
In the following sequence of reactions, what is D?
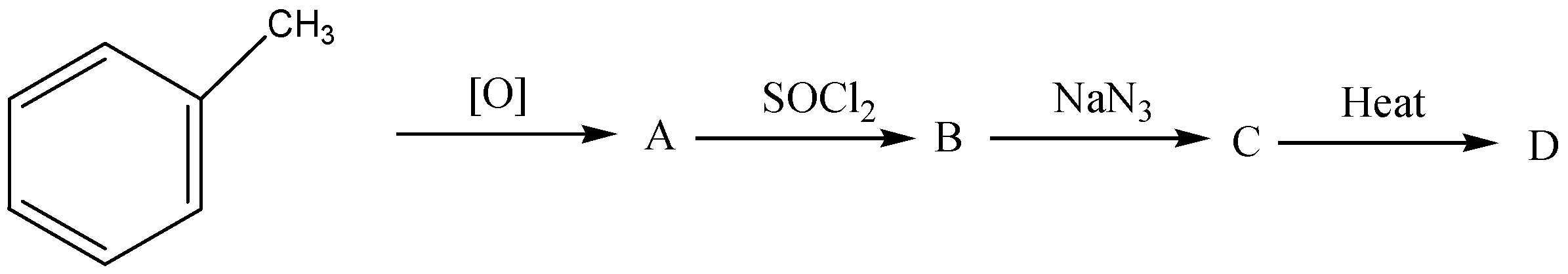
A.Primary amine
B.An amide
C.Phenyl isocyanate
D.A chain lengthened hydrocarbon

Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: When a chemical reaction is done then we write for the equation for the reaction. Chemical reactions involving organic compounds are organic reactions. The essential types are substitution reactions, addition reactions, elimination reactions, pericyclic reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
If we find out what is D then first find out what is A, B and C then the reaction sequence is complete.
First we find out A.
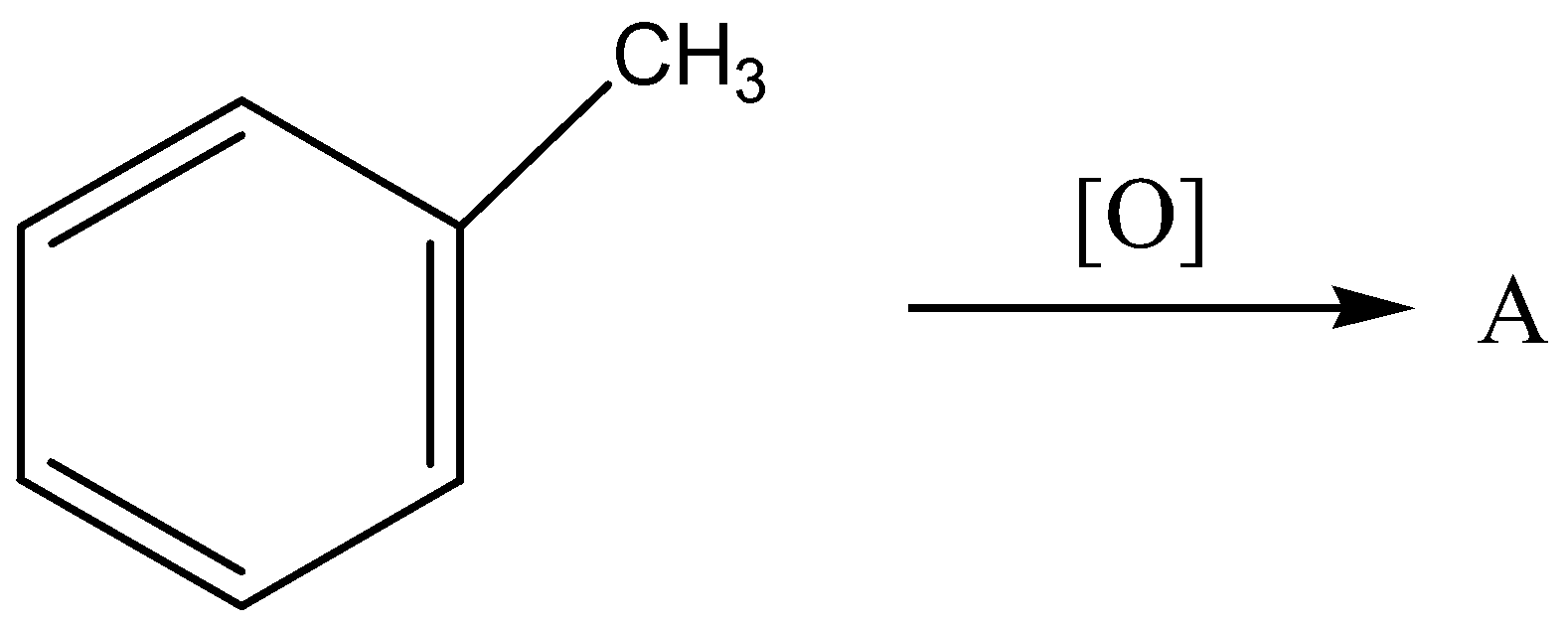
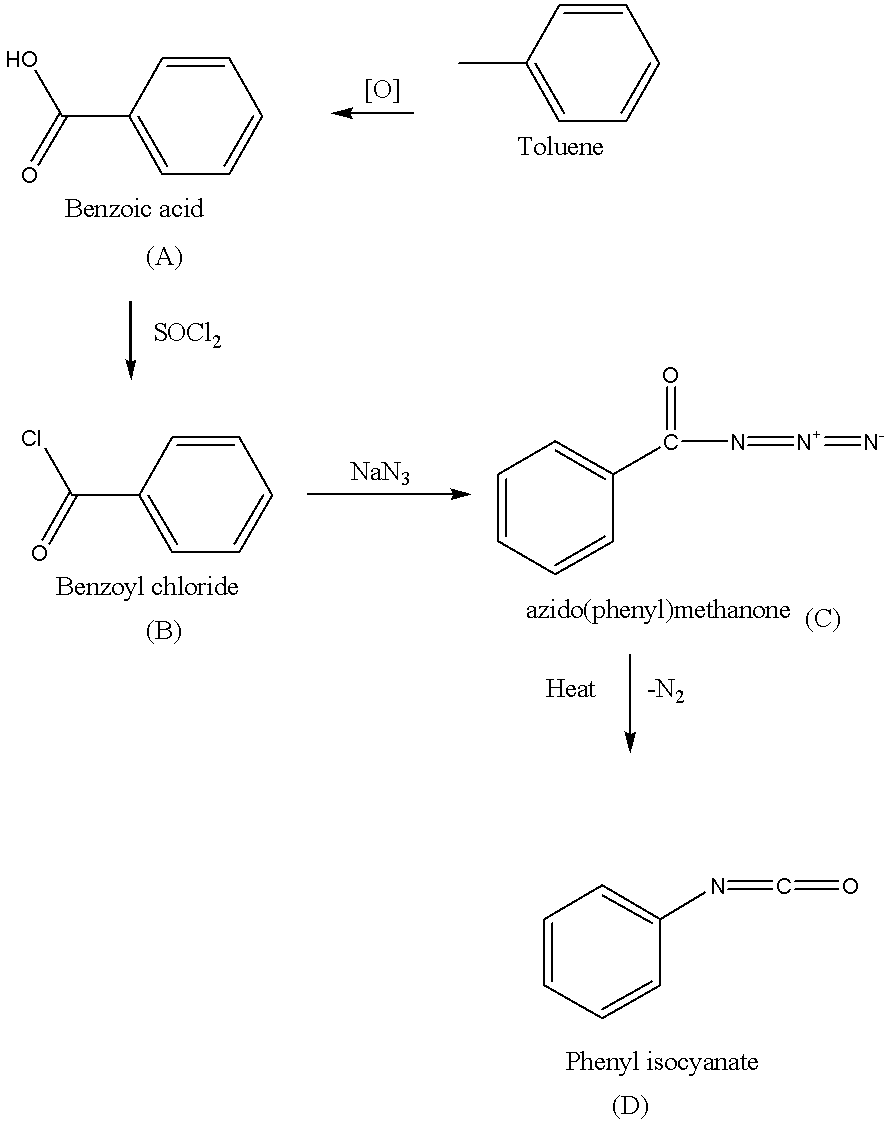
The starting compound is a toluene (also known as methyl benzene), the oxidation of toluene as follows,
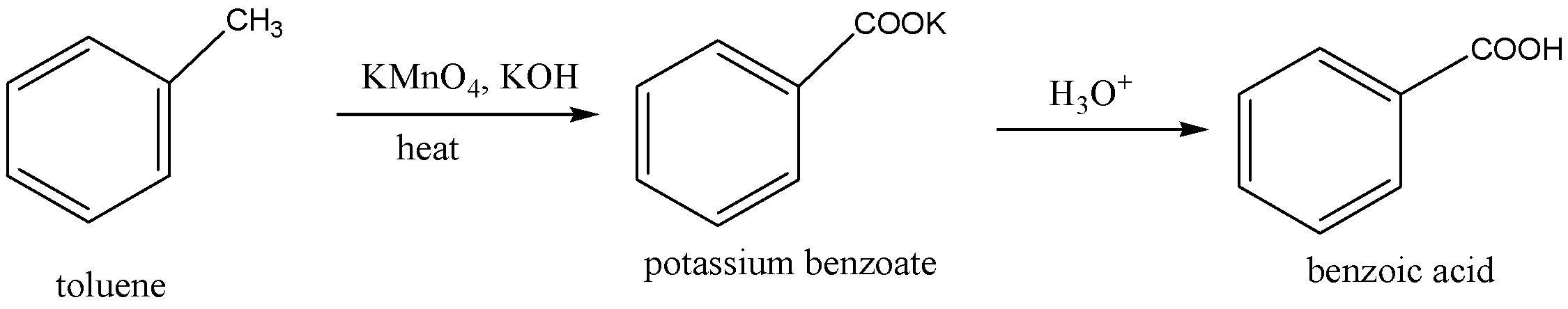
The methyl group in the toluene is oxidized by the use of potassium permanganate. Potassium hydroxide $(KOH)$ is used in the above oxidation to provide alkaline medium, because potassium permanganate have $M{n^{ + 7}}$, which is stable in alkaline medium. Then hydrolysis is carried out to give A(benzoic acid).

