
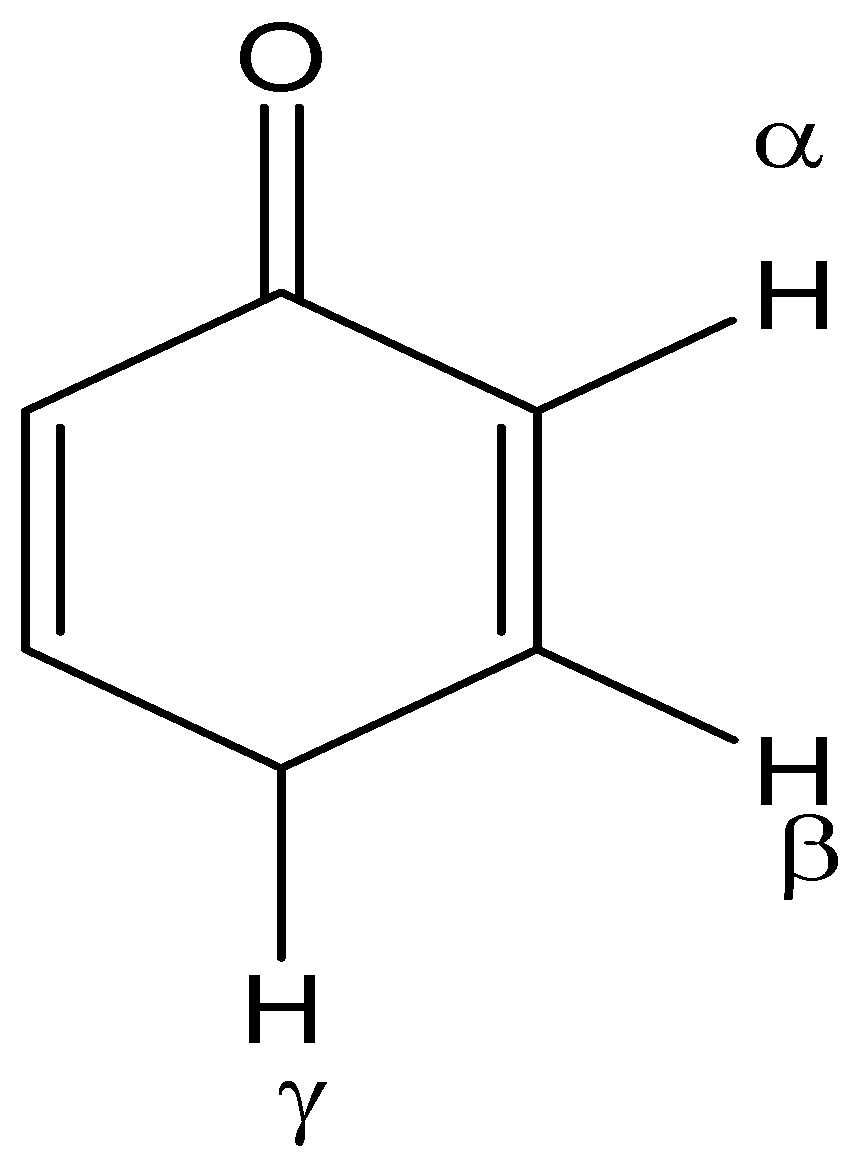
In the enolization of the given molecule, the H-atom involved is:
A. $\alpha - H$
B. $\beta - H$
C. $\gamma - H$
D. Cannot be enolized

Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: We know that the phenomenon of a substance reacting chemically according to two possible structures is called Tautomerism. Substances which are isomeric under certain conditions may be tautomeric under drastic conditions therefore it is referred as dynamic isomerism. We have to know that enols are derivatives of vinyl alcohol, that carbon-carbon double bond connected to hydroxyl groups.
Complete step by step answer:
We must remember that tautomerism is a special case of functional isomerism where the isomers remain present together in equilibrium due to their interconvertible nature.
