
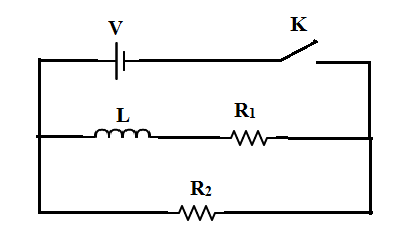
In the circuit shown below, the key K is closed at t = 0. The current through the battery is:
A. $\dfrac{V R_1 R_2}{\sqrt{R_1^2 + R_2^2}}$ at t = 0 and $\dfrac{V}{R_2}$ at t = $\infty$.
B. $\dfrac{V}{R_2}$ at t = 0 and $\dfrac{V (R_1 + R_2) }{R_1 R_2}$ at t = $\infty$.
C. $\dfrac{V}{R_2}$ at t = 0 and $\dfrac{V R_1 R_2}{\sqrt{R_1^2 + R_2^2}}$ at t = $\infty$.
D. $\dfrac{V (R_1 + R_2) }{R_1 R_2}$ at t = 0 and $\dfrac{V}{R_2}$ at t = $\infty$.

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: An inductor has an expression for current in it that is time dependent. As the key is pressed, the current slowly builds in the circuit and if any time varying currents are present, the inductor tends to oppose the change in current.
Complete answer:
For a circuit consisting of only an inductor L, resistance R and a battery, the current equation is of the type:
$I = I_0 (1 - e^{-Rt/L})$.
This clearly shows time varying behaviour of the current in the inductor. At t = 0, there is no current flowing through the inductor, it acts as an open switch. This happens because as the current starts to build in the circuit, the inductor tends to oppose the building of current because of Lenz law. Therefore, even in our given circuit, the inductor acts as an open switch at t = 0, so that the entire branch containing the inductor has no contribution. Therefore, the current in the circuit is only calculated by noting the contribution of the resistance in the lower branch $R_2$.
So, at t = 0 the current in the circuit is:
$\dfrac{V}{R_2}$.
After sufficient time has passed, the current stabilizes in the circuit and the inductor acts as a closed switch with a saturation current $I_0$ flowing through it (see the equation written in the beginning). Therefore, for the circuit given in question, the current flowing will come as a contribution of parallel combination of the two resistances, which can be written as:
$\dfrac{V}{\dfrac{R_1 R_2}{R_1 + R_2}} = \dfrac{V(R_1 + R_2)}{R_1 R_2}$
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note:
One can also remember the graph for the growth of current in the inductor as it just shows saturation after infinite time. One should remember here that we are not taking any resistance for the inductor after infinite time. It acts just as a closed switch.
Complete answer:
For a circuit consisting of only an inductor L, resistance R and a battery, the current equation is of the type:
$I = I_0 (1 - e^{-Rt/L})$.
This clearly shows time varying behaviour of the current in the inductor. At t = 0, there is no current flowing through the inductor, it acts as an open switch. This happens because as the current starts to build in the circuit, the inductor tends to oppose the building of current because of Lenz law. Therefore, even in our given circuit, the inductor acts as an open switch at t = 0, so that the entire branch containing the inductor has no contribution. Therefore, the current in the circuit is only calculated by noting the contribution of the resistance in the lower branch $R_2$.
So, at t = 0 the current in the circuit is:
$\dfrac{V}{R_2}$.
After sufficient time has passed, the current stabilizes in the circuit and the inductor acts as a closed switch with a saturation current $I_0$ flowing through it (see the equation written in the beginning). Therefore, for the circuit given in question, the current flowing will come as a contribution of parallel combination of the two resistances, which can be written as:
$\dfrac{V}{\dfrac{R_1 R_2}{R_1 + R_2}} = \dfrac{V(R_1 + R_2)}{R_1 R_2}$
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note:
One can also remember the graph for the growth of current in the inductor as it just shows saturation after infinite time. One should remember here that we are not taking any resistance for the inductor after infinite time. It acts just as a closed switch.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