(A)
$A \to B$ as follows,
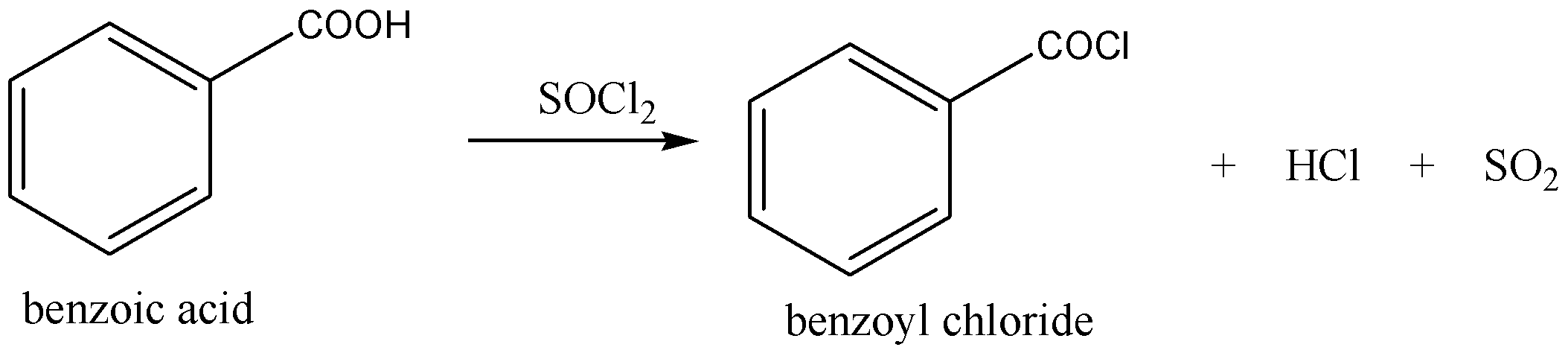
In the above reaction first nucleophile is attack on the thionyl chloride\[{\text{(SOC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}})\], the hydroxyl group is converted to a chlorosulfite intermediate, its make a better leaving group and while the chlorine ion act as a nucleophile and lastly deprotonation to B(give benzoyl chloride).
$B \to C \to D$ Sequence as follows,
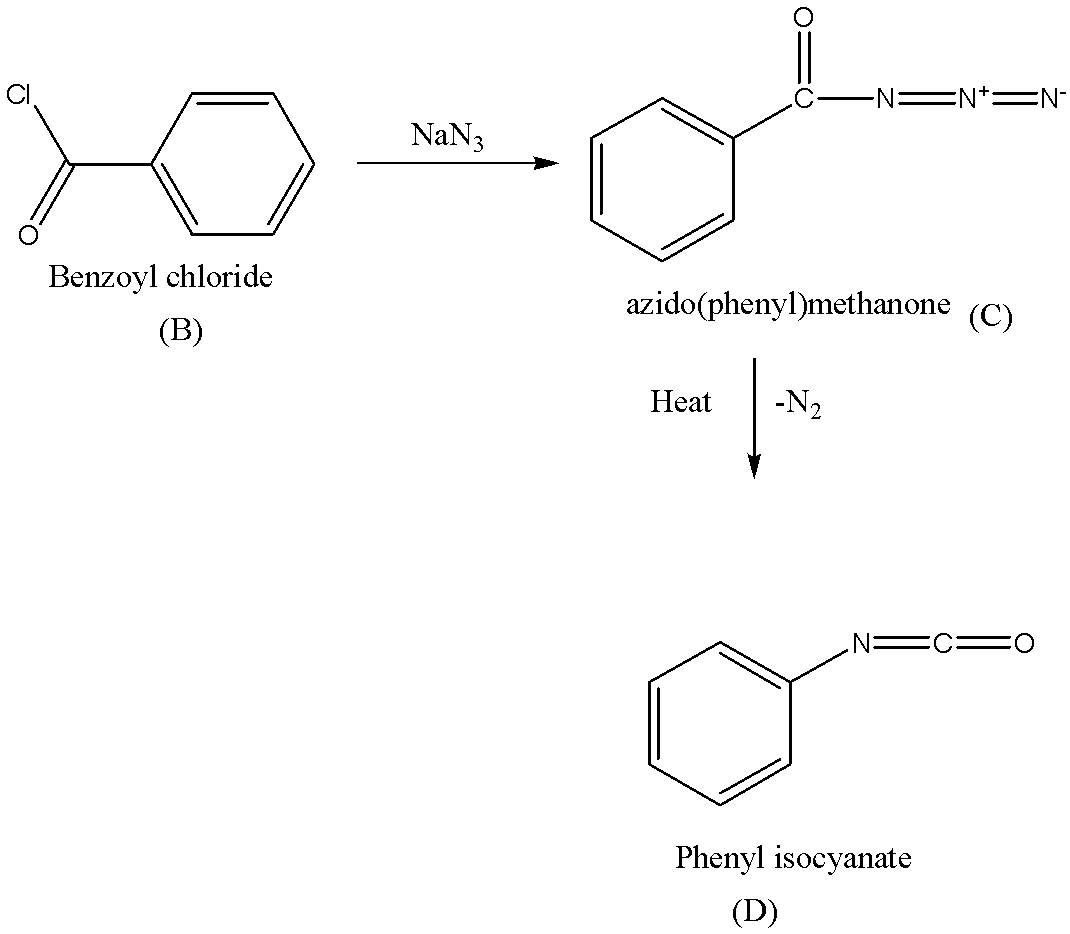
Benzoyl chloride (B) reacts with sodium azide$(Na{N_3})$to give azido(phenyl)methanone (C).
C is heated to give D (phenyl isocyanate).
The reaction sequence is as follows,
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Sequence $B \to C \to D$ in the above reaction is known as Curtius rearrangement or Curtius degradation, which is a thermal decomposition of acyl azide to give isocyanate with the liberation of nitrogen. The reaction mechanism describes the sequence of elementary reactions that has got to occur from the reactants to products. Reaction intermediates are formed in one stop then consumed during a later step of the reaction mechanism.
Complete step by step answer:
If we find out what is D then first find out what is A, B and C then the reaction sequence is complete.
First we find out A.

