
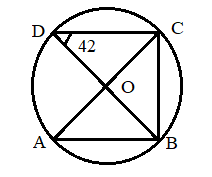
In the given circle ABCD, O is the center and $\angle BDC = 42^\circ $. The $\angle ACB$ is equal to
A) $42^\circ $
B) $45^\circ $
C) $48^\circ $
D) $60^\circ $

Answer
588k+ views
Hint: As the two sides of the $\Delta OCD$ is equal (radius). The corresponding angles are equal. Since the diameter makes a right angle on the circle. Now, the sum of the angles $\angle OCB$ and $\angle OCD$ is $90^\circ $. Then, find \[\angle OBC\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:-
$\angle BDC = 42^\circ $
$OC = OD$ are the radius of the circle.
Then, find the value of angle OCD,
As OC and OD are radii. Then $\Delta ODC$ is the isosceles triangle.
So, $\angle ODC = \angle OCD$
Put the value of angle ODC in the equation,
$\angle OCD = 42^\circ $
Now, this $\angle DCB$ is the sum of the angles COB and ACB.
$\angle DCB = \angle OCB + \angle OCD$
Since OB and OD are the radii.
The theorem states that the diameter of a circle subtends a right angle on any point of the circle.
So, $\angle DCB$ is a right angle.
Substitute the values in the above equation,
$90^\circ = 42^\circ + \angle OCB$
Move the value $42^\circ $ on the left side of the equation,
$\angle OCB = 90^\circ - 42^\circ $
Subtract 42 from 90 to get the value of the angle OCB.
$\angle OCB = 48^\circ $
Option C is the correct answer.
Note: This can be done in another way also.
Given:-
$\angle BDC = 42^\circ $
$OC = OD$ are the radius of the circle.
Then, find the value of angle OCD,
As OC and OD are radii. Then $\Delta ODC$ is the isosceles triangle.
So, $\angle ODC = \angle OCD$
Put the value of angle ODC in the equation,
$\angle OCD = 42^\circ $
Now, in $\Delta OCD$,
$\angle ODC + \angle OCD + \angle COD = 180^\circ $
Put the values of $\angle OCD$ and $ODC$,
$42^\circ + 42^\circ + \angle COD = 180^\circ $
Add the terms and move to other sides,
$\angle COD = 180^\circ - 84^\circ $
Subtract the terms on the right side of the equation,
$\angle COD = 96^\circ $
Since BOD is a straight line. Then,
$\angle COD + \angle BOC = 180^\circ $
Put the value of $\angle COD$ the equation,
$96^\circ + \angle BOC = 180^\circ $
Move the term on the other side and subtract from $180^\circ $,
$\angle BOC = 84^\circ $
As OC and OB are radii. Then $\Delta OBC$ is the isosceles triangle.
So, $\angle OBC = \angle OCB$
Now, in $\Delta OBC$,
\[\angle OBC + \angle OCB + \angle BOC = 180^\circ \]
Put the value of angle BOC in the equation,
$2\angle OCB + 84^\circ = 180^\circ $
Add the terms and move to other sides and subtract the terms on the right side of the equation,
$2\angle OCB = 96^\circ $
Divide both sides by 2,
$\angle OCB = 48^\circ $
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:-
$\angle BDC = 42^\circ $
$OC = OD$ are the radius of the circle.
Then, find the value of angle OCD,
As OC and OD are radii. Then $\Delta ODC$ is the isosceles triangle.
So, $\angle ODC = \angle OCD$
Put the value of angle ODC in the equation,
$\angle OCD = 42^\circ $
Now, this $\angle DCB$ is the sum of the angles COB and ACB.
$\angle DCB = \angle OCB + \angle OCD$
Since OB and OD are the radii.
The theorem states that the diameter of a circle subtends a right angle on any point of the circle.
So, $\angle DCB$ is a right angle.
Substitute the values in the above equation,
$90^\circ = 42^\circ + \angle OCB$
Move the value $42^\circ $ on the left side of the equation,
$\angle OCB = 90^\circ - 42^\circ $
Subtract 42 from 90 to get the value of the angle OCB.
$\angle OCB = 48^\circ $
Option C is the correct answer.
Note: This can be done in another way also.
Given:-
$\angle BDC = 42^\circ $
$OC = OD$ are the radius of the circle.
Then, find the value of angle OCD,
As OC and OD are radii. Then $\Delta ODC$ is the isosceles triangle.
So, $\angle ODC = \angle OCD$
Put the value of angle ODC in the equation,
$\angle OCD = 42^\circ $
Now, in $\Delta OCD$,
$\angle ODC + \angle OCD + \angle COD = 180^\circ $
Put the values of $\angle OCD$ and $ODC$,
$42^\circ + 42^\circ + \angle COD = 180^\circ $
Add the terms and move to other sides,
$\angle COD = 180^\circ - 84^\circ $
Subtract the terms on the right side of the equation,
$\angle COD = 96^\circ $
Since BOD is a straight line. Then,
$\angle COD + \angle BOC = 180^\circ $
Put the value of $\angle COD$ the equation,
$96^\circ + \angle BOC = 180^\circ $
Move the term on the other side and subtract from $180^\circ $,
$\angle BOC = 84^\circ $
As OC and OB are radii. Then $\Delta OBC$ is the isosceles triangle.
So, $\angle OBC = \angle OCB$
Now, in $\Delta OBC$,
\[\angle OBC + \angle OCB + \angle BOC = 180^\circ \]
Put the value of angle BOC in the equation,
$2\angle OCB + 84^\circ = 180^\circ $
Add the terms and move to other sides and subtract the terms on the right side of the equation,
$2\angle OCB = 96^\circ $
Divide both sides by 2,
$\angle OCB = 48^\circ $
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




