
In the given circuit diagram, the current through the $1\Omega $ resistor is given by $Iamp$. Fill $2I$ in OMR sheet.
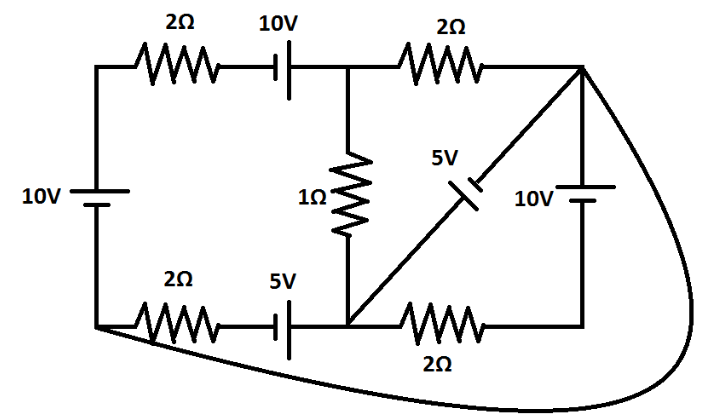

Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint:In this question, we need to find the current passing through the resistor of $1\Omega $. For this, first we need to know the potential difference for this resistor. Then, we will apply ohm’s law to find the required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will find the potential difference across the resistor of $1\Omega $. For this, we will consider the diagram as shown in the figure.
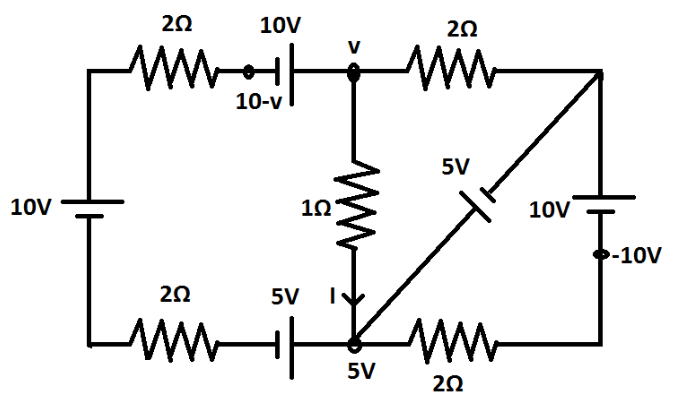
We will take the voltage of the upper-middle point to be $v$.
Now, we will consider the voltage drop which is given by:
\[
\dfrac{{(v - 10) - 10}}{2} + \dfrac{{v - 0}}{2} + \dfrac{{v - 5}}{1} = 0\; \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{30}}{4} = \dfrac{{15}}{2}V \\ \]
We will now apply the ohm’s law to find the required current.
$I = \dfrac{{v - 5}}{R} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{15}}{2} - 5}}{1} = \dfrac{{15 - 10}}{2} = \dfrac{5}{2}A$
Thus, the current flowing through the resistor of $1\Omega $ is $\dfrac{5}{2}A$.
But, here, we are asked to find the value of $2I$.
$ \therefore 2I = 2 \times \dfrac{5}{2} = 5A$
Hence, our final answer is $5A$.
Note:Here, we have used the application of Ohm’s law to determine our final answer. Ohm’s law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided all physical conditions and temperature remain constant. We can write it mathematically as:
$
V \propto I \\
\Rightarrow V = IR \\ $
Where, $V$is the potential difference, $I$ is the current and $R$ is the resistance.Ohm’s law is used to validate the static values of circuit components such as current levels, voltage supplies, and voltage drops. It is also important to know that Ohm’s law is not a universal law. This is because ohm’s law is only applicable to ohmic conductors such as iron and copper but is not applicable to non-ohmic conductors such as semiconductors.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will find the potential difference across the resistor of $1\Omega $. For this, we will consider the diagram as shown in the figure.

We will take the voltage of the upper-middle point to be $v$.
Now, we will consider the voltage drop which is given by:
\[
\dfrac{{(v - 10) - 10}}{2} + \dfrac{{v - 0}}{2} + \dfrac{{v - 5}}{1} = 0\; \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{30}}{4} = \dfrac{{15}}{2}V \\ \]
We will now apply the ohm’s law to find the required current.
$I = \dfrac{{v - 5}}{R} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{15}}{2} - 5}}{1} = \dfrac{{15 - 10}}{2} = \dfrac{5}{2}A$
Thus, the current flowing through the resistor of $1\Omega $ is $\dfrac{5}{2}A$.
But, here, we are asked to find the value of $2I$.
$ \therefore 2I = 2 \times \dfrac{5}{2} = 5A$
Hence, our final answer is $5A$.
Note:Here, we have used the application of Ohm’s law to determine our final answer. Ohm’s law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided all physical conditions and temperature remain constant. We can write it mathematically as:
$
V \propto I \\
\Rightarrow V = IR \\ $
Where, $V$is the potential difference, $I$ is the current and $R$ is the resistance.Ohm’s law is used to validate the static values of circuit components such as current levels, voltage supplies, and voltage drops. It is also important to know that Ohm’s law is not a universal law. This is because ohm’s law is only applicable to ohmic conductors such as iron and copper but is not applicable to non-ohmic conductors such as semiconductors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