The starting compound is a toluene (also known as methyl benzene), the oxidation of toluene as follows,

The methyl group in the toluene is oxidized by the use of potassium permanganate. Potassium hydroxide $(KOH)$ is used in the above oxidation to provide alkaline medium, because potassium permanganate have $M{n^{ + 7}}$, which is stable in alkaline medium. Then hydrolysis is carried out to give A(benzoic acid).

(A)
$A \to B$ as follows,

In the above reaction first nucleophile is attack on the thionyl chloride\[{\text{(SOC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}})\], the hydroxyl group is converted to a chlorosulfite intermediate, its make a better leaving group and while the chlorine ion act as a nucleophile and lastly deprotonation to B(give benzoyl chloride).
$B \to C \to D$ Sequence as follows,

Benzoyl chloride (B) reacts with sodium azide$(Na{N_3})$to give azido(phenyl)methanone (C).
C is heated to give D (phenyl isocyanate).
The reaction sequence is as follows,

So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Sequence $B \to C \to D$ in the above reaction is known as Curtius rearrangement or Curtius degradation, which is a thermal decomposition of acyl azide to give isocyanate with the liberation of nitrogen. The reaction mechanism describes the sequence of elementary reactions that has got to occur from the reactants to products. Reaction intermediates are formed in one stop then consumed during a later step of the reaction mechanism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




