
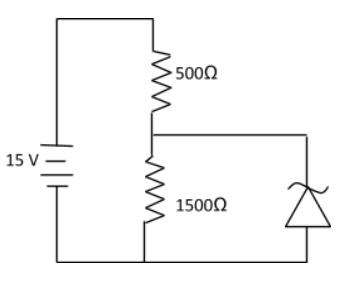
In the given circuit find the current through the Zener diode.
(A) 2.5 mA
(B) 3.3 mA
(C) 5.5 mA
(D) 6.7 mA

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Draw the circuit and show the current in the circuit and apply Kirchhoff’s current law in the circuit. According to Kirchhoff’s current law, the algebraic sum of the currents flowing through a junction is zero. After applying Kirchhoff’s law we found that the current in the Zener diode is the difference of current passing through both resistors.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The voltage of the circuit is ${V_1} = 15\;{\text{V}}$.
The voltage of the zener diode is ${V_2} = 10\;{\text{V}}$.
The value of first resistance is ${R_1} = 500\;{{\Omega }}$.
The value of second resistance is ${R_2} = 1500\;{{\Omega }}$.
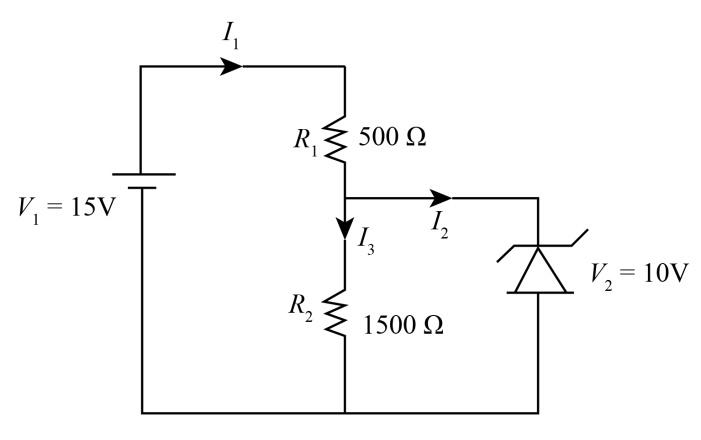
Apply Kirchhoff’s current law in the above circuit
$I_1 - I_2 - I_3 = 0 $ .......................(1)
The expression to calculate ${I_2}$ is
$I_2 = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}$ ......................(2)
Substituting $10\;{\text{V}}$ for ${V_2}$, and $1500\;{{\Omega }}$ for ${R_2}$ in (2), to find the value of ${I_2}$.
$\Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{{10\;{\text{V}}}}{{1500\;{{\Omega }}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{1}{{150}}\;{\text{A}} $.....................(3)
The expression to calculate ${I_1}$ is:
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{{{V_1} - {V_2}}}{{{R_1}}}$ ................(4)
Substituting, $10\;{\text{V}}$ for ${V_2}$, $15\;{\text{V}}$ for ${V_1}$ and $500\;{{\Omega }}$ for ${R_1}$ in (4), to find the value of ${I_1}$.
$\Rightarrow I_1 = \dfrac{{15\;{\text{V - 10}}\;{\text{V}}}}{{500\;{{\Omega }}}} $
$\Rightarrow I_1 = \dfrac{1}{{100}}\;{\text{A}} $................... (5)
From equation (1), (3) and (5)
$\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{{100}}\;{\text{A}}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{{150}}\;{\text{A}}} \right){\text{ - }}\left( {{{\text{I}}_3}} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {I_3} = \dfrac{1}{{300}}\;{\text{A}} \\
\Rightarrow {I_3} = 0.003\;{\text{A}} \times \dfrac{{1000\;{\text{mA}}}}{{1\;{\text{A}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {{\text{I}}_3} = 3.3\;{\text{mA}} \\
$
As shown in diagram ${I_3}$ the current passes through Zener diodes. So, the current passes through the Zener diode is $3.3\;{\text{mA}}$.
Additional Information:
In a Zener diode, current flows in reverse as well as forward direction when the voltage exceeds break down voltage. This breakdown voltage is known as Zener voltage. Zener diodes are widely used as voltage regulators. Zener diode is also used to limit the current through the diode and drop the excess voltage in the conducting diode.
Note:
Zener diode is the special diode which works in reverse biased and breakdown regions. Zener diodes are used as voltage regulators. When a Zener diode is connected in forward bias then its characteristics are just the same as ordinary diodes.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The voltage of the circuit is ${V_1} = 15\;{\text{V}}$.
The voltage of the zener diode is ${V_2} = 10\;{\text{V}}$.
The value of first resistance is ${R_1} = 500\;{{\Omega }}$.
The value of second resistance is ${R_2} = 1500\;{{\Omega }}$.

Apply Kirchhoff’s current law in the above circuit
$I_1 - I_2 - I_3 = 0 $ .......................(1)
The expression to calculate ${I_2}$ is
$I_2 = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}$ ......................(2)
Substituting $10\;{\text{V}}$ for ${V_2}$, and $1500\;{{\Omega }}$ for ${R_2}$ in (2), to find the value of ${I_2}$.
$\Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{{10\;{\text{V}}}}{{1500\;{{\Omega }}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{1}{{150}}\;{\text{A}} $.....................(3)
The expression to calculate ${I_1}$ is:
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{{{V_1} - {V_2}}}{{{R_1}}}$ ................(4)
Substituting, $10\;{\text{V}}$ for ${V_2}$, $15\;{\text{V}}$ for ${V_1}$ and $500\;{{\Omega }}$ for ${R_1}$ in (4), to find the value of ${I_1}$.
$\Rightarrow I_1 = \dfrac{{15\;{\text{V - 10}}\;{\text{V}}}}{{500\;{{\Omega }}}} $
$\Rightarrow I_1 = \dfrac{1}{{100}}\;{\text{A}} $................... (5)
From equation (1), (3) and (5)
$\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{{100}}\;{\text{A}}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{{150}}\;{\text{A}}} \right){\text{ - }}\left( {{{\text{I}}_3}} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {I_3} = \dfrac{1}{{300}}\;{\text{A}} \\
\Rightarrow {I_3} = 0.003\;{\text{A}} \times \dfrac{{1000\;{\text{mA}}}}{{1\;{\text{A}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {{\text{I}}_3} = 3.3\;{\text{mA}} \\
$
As shown in diagram ${I_3}$ the current passes through Zener diodes. So, the current passes through the Zener diode is $3.3\;{\text{mA}}$.
Additional Information:
In a Zener diode, current flows in reverse as well as forward direction when the voltage exceeds break down voltage. This breakdown voltage is known as Zener voltage. Zener diodes are widely used as voltage regulators. Zener diode is also used to limit the current through the diode and drop the excess voltage in the conducting diode.
Note:
Zener diode is the special diode which works in reverse biased and breakdown regions. Zener diodes are used as voltage regulators. When a Zener diode is connected in forward bias then its characteristics are just the same as ordinary diodes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




