
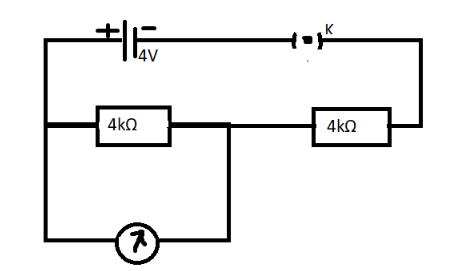
In the circuit shown below, if the resistance of voltmeter is $ {{4K}}\Omega $ , then the error in the reading of voltmeter will be
(A) 50 %
(B) 68 %
(C) 17 %
(D) 33.3%

Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: We only need to apply the ohm’s law on the following circuit. Then by simply putting the values in the formula we can get the answer.
Formula used: As required here we need ohm’s law:
$ \begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{{{V = iR}}}
\end{array} $
Here, $ {{V}} $ is the voltage,
$ {{i}} $ is the current passing through the circuit,
$ {{R}} $ is the resistance of the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
We are already provided with the resistances of $ {{4K}}\Omega $ connected in series.
And $ {{4K}}\Omega $ means 4000 $ \Omega $
When the voltmeter is ideal,
So, no current is passing through the voltmeter.
At that moment the current that we will get is:
$ {{I = }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{{4000 + 4000}}}}{{ = 0}}.{{5mA}} $
When the reading of the voltmeter is $ {{V}} $ :
$ {{V = 4000I = 4000}}\left( {\dfrac{{{{0}}.{{5}}}}{{{{1000}}}}} \right){{ = 2V}} $
When we apply the resistances to the circuit in parallel:
$ {{I' = }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{{4000}}}}{{ + }}\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{{4000}}}}} \right){{ + 4000}}}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{{2000 + 4000}}}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{2}}}{{{3}}}{{A}} $
The corresponding reading of the voltmeter:
$ {{V' = 4000I' = 4000}}\left( {\dfrac{{{2}}}{{{3}}} \times {{1}}{{{0}}^{{{ - 3}}}}} \right){{ = 2}}.{{67V}} $
Now, the error in voltmeter $ {{ = }}\dfrac{{{{2}}{{.67 - 2}}}}{{{2}}}{{ \times 100 = 33}}{{.3}} $
$ {{ = }}\dfrac{{{{2}}.{{67 - 2}}}}{{{2}}} \times {{100 = 33}}.{{3}} $ %
So, we need to see from the above options, and select the appropriate value.
Thus, the correct answer is option D.
Additional Information
Ohm's law is the fundamental law in the field of electricity. It was discovered by George Ohm, and named after him. Ohm's law provides the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. It states that the voltage across any resistance is equal to current times the resistance.
Note:
Some common applications of ohm’s law in our daily lives are electric Kettles and irons, mobile and laptop charger, conventional domestic fans. It provides variable output voltage based on the resistance and the overall working is controlled by Ohm's Law. The working of heaters, kettles and other equipment also follows this law. Mobile phone & laptop chargers use DC power supply in operations. Ohm's Law states that the current flowing in a circuit is directly proportional to the applied potential difference and inversely proportional to the resistance in the circuit. In other words, by doubling the voltage across a circuit the current will also double.
Formula used: As required here we need ohm’s law:
$ \begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{{{V = iR}}}
\end{array} $
Here, $ {{V}} $ is the voltage,
$ {{i}} $ is the current passing through the circuit,
$ {{R}} $ is the resistance of the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
We are already provided with the resistances of $ {{4K}}\Omega $ connected in series.
And $ {{4K}}\Omega $ means 4000 $ \Omega $
When the voltmeter is ideal,
So, no current is passing through the voltmeter.
At that moment the current that we will get is:
$ {{I = }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{{4000 + 4000}}}}{{ = 0}}.{{5mA}} $
When the reading of the voltmeter is $ {{V}} $ :
$ {{V = 4000I = 4000}}\left( {\dfrac{{{{0}}.{{5}}}}{{{{1000}}}}} \right){{ = 2V}} $
When we apply the resistances to the circuit in parallel:
$ {{I' = }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{{4000}}}}{{ + }}\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{{4000}}}}} \right){{ + 4000}}}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{{2000 + 4000}}}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{2}}}{{{3}}}{{A}} $
The corresponding reading of the voltmeter:
$ {{V' = 4000I' = 4000}}\left( {\dfrac{{{2}}}{{{3}}} \times {{1}}{{{0}}^{{{ - 3}}}}} \right){{ = 2}}.{{67V}} $
Now, the error in voltmeter $ {{ = }}\dfrac{{{{2}}{{.67 - 2}}}}{{{2}}}{{ \times 100 = 33}}{{.3}} $
$ {{ = }}\dfrac{{{{2}}.{{67 - 2}}}}{{{2}}} \times {{100 = 33}}.{{3}} $ %
So, we need to see from the above options, and select the appropriate value.
Thus, the correct answer is option D.
Additional Information
Ohm's law is the fundamental law in the field of electricity. It was discovered by George Ohm, and named after him. Ohm's law provides the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. It states that the voltage across any resistance is equal to current times the resistance.
Note:
Some common applications of ohm’s law in our daily lives are electric Kettles and irons, mobile and laptop charger, conventional domestic fans. It provides variable output voltage based on the resistance and the overall working is controlled by Ohm's Law. The working of heaters, kettles and other equipment also follows this law. Mobile phone & laptop chargers use DC power supply in operations. Ohm's Law states that the current flowing in a circuit is directly proportional to the applied potential difference and inversely proportional to the resistance in the circuit. In other words, by doubling the voltage across a circuit the current will also double.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




