
In the following ray diagram the correctly marked angles are
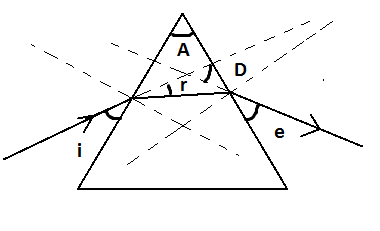
A) $\angle i$ and $\angle e$
B) \[\angle A\]and $\angle D$
C) $\angle i,\angle e$ and $\angle D$
D) $\angle r,\angle A$ and $\angle D$

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: If the medium is denser than light entering it bends towards the normal, if it is rarer then light entering it bends away from the normal. The denser medium has a higher refractive index than the rarer medium.
Complete step by step answer:
For this question, you must know all definitions rather than knowing the concepts.
Let us start with the definitions:
1. Glass prism: A glass prism is an optical device with sharp and polished edges and faces. The faces refract light incidents on them.
2. The angle of the prism (\[\angle A\]): The angle prism is the topmost angle of the prism, it is denoted as A. In the diagram below the angle, QPR is the angle of the prism, $\angle QPR = \angle A$.
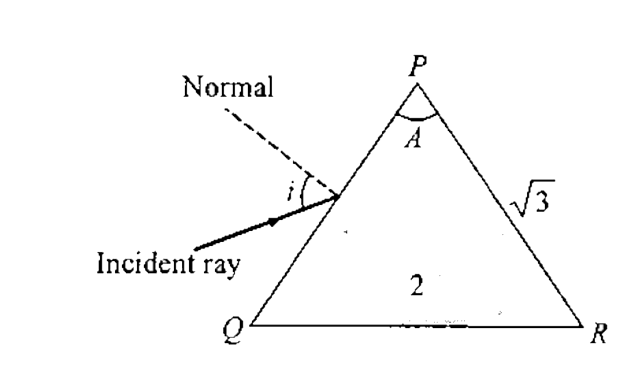
3. The angle of incidence: When light is incident on any face of the prism the angle made by the incident light ray with the normal on that face is called the angle of incidence. Angle $I$ is the angle of incident, $\angle i$= angle of incidence.
4. The angle of refraction: The angle made by the refracted ray inside the prism with the normal at the face of refraction is called the angle of refraction. It is denoted by r.
5. The angle of emergence: the angle made by the emergent ray with the normal of the final refracting face is called the angle of emergence. It is denoted by e.
6. The angle of deviation: the angle by which the final emergent ray has deviated from the incident path is called the angle of deviation. Mathematically it is written as;
$\angle D = \angle i + \angle e - \angle A$.
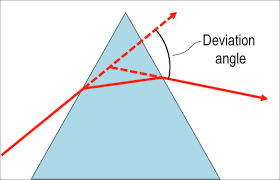
The above diagram shows the angle of deviation.
Now as we know all the definitions we can move on and solve the question.
According to definition 3 and definition 5;
The angle of incidence is marked wrong and so is the angle of emergence.
Now, according to definition 2, definition 4, and definition 6;
The angle of the prism, angle of refraction, and angle of deviation are marked correct.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note:
- Angle of the prism changes with the orientation of the prism, for instance, if the prism PQR is placed such that face PR is the base then the angle of the prism will be angle PQR.
- All other angles depend on the angle of incidence.
Complete step by step answer:
For this question, you must know all definitions rather than knowing the concepts.
Let us start with the definitions:
1. Glass prism: A glass prism is an optical device with sharp and polished edges and faces. The faces refract light incidents on them.
2. The angle of the prism (\[\angle A\]): The angle prism is the topmost angle of the prism, it is denoted as A. In the diagram below the angle, QPR is the angle of the prism, $\angle QPR = \angle A$.

3. The angle of incidence: When light is incident on any face of the prism the angle made by the incident light ray with the normal on that face is called the angle of incidence. Angle $I$ is the angle of incident, $\angle i$= angle of incidence.
4. The angle of refraction: The angle made by the refracted ray inside the prism with the normal at the face of refraction is called the angle of refraction. It is denoted by r.
5. The angle of emergence: the angle made by the emergent ray with the normal of the final refracting face is called the angle of emergence. It is denoted by e.
6. The angle of deviation: the angle by which the final emergent ray has deviated from the incident path is called the angle of deviation. Mathematically it is written as;
$\angle D = \angle i + \angle e - \angle A$.

The above diagram shows the angle of deviation.
Now as we know all the definitions we can move on and solve the question.
According to definition 3 and definition 5;
The angle of incidence is marked wrong and so is the angle of emergence.
Now, according to definition 2, definition 4, and definition 6;
The angle of the prism, angle of refraction, and angle of deviation are marked correct.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note:
- Angle of the prism changes with the orientation of the prism, for instance, if the prism PQR is placed such that face PR is the base then the angle of the prism will be angle PQR.
- All other angles depend on the angle of incidence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




