
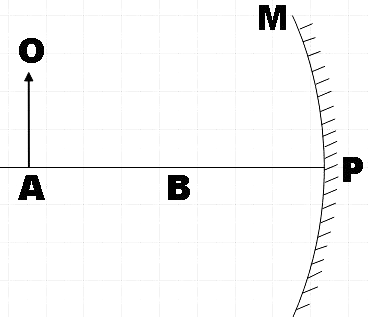
In the diagram, M is a concave mirror and A is a point on its principle axis. If an object O is kept at A, the image is formed at $A$ itself. B is the centre of AP. What is the point B called?

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Firstly you could recall the image of formation of an object kept in front of a concave mirror at different points. Thus, you could remember when the image is formed at the same point at which the object is kept. Thereby, you will be able to identify point A and then you could find B from that.
Complete answer:
In the question, we are given a concave mirror M. We are told that the image of an object O kept at a point A is formed at the same point. If P was the pole of the given concave mirror, A and B lie on the principle axis, then, we are asked to find what B is called if it was the midpoint of AP.
In order to answer this, let us recall the image formation by a concave mirror. We could recall where the images are formed when the object is kept at infinity, beyond the centre of curvature (C), at the centre of curvature, between C and focal point (F), at F, and between F and pole of the mirror (P).
Only recalling these image formations for objects kept at different points, you may find that the image is formed at the same point only when the object is kept at the centre of curvature C. Let us depict this in a diagram.
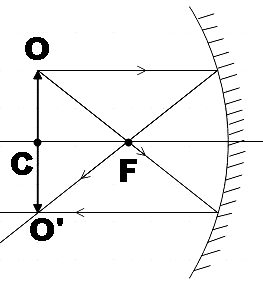
So we found that the point A in the question is the centre of curvature of the given mirror. And we know that focal point is the midpoint of the line joining the pole of the mirror and centre of curvature. Thus, we could conclude that point B is the focal point of the mirror.
Note:
For the image formation in the solution, we have used two common laws followed for the image formation of spherical mirrors. The ray parallel to the principle axis will pass through the focal point after reflection at mirror and vice-versa. You may also observe that the image formed is inverted but has the same height as that of the object.
Complete answer:
In the question, we are given a concave mirror M. We are told that the image of an object O kept at a point A is formed at the same point. If P was the pole of the given concave mirror, A and B lie on the principle axis, then, we are asked to find what B is called if it was the midpoint of AP.
In order to answer this, let us recall the image formation by a concave mirror. We could recall where the images are formed when the object is kept at infinity, beyond the centre of curvature (C), at the centre of curvature, between C and focal point (F), at F, and between F and pole of the mirror (P).
Only recalling these image formations for objects kept at different points, you may find that the image is formed at the same point only when the object is kept at the centre of curvature C. Let us depict this in a diagram.

So we found that the point A in the question is the centre of curvature of the given mirror. And we know that focal point is the midpoint of the line joining the pole of the mirror and centre of curvature. Thus, we could conclude that point B is the focal point of the mirror.
Note:
For the image formation in the solution, we have used two common laws followed for the image formation of spherical mirrors. The ray parallel to the principle axis will pass through the focal point after reflection at mirror and vice-versa. You may also observe that the image formed is inverted but has the same height as that of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