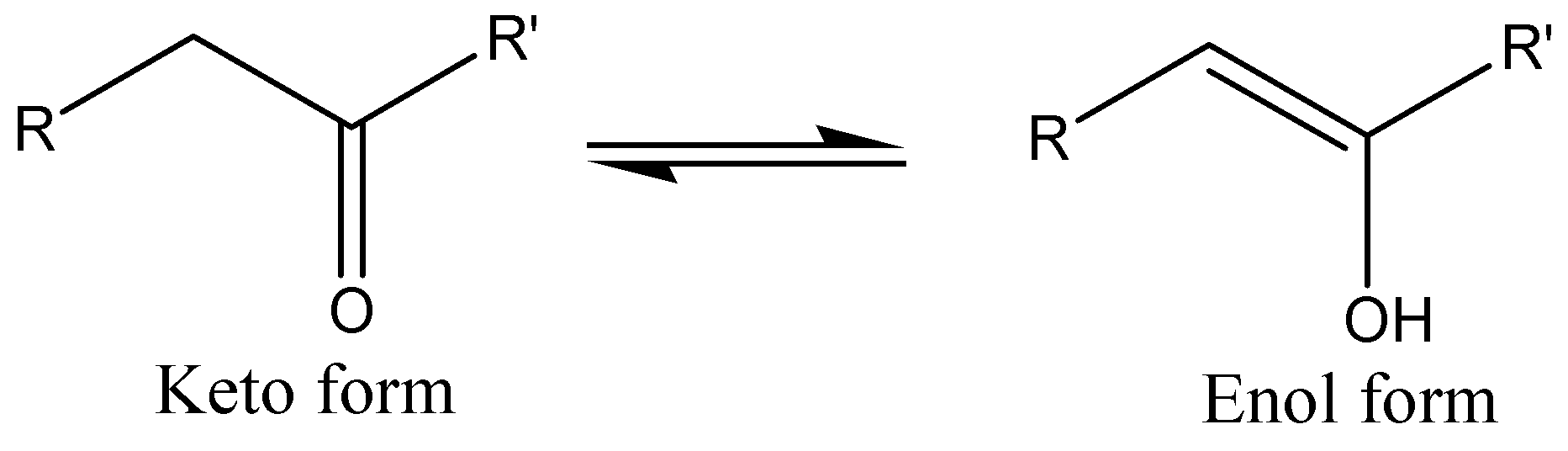
Keto enol tautomerism is the most common tautomerism involving a carbonyl compound having an alpha hydrogen atom and its enol form. In the cases where there is hydrogen or OH group the equilibrium lies mainly to the left and keto form predominates.
The compound containing active methylene group reacts with a strong base and the proton removal may take place from both, keto and enol forms and the resultant enolate ion by resonance stabilization is in both cases.
When organic carbonyl gets deprotonated enolate anions are formed which are strong nucleophiles. We have to know that enolization is generally carried out when keto form gets converted into enol form which is nothing but tautomerization.
Let us now see the enol of given molecule and find the hydrogen atom involved:
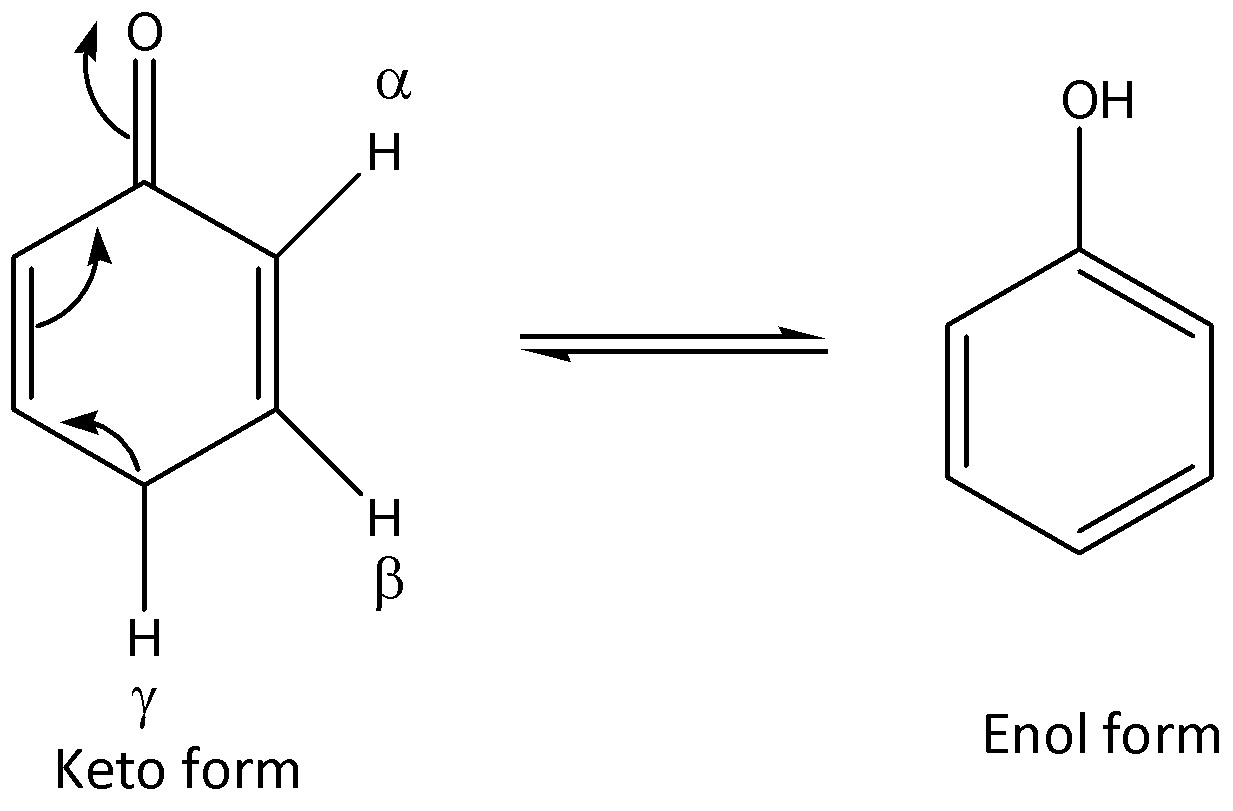
We can see that the gamma hydrogen is involved to get the enol form of the molecule.
So, the correct answer is Option C .
Note:
We can also say that gamma hydrogen is $s{p^3}$ hybridized and the conjugate base is resonance stabilized. Therefore gamma hydrogen is involved in the enolization of the given molecule. We have to know that enolization could take place either in acidic condition (or) basic condition. The best condition for enolization is base-catalyzed enolization. Compounds like acetaldehyde, acetone, and ethyl acetate exist mainly in keto form. On the other hand acetoacetic ester and acetyl acetone exist in the enol form to a considerable extent.
Complete step by step answer:
