 4$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {5q + 3q} \right)}}{{15}} = 16$
$ \Rightarrow 8q = 15 \times 16$
$ \Rightarrow q = \dfrac{{\left( {15 \times 16} \right)}}{8} = 30\mu C$
$\left| {{V_A} - {V_B}} \right| = \dfrac{q}{3} = \dfrac{{30}}{3} = 10Volt$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
Kirchhoff’s law is also known as the conservation of energy, as moving around a closed loop, or a circuit, we will end up back to where we started in the circuit and thus back to the same initial potential with no loss of voltage around the loop. Therefore, any voltage drops around the loop must be equal to any voltage sources met along the way.
Note:
It is important to pay special attention to the algebraic signs of the voltage drops across the elements and the emf’s of the source, while applying Kirchhoff’s law to a specific circuit element as there are chances of making mistakes in the calculations.
Formula used:
$\Sigma I = 0$
Complete answer:
Kirchhoff’s first law also known as the current law is given as the sum of the current entering in a junction is equal to the sum of the current leaving the junction.
Mathematically, it is given as
$\Sigma I = 0$ ; where I is denoted as the current in the circuit.
The second law of Kirchhoff’s states that the algebraic sum of all the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is equal to zero for a closed loop series path.

Using Kirchhoff’s voltage law in the loop ABCDA,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{q}{3} + 4 + \dfrac{q}{5} - 20 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{q}{3} + \dfrac{q}{5} = 20 - 4$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {5q + 3q} \right)}}{{15}} = 16$
$ \Rightarrow 8q = 15 \times 16$
$ \Rightarrow q = \dfrac{{\left( {15 \times 16} \right)}}{8} = 30\mu C$
$\left| {{V_A} - {V_B}} \right| = \dfrac{q}{3} = \dfrac{{30}}{3} = 10Volt$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
Kirchhoff’s law is also known as the conservation of energy, as moving around a closed loop, or a circuit, we will end up back to where we started in the circuit and thus back to the same initial potential with no loss of voltage around the loop. Therefore, any voltage drops around the loop must be equal to any voltage sources met along the way.
Note:
It is important to pay special attention to the algebraic signs of the voltage drops across the elements and the emf’s of the source, while applying Kirchhoff’s law to a specific circuit element as there are chances of making mistakes in the calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




