
In the following reaction, B is:
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow{Bro\min ation}B\xrightarrow{NaN{{O}_{2}}/HCl}C\xrightarrow[Boiling]{{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH}$
(A) Salicylic acid
(B) Benzoic acid
(C) Phenol
(D) 2, 4, 6-Tribromoaniline
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: As we need to find the product B after bromination of a compound, the product will have bromine substitute in it.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us see when the aniline goes for bromination what happens.
The $N{{H}_{2}}$ group in the aniline is a highly activating group. The lone pair of electrons present on the N releases the electron density to the benzene ring. This activates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution reactions at ortho and para positions.
In bromination $B{{r}^{+}}$ is the electrophile. The multiple substitution takes place around the ring in all the activated positions.
1. Ortho- Structure has high electron density at ortho position. So, electrophile can attack the ortho position.
2. Para- Structure has high electron density at para position also. So, electrophile can attack the para position too.
Thus, when bromine water is added to aniline (also known as phenylamine), the bromine water is decolourised and the white precipitate is formed. In short, bromination of aniline takes place resulting in the multiple substitutions of an electrophile at activated positions i.e. ortho and para.
Thus, the end product will be 2, 4, 6-Tribromoaniline.
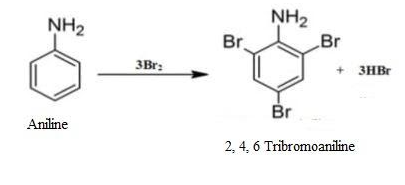
Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: Do note that the option (A), (B) and (C) can never be the answer factually as, bromination of any compound won’t result in formation of all those products given in the respective options i.e. salicylic acid, benzoic acid and phenol.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us see when the aniline goes for bromination what happens.
The $N{{H}_{2}}$ group in the aniline is a highly activating group. The lone pair of electrons present on the N releases the electron density to the benzene ring. This activates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution reactions at ortho and para positions.
In bromination $B{{r}^{+}}$ is the electrophile. The multiple substitution takes place around the ring in all the activated positions.
1. Ortho- Structure has high electron density at ortho position. So, electrophile can attack the ortho position.
2. Para- Structure has high electron density at para position also. So, electrophile can attack the para position too.
Thus, when bromine water is added to aniline (also known as phenylamine), the bromine water is decolourised and the white precipitate is formed. In short, bromination of aniline takes place resulting in the multiple substitutions of an electrophile at activated positions i.e. ortho and para.
Thus, the end product will be 2, 4, 6-Tribromoaniline.

Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: Do note that the option (A), (B) and (C) can never be the answer factually as, bromination of any compound won’t result in formation of all those products given in the respective options i.e. salicylic acid, benzoic acid and phenol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




