
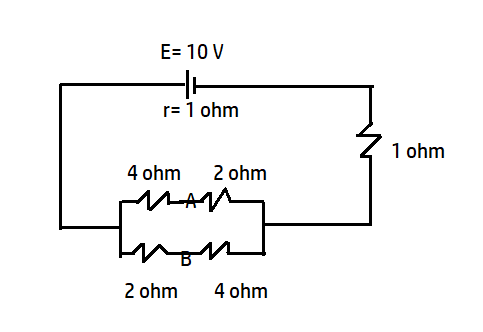
In the circuit shown below, the cell has an emf of 10 V and internal resistance of 1 Ohm. The other resistances are shown. Find the potential difference between point A and B.

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: fist of all we need to find the value of current in the two branches containing the point A & B. then by using the Ohm’s law there we can find the value of potential at A and B and then the potential difference can be find out.
Complete step by step answer:
Internal resistance of the battery, r= 1 \[\Omega \]
The branch containing point A. 4 \[\Omega \]and 2 \[\Omega \]are in series, so, net resistance is 6 \[\Omega \] and for the branch containing 2 \[\Omega \] and 4 \[\Omega \] are in series so the net resistance for this branch is 6 \[\Omega \]. Now both the 6 \[\Omega \] resistors are in parallel, so, the equivalent resistance is given as \[R=\dfrac{{{R}_{1}}{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{6\times 6}{6+6}=3\Omega \]
Now 3 \[\Omega \] and 1 \[\Omega \] are in series, so the net resistance of the circuit is 3+1=4 \[\Omega \]
Total internal resistance in the circuit= 1 \[\Omega \]
Total external resistance in the circuit=4 \[\Omega \]
Using ohm’s law \[I=\dfrac{V}{R+r}=\dfrac{10}{4+1}=2A\]
Now talking about the two branches having points A and B. the resistance of both the branches are equal, so the current in both the branches must be equal and that will be 1A each.
Hence, the potential difference between the points A & B is
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{B}}=IR \\
& =1\times (2-4) \\
& =-2V \\
\end{align}\]
So the answer is -2 V
So the answer is -2 V.
Note:
Since the direction of current was opposite, that’s why the potential gets subtracted, if the direction of current were to be in the same direction, the value of voltages at A and B would have been added. The potential difference between the points A & B comes out to be negative, which means the value of potential at B is higher than the value of potential at A.
Complete step by step answer:
Internal resistance of the battery, r= 1 \[\Omega \]
The branch containing point A. 4 \[\Omega \]and 2 \[\Omega \]are in series, so, net resistance is 6 \[\Omega \] and for the branch containing 2 \[\Omega \] and 4 \[\Omega \] are in series so the net resistance for this branch is 6 \[\Omega \]. Now both the 6 \[\Omega \] resistors are in parallel, so, the equivalent resistance is given as \[R=\dfrac{{{R}_{1}}{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{6\times 6}{6+6}=3\Omega \]
Now 3 \[\Omega \] and 1 \[\Omega \] are in series, so the net resistance of the circuit is 3+1=4 \[\Omega \]
Total internal resistance in the circuit= 1 \[\Omega \]
Total external resistance in the circuit=4 \[\Omega \]
Using ohm’s law \[I=\dfrac{V}{R+r}=\dfrac{10}{4+1}=2A\]
Now talking about the two branches having points A and B. the resistance of both the branches are equal, so the current in both the branches must be equal and that will be 1A each.
Hence, the potential difference between the points A & B is
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{B}}=IR \\
& =1\times (2-4) \\
& =-2V \\
\end{align}\]
So the answer is -2 V
So the answer is -2 V.
Note:
Since the direction of current was opposite, that’s why the potential gets subtracted, if the direction of current were to be in the same direction, the value of voltages at A and B would have been added. The potential difference between the points A & B comes out to be negative, which means the value of potential at B is higher than the value of potential at A.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