We must remember that tautomerism is a special case of functional isomerism where the isomers remain present together in equilibrium due to their interconvertible nature.
Keto enol tautomerism is the most common tautomerism involving a carbonyl compound having an alpha hydrogen atom and its enol form. In the cases where there is hydrogen or OH group the equilibrium lies mainly to the left and keto form predominates.

The compound containing active methylene group reacts with a strong base and the proton removal may take place from both, keto and enol forms and the resultant enolate ion by resonance stabilization is in both cases.
When organic carbonyl gets deprotonated enolate anions are formed which are strong nucleophiles. We have to know that enolization is generally carried out when keto form gets converted into enol form which is nothing but tautomerization.
Let us now see the enol of given molecule and find the hydrogen atom involved:

We can see that the gamma hydrogen is involved to get the enol form of the molecule.
So, the correct answer is Option C .
Note:
We can also say that gamma hydrogen is $s{p^3}$ hybridized and the conjugate base is resonance stabilized. Therefore gamma hydrogen is involved in the enolization of the given molecule. We have to know that enolization could take place either in acidic condition (or) basic condition. The best condition for enolization is base-catalyzed enolization. Compounds like acetaldehyde, acetone, and ethyl acetate exist mainly in keto form. On the other hand acetoacetic ester and acetyl acetone exist in the enol form to a considerable extent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




