
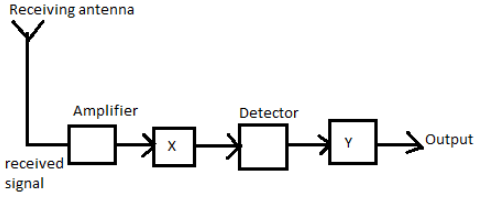
In the given block diagram of a receiver, identify the boxes labelled as X and Y and write their functions.

Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint:A communication system's block diagram would have five blocks, namely the source of input, transmitter, channel, receiver and destination blocks. This information is converted into physical quantity by the information source.
Complete step by step answer:
Receiving antenna: The reverse phase is done by receiving antennas when they absorb radio-frequency radiation and transform it into the necessary signals (e.g Conversely, a non-directional device is required where the transmitter or receiver is not stationary, as in cellular communication.
Amplifier: An amplifier increases the amplitude of the receiver. Otherwise the receiver signal may not be strong. An amplifier is the unit that converts the source equipment 's low voltage signals into a signal with ample gain to be used to control a pair of speakers.
Detector: In radio, a detector is a system or circuit that collects data from a modulated radio frequency current or voltage. The system in the receiver circuit that performed this purpose was called a detector.
X is the If stage. Moving the frequency of the carrier to a lower frequency is the intermediate step. The amplifier is Y. To compensate for the signal's attenuation, it increases the amplitude of the sensed signal. Otherwise, the detected ones might not be good enough to use.
Hence,X is the If stage and Y is the amplifier.
Note:An antenna that transforms some of the energy from the incoming radio wave into a tiny radio frequency AC voltage that is applied to the input of the receiver is attached to a radio receiver. An antenna normally consists of an array of conductors of metal.Receiver, in electronics, any of the different instruments that accept and transform (often with amplification) signals, such as radio waves, into a useful form.
Complete step by step answer:
Receiving antenna: The reverse phase is done by receiving antennas when they absorb radio-frequency radiation and transform it into the necessary signals (e.g Conversely, a non-directional device is required where the transmitter or receiver is not stationary, as in cellular communication.
Amplifier: An amplifier increases the amplitude of the receiver. Otherwise the receiver signal may not be strong. An amplifier is the unit that converts the source equipment 's low voltage signals into a signal with ample gain to be used to control a pair of speakers.
Detector: In radio, a detector is a system or circuit that collects data from a modulated radio frequency current or voltage. The system in the receiver circuit that performed this purpose was called a detector.
X is the If stage. Moving the frequency of the carrier to a lower frequency is the intermediate step. The amplifier is Y. To compensate for the signal's attenuation, it increases the amplitude of the sensed signal. Otherwise, the detected ones might not be good enough to use.
Hence,X is the If stage and Y is the amplifier.
Note:An antenna that transforms some of the energy from the incoming radio wave into a tiny radio frequency AC voltage that is applied to the input of the receiver is attached to a radio receiver. An antenna normally consists of an array of conductors of metal.Receiver, in electronics, any of the different instruments that accept and transform (often with amplification) signals, such as radio waves, into a useful form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




