
In the given circuit, charge ${Q_2}$ on the 2μF capacitor changes as $C$ is varied from 1μF to 3μF. ${Q_2}$ as a function of ‘$C$’ is given properly by:
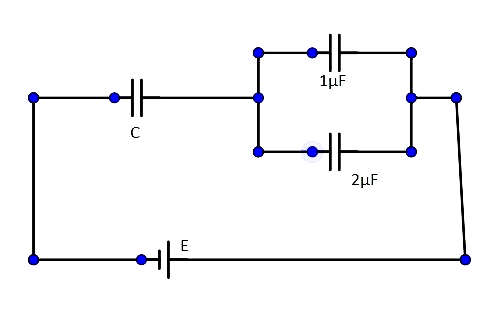
(Figures are drawn schematically and are not to scale).
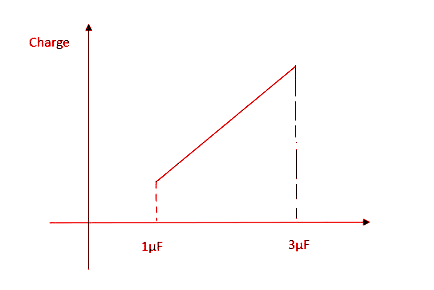
A.
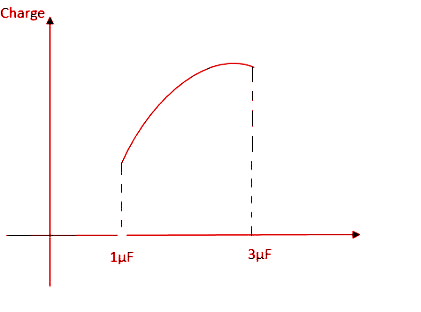
B.
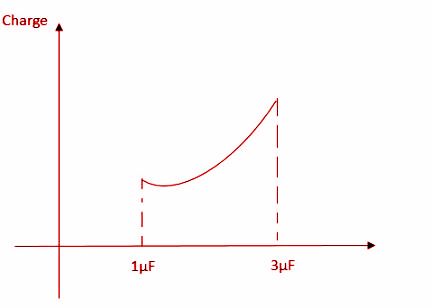
C.
D.





Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: The capacitors 1μF and 2μF are arranged in parallel and this system is arranged with the capacitor 3μF in series. The charge will increase until the capacitance is equal to 3.
Complete step-by-step answer: It is given that the capacitors 1μF and 2μF are arranged in parallel and this system is arranged with the capacitor 3μF in series.
Let the charge on the capacitor $C$ be $Q$.
Charge on the combination of 1μF and 2μF is also $Q$. This is because they are connected in series.
From the law of arrangement of capacitors, ${Q_2} = \dfrac{2}{{1 + 2}}Q = \dfrac{2}{3}Q$.
But, it is known to us that, $Q = E\left( {\dfrac{{3C}}{{3 + C}}} \right)$, from the law of arrangement of capacitors.
$\therefore {Q_2} = \dfrac{2}{3}E\left( {\dfrac{{3C}}{{3 + C}}} \right) = \dfrac{{2EC}}{{3 + C}}$
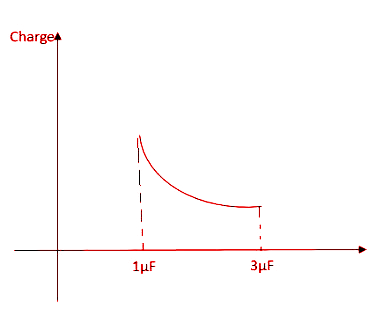
As we can see, since the value of $C$ is between 1µF and 3µF, ${Q_2}$ will increase until $C = 3$.
Options A and D are thus eliminated.
The slope of the curve is given by the formula, $\dfrac{y}{x}$.
Thus, the slope in this case is given by,
$\dfrac{{{\text{d}}\left( {{\text{Charge}}} \right)}}{{{\text{dC}}}} = \dfrac{{\left( {3 + C} \right)2E - 2EC}}{{{{\left( {3 + C} \right)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{6E}}{{{{\left( {3 + C} \right)}^2}}}$.
Thus, slope decreases as $C$ increases.
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: A capacitor is a device for storing separated charge. No single electronic component plays a more important role today than the capacitor. This device is used to store information in computer memories, to regulate voltages in power supplies, to establish electrical fields, to store electrical energy, to detect and produce electromagnetic waves, and to measure time. Any two conductors separated by an insulating medium form a capacitor.
Complete step-by-step answer: It is given that the capacitors 1μF and 2μF are arranged in parallel and this system is arranged with the capacitor 3μF in series.
Let the charge on the capacitor $C$ be $Q$.
Charge on the combination of 1μF and 2μF is also $Q$. This is because they are connected in series.
From the law of arrangement of capacitors, ${Q_2} = \dfrac{2}{{1 + 2}}Q = \dfrac{2}{3}Q$.
But, it is known to us that, $Q = E\left( {\dfrac{{3C}}{{3 + C}}} \right)$, from the law of arrangement of capacitors.
$\therefore {Q_2} = \dfrac{2}{3}E\left( {\dfrac{{3C}}{{3 + C}}} \right) = \dfrac{{2EC}}{{3 + C}}$
As we can see, since the value of $C$ is between 1µF and 3µF, ${Q_2}$ will increase until $C = 3$.
Options A and D are thus eliminated.
The slope of the curve is given by the formula, $\dfrac{y}{x}$.
Thus, the slope in this case is given by,
$\dfrac{{{\text{d}}\left( {{\text{Charge}}} \right)}}{{{\text{dC}}}} = \dfrac{{\left( {3 + C} \right)2E - 2EC}}{{{{\left( {3 + C} \right)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{6E}}{{{{\left( {3 + C} \right)}^2}}}$.
Thus, slope decreases as $C$ increases.
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: A capacitor is a device for storing separated charge. No single electronic component plays a more important role today than the capacitor. This device is used to store information in computer memories, to regulate voltages in power supplies, to establish electrical fields, to store electrical energy, to detect and produce electromagnetic waves, and to measure time. Any two conductors separated by an insulating medium form a capacitor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




