
In the following diagram, the potential difference across 6V cell is:
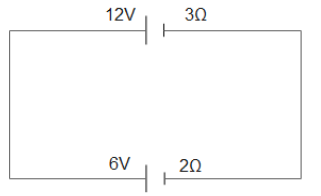
A) 6V
B) 5.6V
C) 8.2V
D) 8.4V

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: First we have to observe the given circuit there is mentioned voltage and resistance with this help we find current flowing through the circuit. By applying this current value we calculate potential difference across 6V cells.
Formula used:
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
$V = E + IR$
Complete answer:
In the given diagram the positive end of the battery is connected to the same end of the wire so the current flows in the opposite direction.
We know that ohm's law
$V = IR$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
where V is the voltage
I is the current flowing through the circuit.
R is the resistance applied in the circuit.
Total resistance applied
$
\Rightarrow R = 3 + 2 \\
\therefore R = 5 \\
$
Substitute this value in the formula we get.
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{\left( {12 - 6} \right)}}{5}$
$
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{6}{5} \\
\therefore I = 1.2A \\
$
Therefore the total current flowing through the circuit is 1.2 A.
Lets calculate the potential difference across the 6V cell.
$V = E + IR$
V is the potential difference, nothing but voltage.
E is the EMF.
I is the total current flowing through the circuit which we got earlier.
R is the resistance applied through the 6v cell.
By substituting values we get.
$ \Rightarrow V = 6 + \left( {1.2 \times 2} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow V = 6 + 2.4$
$\therefore V = 8.4$V
Hence, the potential difference across the 6V cell is 8.4 V.
The given option D is the correct answer.
Additional information:
EMF long-form is an electromotive force, which states that it is the maximum voltage the circuit can attain.
When we place a voltmeter across the considered cell shows an EMF.
The potential difference is nothing but the difference of the voltage before and after experiencing the resistance effect.
Ohm's law states that an electric current is proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
Note:
We can solve this question by applying Kirchoff's voltage law in the loop from this we get total current flowing through the circuit. Next step we find potential differences across the 6V cell.
Formula used:
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
$V = E + IR$
Complete answer:
In the given diagram the positive end of the battery is connected to the same end of the wire so the current flows in the opposite direction.
We know that ohm's law
$V = IR$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
where V is the voltage
I is the current flowing through the circuit.
R is the resistance applied in the circuit.
Total resistance applied
$
\Rightarrow R = 3 + 2 \\
\therefore R = 5 \\
$
Substitute this value in the formula we get.
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{\left( {12 - 6} \right)}}{5}$
$
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{6}{5} \\
\therefore I = 1.2A \\
$
Therefore the total current flowing through the circuit is 1.2 A.
Lets calculate the potential difference across the 6V cell.
$V = E + IR$
V is the potential difference, nothing but voltage.
E is the EMF.
I is the total current flowing through the circuit which we got earlier.
R is the resistance applied through the 6v cell.
By substituting values we get.
$ \Rightarrow V = 6 + \left( {1.2 \times 2} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow V = 6 + 2.4$
$\therefore V = 8.4$V
Hence, the potential difference across the 6V cell is 8.4 V.
The given option D is the correct answer.
Additional information:
EMF long-form is an electromotive force, which states that it is the maximum voltage the circuit can attain.
When we place a voltmeter across the considered cell shows an EMF.
The potential difference is nothing but the difference of the voltage before and after experiencing the resistance effect.
Ohm's law states that an electric current is proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
Note:
We can solve this question by applying Kirchoff's voltage law in the loop from this we get total current flowing through the circuit. Next step we find potential differences across the 6V cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




