
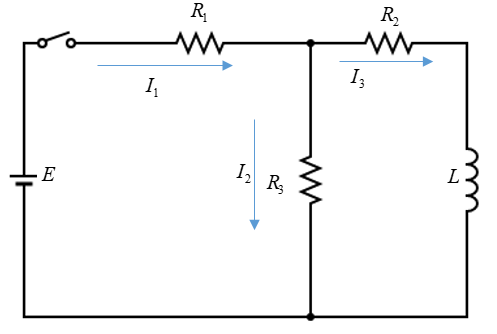
In the circuit shown in figure in adjoining figure $ E = 10V,{R_1} = 1\Omega ,{R_2} = 2\Omega ,{R_3} = 3\Omega $ and $ L = 2H $ . Calculate value of current $ {i_1},{i_2} $ and $ {i_3} $ immediately after key S is closed.
(A) 3.3 amp, 3.3 amp, 3,3 amp
(B) 3.3 amp, 3.3 amp, 0 amp
(C) 3.3 amp, 0 amp, 0 amp
(D) 3.3 amp, 3.3 amp, 1.1 amp

Answer
543.3k+ views
Hint :In an inductor coil a steady current flow, the magnetic flux due to the current remains constant. In this case when the key is closed the inductor due to self-inductance opposes the flow of current and immediately after the switch closes for a time period the inductor works as an open circuit, so no current flows through it.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As mentioned in the hint immediately after closure of switch for a time there will be no current in the inductor i.e $ {i_3} = 0 $ .
Now the circuit is simplified as shown in figure:

Since current through the inductor can’t change instantaneously, in this case we can take it out of the circuit as shown in figure and then we can redraw and further simplify it as shown, so there are just two resistors connected in series as shown and a battery in the circuit.
$ {R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_3} = 1\Omega + 2\Omega = 3\Omega $
$ {i_1} = {i_2} = \dfrac{E}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{10V}}{{3\Omega }} = 3.33A $
Currently through $ {R_1} $ and $ {R_3} $ is $ 3.33A $ . And current through $ {R_2} $ is zero.
Hence the correct option is (b).
Additional Information:
If current in a circuit changes at a rate of $ \dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} $ then EMF induced in the circuit of coil or conductor is given as $ e = L\left| {\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}} \right| $ .
According to Lenz’s law the direction of induced EMF is such that it opposes the causes of induction which is change in current thus sign of $ e $ and $ \dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} $ are opposite in above equation which can be written without modulus as $ e = - L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} $ , here L is a proportionality constant called ‘coefficient of self-Inductance’ or simply ‘the inductance’.
Note :
In the above problem had there been a question where a current is a function of time a current in the inductor is asked after some time has passed, we would have had a non-zero current through the inductor.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As mentioned in the hint immediately after closure of switch for a time there will be no current in the inductor i.e $ {i_3} = 0 $ .
Now the circuit is simplified as shown in figure:

Since current through the inductor can’t change instantaneously, in this case we can take it out of the circuit as shown in figure and then we can redraw and further simplify it as shown, so there are just two resistors connected in series as shown and a battery in the circuit.
$ {R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_3} = 1\Omega + 2\Omega = 3\Omega $
$ {i_1} = {i_2} = \dfrac{E}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{10V}}{{3\Omega }} = 3.33A $
Currently through $ {R_1} $ and $ {R_3} $ is $ 3.33A $ . And current through $ {R_2} $ is zero.
Hence the correct option is (b).
Additional Information:
If current in a circuit changes at a rate of $ \dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} $ then EMF induced in the circuit of coil or conductor is given as $ e = L\left| {\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}} \right| $ .
According to Lenz’s law the direction of induced EMF is such that it opposes the causes of induction which is change in current thus sign of $ e $ and $ \dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} $ are opposite in above equation which can be written without modulus as $ e = - L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} $ , here L is a proportionality constant called ‘coefficient of self-Inductance’ or simply ‘the inductance’.
Note :
In the above problem had there been a question where a current is a function of time a current in the inductor is asked after some time has passed, we would have had a non-zero current through the inductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




