
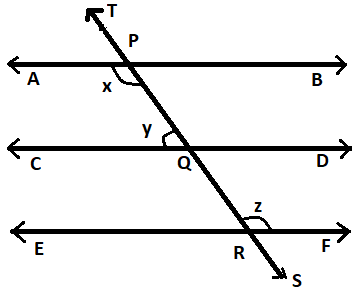
In the figure given below, if $AB\parallel CD,CD\parallel EF$ and $y:z = 3:7,$ find $x$

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: Given three parallel lines equidistant from each other. A transversal line intersects these three parallel lines lying in the same plane at three distinct points. The angles formed when this transversal line intersects these three lines are the corresponding angles. These corresponding angles are congruent angles as these three lines are parallel. The transversal and parallel lines are corresponding pairs.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that there are three parallel lines AB, CD, and EF.
The transverse line TS intersects these three parallel lines AB, CD, and EF at three distinct points at P, Q, and R respectively.
Given that the following angles are denoted by:
$ \Rightarrow \angle APQ = \angle x$
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQC = \angle y$
$ \Rightarrow \angle QRF = \angle z$
Now as a straight line makes an angle of ${180^ \circ }$, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \angle APQ = \angle x$
\[ \Rightarrow \angle APQ + \angle APT = {180^ \circ }\]
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQC = \angle y$
As $\angle APT,\angle PQC$ are corresponding angles, which are given below:
$ \Rightarrow \angle APT = \angle PQC$
\[\therefore \angle x + \angle y = {180^ \circ }\]
As $AB,CD$ are parallel lines , hence $\angle APQ,\angle PQD$ are transversal angles.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle APQ = \angle PQD\]
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQD = \angle x$
As $CD,EF$ are parallel lines, hence $\angle PQC,\angle QRE$ are transversal angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQC = \angle QRE$
$ \Rightarrow \angle QRE = y$
Also given that $\angle QRF = \angle z$
$ \Rightarrow \angle QRE + \angle QRF = {180^ \circ }$
$\therefore y + z = {180^ \circ }$
As $CD,EF$ are parallel lines, hence $\angle PQD,\angle QRF$ are corresponding angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQD = \angle QRF$
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQD = \angle x$
$\therefore \angle x = \angle z$
Given that $y:z = 3:7,$ which is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{z} = \dfrac{3}{7}$
$ \Rightarrow z = \dfrac{7}{3}y$
But we know that $x = z$
$\therefore x = \dfrac{7}{3}y$
$\because \angle x + \angle y = {180^ \circ }$
Substituting the $x = \dfrac{7}{3}y$ in the above expression:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{7}{3}\angle y + \angle y = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{10}}{3}\angle y = {180^ \circ }$
$\therefore \angle y = {54^ \circ }$
Now solving the value of $x$, from the expression $\angle x + \angle y = {180^ \circ }$, which is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \angle x + {54^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }$
$\therefore \angle x = {126^ \circ }$
The value of angle $x$ is ${126^ \circ }$.
Note: Please note that there is a difference between the corresponding angles and the transversal angles. When two parallel lines are intersected by another line which is called the transversal line, the angles in the matching corners are called the corresponding angles. These corresponding angles are equal when the two lines are parallel. Transversal angles are those angles at the point of intersection, the angles which are opposite to each other.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that there are three parallel lines AB, CD, and EF.
The transverse line TS intersects these three parallel lines AB, CD, and EF at three distinct points at P, Q, and R respectively.
Given that the following angles are denoted by:
$ \Rightarrow \angle APQ = \angle x$
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQC = \angle y$
$ \Rightarrow \angle QRF = \angle z$
Now as a straight line makes an angle of ${180^ \circ }$, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \angle APQ = \angle x$
\[ \Rightarrow \angle APQ + \angle APT = {180^ \circ }\]
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQC = \angle y$
As $\angle APT,\angle PQC$ are corresponding angles, which are given below:
$ \Rightarrow \angle APT = \angle PQC$
\[\therefore \angle x + \angle y = {180^ \circ }\]
As $AB,CD$ are parallel lines , hence $\angle APQ,\angle PQD$ are transversal angles.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle APQ = \angle PQD\]
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQD = \angle x$
As $CD,EF$ are parallel lines, hence $\angle PQC,\angle QRE$ are transversal angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQC = \angle QRE$
$ \Rightarrow \angle QRE = y$
Also given that $\angle QRF = \angle z$
$ \Rightarrow \angle QRE + \angle QRF = {180^ \circ }$
$\therefore y + z = {180^ \circ }$
As $CD,EF$ are parallel lines, hence $\angle PQD,\angle QRF$ are corresponding angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQD = \angle QRF$
$ \Rightarrow \angle PQD = \angle x$
$\therefore \angle x = \angle z$
Given that $y:z = 3:7,$ which is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{z} = \dfrac{3}{7}$
$ \Rightarrow z = \dfrac{7}{3}y$
But we know that $x = z$
$\therefore x = \dfrac{7}{3}y$
$\because \angle x + \angle y = {180^ \circ }$
Substituting the $x = \dfrac{7}{3}y$ in the above expression:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{7}{3}\angle y + \angle y = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{10}}{3}\angle y = {180^ \circ }$
$\therefore \angle y = {54^ \circ }$
Now solving the value of $x$, from the expression $\angle x + \angle y = {180^ \circ }$, which is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \angle x + {54^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }$
$\therefore \angle x = {126^ \circ }$
The value of angle $x$ is ${126^ \circ }$.
Note: Please note that there is a difference between the corresponding angles and the transversal angles. When two parallel lines are intersected by another line which is called the transversal line, the angles in the matching corners are called the corresponding angles. These corresponding angles are equal when the two lines are parallel. Transversal angles are those angles at the point of intersection, the angles which are opposite to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




