
In the figure, $ABC$ is a triangle in which $\angle ABC < 90^\circ $ and $AD \bot BC$. Prove that $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} - 2BC.BD$.
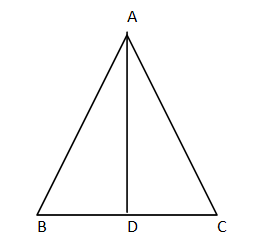

Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Here we are given that $AD \bot BC$. So we got two right angled triangles. So using the Pythagoras theorem in the $\Delta ABD$
$A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}$ and in the triangle $ADC$, we get that
$A{C^2} = A{D^2} + D{C^2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
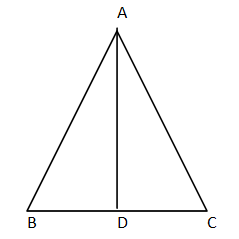
In the given figure in the triangle $ABC$ where $\angle B < 90^\circ $
To prove: $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} - 2BC.BD$
And$AD$ is the product such that$AD \bot BC$. Therefore we have got two right angled triangles.
Here we get that $AD \bot BC$.
So now in$\Delta ABD$
$AD \bot BC$ so $\angle ADB = 90^\circ $
So we can use the Pythagoras theorem where
${({\text{hypotenuse)}}^2} = {({\text{base)}}^2} + {{\text{(perpendicular)}}^2}$
In$\Delta ABD$
$A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}$$ - - - - - (1)$
In $\Delta ADC$
$AD \bot BC$
So $\angle ADC = 90^\circ $
Hence we get that
$A{C^2} = A{D^2} + D{C^2}$$ - - - - (2)$
Now we substitute $DC = BC - BD$ and also the value got from (1)
So putting these in the equation (2), we get
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} - B{D^2} + B{C^2} + B{D^2} - 2BC.BD$
So we get that
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} - 2BC.BD$
Hence proved.
Note: In the right angled triangle we use the Pythagoras theorem. In that right angled triangle, the side opposite to the $90^\circ $ is considered as hypotenuse of that triangle and we can use Pythagoras theorem as ${({\text{hypotenuse)}}^2} = {({\text{base)}}^2} + {{\text{(perpendicular)}}^2}$
$A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}$ and in the triangle $ADC$, we get that
$A{C^2} = A{D^2} + D{C^2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:

In the given figure in the triangle $ABC$ where $\angle B < 90^\circ $
To prove: $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} - 2BC.BD$
And$AD$ is the product such that$AD \bot BC$. Therefore we have got two right angled triangles.
Here we get that $AD \bot BC$.
So now in$\Delta ABD$
$AD \bot BC$ so $\angle ADB = 90^\circ $
So we can use the Pythagoras theorem where
${({\text{hypotenuse)}}^2} = {({\text{base)}}^2} + {{\text{(perpendicular)}}^2}$
In$\Delta ABD$
$A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}$$ - - - - - (1)$
In $\Delta ADC$
$AD \bot BC$
So $\angle ADC = 90^\circ $
Hence we get that
$A{C^2} = A{D^2} + D{C^2}$$ - - - - (2)$
Now we substitute $DC = BC - BD$ and also the value got from (1)
So putting these in the equation (2), we get
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} - B{D^2} + B{C^2} + B{D^2} - 2BC.BD$
So we get that
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} - 2BC.BD$
Hence proved.
Note: In the right angled triangle we use the Pythagoras theorem. In that right angled triangle, the side opposite to the $90^\circ $ is considered as hypotenuse of that triangle and we can use Pythagoras theorem as ${({\text{hypotenuse)}}^2} = {({\text{base)}}^2} + {{\text{(perpendicular)}}^2}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




