
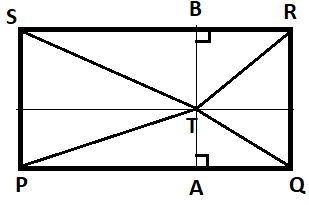
In the figure point $T$ is the interior of the rectangle $PQRS$.
Prove that $T{S^2} + T{Q^2} = T{P^2} + T{R^2}$
As shown in the figure, draw segment $AB\parallel PS$ and $ATB$.

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: First of all this is a very simple problem, and basic mathematics are needed here to solve this. In order to understand how to approach this problem, we have to know about the basic properties of a rectangle, and the properties of a right angled triangle. We should have an idea about the Pythagoras theorem, where if a right-angled triangle named ABC with hypotenuse AC and the other two sides AB and BC, then the Pythagoras theorem is given by:
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given that there is a rectangle $PQRS$
Now $T$ is any interior point in the rectangle $PQRS$.
Now the AB line segment is parallel to PS and RQ.
The line segment AB is perpendicular to RS and PQ, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow AB \bot RS$ and $AB \bot PQ$
Now consider the triangle PTA, this is a right angled triangle. Hence it obeys the Pythagoras theorem, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} = P{A^2} + A{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} - P{A^2} = A{T^2}$
Now consider the triangle ATQ, this is a right angled triangle. Hence it obeys the Pythagoras theorem, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow Q{T^2} = Q{A^2} + A{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow Q{T^2} - Q{A^2} = A{T^2}$
From the above two expressions equating the $A{T^2}$ expressions, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} - P{A^2} = A{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow Q{T^2} - Q{A^2} = A{T^2}$
$\therefore P{T^2} - P{A^2} = Q{T^2} - Q{A^2}$
Now consider the triangle SBT, this is a right angled triangle. Hence it obeys the Pythagoras theorem, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} = S{B^2} + B{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} - S{B^2} = B{T^2}$
Now consider the triangle BRT, this is a right angled triangle. Hence it obeys the Pythagoras theorem, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow R{T^2} = R{B^2} + B{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow R{T^2} - R{B^2} = B{T^2}$
From the above two expressions equating the $B{T^2}$ expressions, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} - S{B^2} = B{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow R{T^2} - R{B^2} = B{T^2}$
$\therefore S{T^2} - S{B^2} = R{T^2} - R{B^2}$
From the rectangle it is clear that as AB is perpendicular to RS and PQ, which is given by:
$ \Rightarrow AB \bot RS$ and $AB \bot PQ$
$\therefore SB = PA$ and $RB = QA$
Substituting these expressions in the equation $S{T^2} - S{B^2} = R{T^2} - R{B^2}$, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} - P{A^2} = R{T^2} - Q{A^2}$
Now subtracting both the equations obtained, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} - P{A^2} = Q{T^2} - Q{A^2}$
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} - P{A^2} = R{T^2} - Q{A^2}$
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} - S{T^2} = Q{T^2} - R{T^2}$
Rearranging the terms gives:
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} + R{T^2} = Q{T^2} + S{T^2}$
$\therefore T{S^2} + T{Q^2} = T{P^2} + T{R^2}$
Hence proved.
Note: While solving such kind of problems always Pythagoras theorem helps, which is important to keep that in mind. This problem can be done in the same way but slight changes, here instead of substituting the values of $SB = PA$ and $RB = QA$ in the second equation, and subtracting the two equations, we can substitute the values of $PA = SB$ and $QA = RB$ in the first equation, and subtract the resulting two equations to get the same result.
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given that there is a rectangle $PQRS$
Now $T$ is any interior point in the rectangle $PQRS$.
Now the AB line segment is parallel to PS and RQ.
The line segment AB is perpendicular to RS and PQ, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow AB \bot RS$ and $AB \bot PQ$
Now consider the triangle PTA, this is a right angled triangle. Hence it obeys the Pythagoras theorem, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} = P{A^2} + A{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} - P{A^2} = A{T^2}$
Now consider the triangle ATQ, this is a right angled triangle. Hence it obeys the Pythagoras theorem, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow Q{T^2} = Q{A^2} + A{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow Q{T^2} - Q{A^2} = A{T^2}$
From the above two expressions equating the $A{T^2}$ expressions, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} - P{A^2} = A{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow Q{T^2} - Q{A^2} = A{T^2}$
$\therefore P{T^2} - P{A^2} = Q{T^2} - Q{A^2}$
Now consider the triangle SBT, this is a right angled triangle. Hence it obeys the Pythagoras theorem, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} = S{B^2} + B{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} - S{B^2} = B{T^2}$
Now consider the triangle BRT, this is a right angled triangle. Hence it obeys the Pythagoras theorem, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow R{T^2} = R{B^2} + B{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow R{T^2} - R{B^2} = B{T^2}$
From the above two expressions equating the $B{T^2}$ expressions, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} - S{B^2} = B{T^2}$
$ \Rightarrow R{T^2} - R{B^2} = B{T^2}$
$\therefore S{T^2} - S{B^2} = R{T^2} - R{B^2}$
From the rectangle it is clear that as AB is perpendicular to RS and PQ, which is given by:
$ \Rightarrow AB \bot RS$ and $AB \bot PQ$
$\therefore SB = PA$ and $RB = QA$
Substituting these expressions in the equation $S{T^2} - S{B^2} = R{T^2} - R{B^2}$, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} - P{A^2} = R{T^2} - Q{A^2}$
Now subtracting both the equations obtained, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} - P{A^2} = Q{T^2} - Q{A^2}$
$ \Rightarrow S{T^2} - P{A^2} = R{T^2} - Q{A^2}$
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} - S{T^2} = Q{T^2} - R{T^2}$
Rearranging the terms gives:
$ \Rightarrow P{T^2} + R{T^2} = Q{T^2} + S{T^2}$
$\therefore T{S^2} + T{Q^2} = T{P^2} + T{R^2}$
Hence proved.
Note: While solving such kind of problems always Pythagoras theorem helps, which is important to keep that in mind. This problem can be done in the same way but slight changes, here instead of substituting the values of $SB = PA$ and $RB = QA$ in the second equation, and subtracting the two equations, we can substitute the values of $PA = SB$ and $QA = RB$ in the first equation, and subtract the resulting two equations to get the same result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




