
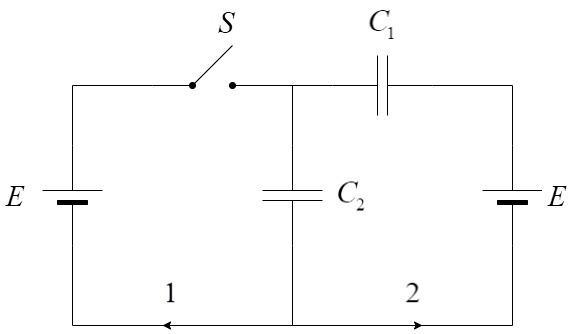
In the given circuit diagram, find the charges which flow through directions 1 and 2 when switch S is closed.

Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint:To find the charge in the capacitor, you must know the definition of the quantity called capacitance.
The capacitance of a capacitor is defined as the amount of charge to be added to the capacitor to raise its potential by 1 volt.
If q is the charge in the capacitor, the capacitance is given by –
$C = \dfrac{q}{V}$
The unit of capacitance is farad (F)
Complete step by step solution:
Let us understand the basic definition of a capacitor: A capacitor is a set of two conductors separated by a finite distance and is used to accumulate the static charges. The gap in between the two conductors is either empty (meaning air as medium) or filled with any insulating material called the dielectric medium, such as paper, rubber etc.
Let us consider the following circuit.
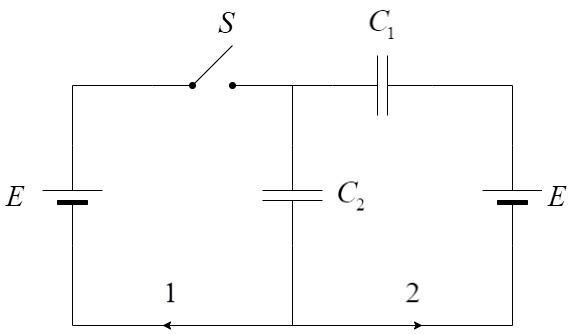
The circuit can be operated in two conditions: Switch is ON and Switch is OF
i) Let us consider the first case where the switch is OFF.

Since the capacitors are in series, the net capacitance in the circuit is,
$\dfrac{1}{C} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{{C_1}{C_2}}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}$
The charge is given by the formula: ${q_0} = CE$ where E is the potential difference.
Hence, ${q_0} = E\left( {\dfrac{{{C_1}{C_2}}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}} \right)$
ii) Let us consider the second case, where the switch is ON.
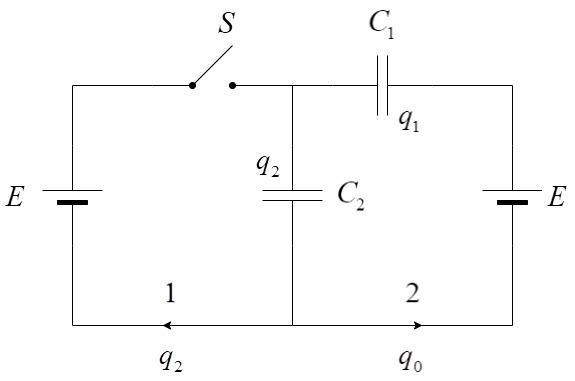
Initially, both capacitors had charge ${q_0}$. Now, when the switch closed, the new charges in these capacitors are : Charge across capacitor, ${C_1}$ is ${q_1}$ and the charge across the capacitor ${C_2}$ is ${q_2}$.
From the capacitor ${C_2}$, the charge ${q_0}$ will flow from there and branch into paths 1 and 2.
Applying Kirchhoff’s Voltage law, we get –
$\dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{C_2}}} = E$
$ \Rightarrow {q_1} = 0$
Therefore,
In the path 2, the charge ${q_0}$ flows until the capacitor ${C_1}$ has its charge reduced from ${q_0}$ to ${q_1}$, which is equal to 0.
In path 1, the remaining new charge on the capacitor ${C_2}$ which is ${q_2}$ will flow in the opposite direction.
Note:Kirchhoff's Voltage Law states that the net voltage drop across the mesh is equal to the emf of the mesh. This explains the law of conservation of energy where it states that the electric energy provided in the mesh will not go unaccounted for.
Also, students should not assume that the capacitance of a conductor depends on the charge and voltage. The capacitance of a conductor is a property of a material which is given by the formula –
$C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}$
where ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity, A is the area of the two conductors and d = the distance of separation between the two conductors.
If q is the charge in the capacitor, the capacitance is given by –
$C = \dfrac{q}{V}$
The unit of capacitance is farad (F)
Complete step by step solution:
Let us understand the basic definition of a capacitor: A capacitor is a set of two conductors separated by a finite distance and is used to accumulate the static charges. The gap in between the two conductors is either empty (meaning air as medium) or filled with any insulating material called the dielectric medium, such as paper, rubber etc.
Let us consider the following circuit.

The circuit can be operated in two conditions: Switch is ON and Switch is OF
i) Let us consider the first case where the switch is OFF.

Since the capacitors are in series, the net capacitance in the circuit is,
$\dfrac{1}{C} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{{C_1}{C_2}}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}$
The charge is given by the formula: ${q_0} = CE$ where E is the potential difference.
Hence, ${q_0} = E\left( {\dfrac{{{C_1}{C_2}}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}} \right)$
ii) Let us consider the second case, where the switch is ON.

Initially, both capacitors had charge ${q_0}$. Now, when the switch closed, the new charges in these capacitors are : Charge across capacitor, ${C_1}$ is ${q_1}$ and the charge across the capacitor ${C_2}$ is ${q_2}$.
From the capacitor ${C_2}$, the charge ${q_0}$ will flow from there and branch into paths 1 and 2.
Applying Kirchhoff’s Voltage law, we get –
$\dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{C_2}}} = E$
$ \Rightarrow {q_1} = 0$
Therefore,
In the path 2, the charge ${q_0}$ flows until the capacitor ${C_1}$ has its charge reduced from ${q_0}$ to ${q_1}$, which is equal to 0.
In path 1, the remaining new charge on the capacitor ${C_2}$ which is ${q_2}$ will flow in the opposite direction.
Note:Kirchhoff's Voltage Law states that the net voltage drop across the mesh is equal to the emf of the mesh. This explains the law of conservation of energy where it states that the electric energy provided in the mesh will not go unaccounted for.
Also, students should not assume that the capacitance of a conductor depends on the charge and voltage. The capacitance of a conductor is a property of a material which is given by the formula –
$C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}$
where ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity, A is the area of the two conductors and d = the distance of separation between the two conductors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




