
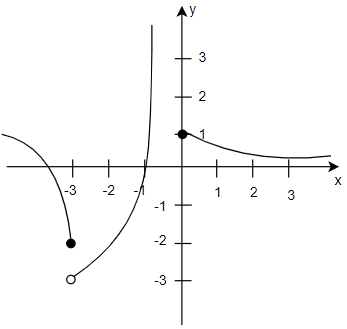
In the following graph how do you determine the value of c such that \[\displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}f\left( x \right)\] exists?

Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: Here we have to determine the value of c such that \[\displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}f\left( x \right)\] exists. We can see that in the graph the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is defined when x = -2 but the value which \[f\left( x \right)\] will approach as x gets closer to -3 from the left is different from the value as it approaches from the right. We can apply the limits by looking at the graph and find the c values.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have to determine the value of c such that \[\displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}f\left( x \right)\] exists.
We can see that in the graph the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is defined when x = -2 but the value which \[f\left( x \right)\] will approach as x gets closer to -3 from the left is different from the value as it approaches from the right.
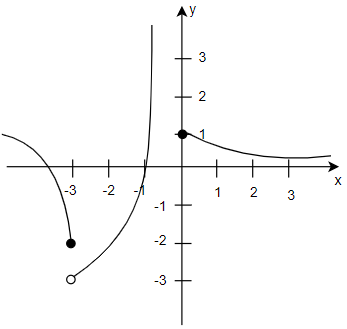
We can now analyse the graph, as x approaches -3 from left \[f\left( x \right)\] approaches (negative 2) however as x approaches -3 from the right \[f\left( x \right)\] approaches (negative 3)
We can now apply the limits, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to -{{3}^{+}}}=-3 \\
& \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to -{{3}^{-}}}=-2 \\
\end{align}\]
Where the limit does not exist at x = -3.
We can now see that, in the same way when x tends to 0, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{0}^{+}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{0}^{-}}}=+\infty \\
\end{align}\]
So, clearly we can assume that c = -3 or c = 0, but the limit does not exist.
Note: here we have already given a graph, from which we can analyse the numbers to be found and we can assume the limit values to find the value for what we have been asked for. We should also know how to apply the limit concept to solve these types.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have to determine the value of c such that \[\displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}f\left( x \right)\] exists.
We can see that in the graph the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is defined when x = -2 but the value which \[f\left( x \right)\] will approach as x gets closer to -3 from the left is different from the value as it approaches from the right.

We can now analyse the graph, as x approaches -3 from left \[f\left( x \right)\] approaches (negative 2) however as x approaches -3 from the right \[f\left( x \right)\] approaches (negative 3)
We can now apply the limits, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to -{{3}^{+}}}=-3 \\
& \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to -{{3}^{-}}}=-2 \\
\end{align}\]
Where the limit does not exist at x = -3.
We can now see that, in the same way when x tends to 0, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{0}^{+}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{0}^{-}}}=+\infty \\
\end{align}\]
So, clearly we can assume that c = -3 or c = 0, but the limit does not exist.
Note: here we have already given a graph, from which we can analyse the numbers to be found and we can assume the limit values to find the value for what we have been asked for. We should also know how to apply the limit concept to solve these types.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




