
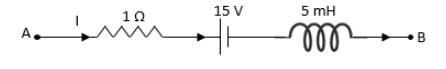
In the circuit (Fig) what is potential difference \[{V_B} - {V_A}\] (in V) When current \[I\] is \[5\,\mu {\text{A}}\] and is decreasing at the rate of \[{10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\]?

Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:Use the expression for Ohm’s law. Also use the formula for emf or potential difference across the inductor. Using these two formulae, calculate the potential difference across the resistor and inductor given in the circuit. Then apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law to the circuit and then calculate the potential difference.
Formulae used:
The expression for Ohm’s law is given by
\[V = IR\] …… (1)
Here, \[V\] is the potential difference across the ends of the conductor, \[I\] is current in the conductor and \[R\] is the resistance of the conductor.
The emf \[e\] induced in a inductor is given by
\[e = L\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}\] …… (2)
Here, \[L\] is the inductance of the inductor and \[\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}\] is the rate of change of current with time.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the current in the given arrangement is \[5\,\mu {\text{A}}\] and the rate of decreases of current is \[{10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\].
\[I = 5\,\mu {\text{A}}\]
\[\Rightarrow\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}} = - {10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\]
We have asked to calculate the potential difference across the ends A and B of the given circuit.Let us first calculate the potential difference across the resistor.Substitute \[5\,\mu {\text{A}}\] for \[I\] and \[1\,\Omega \] for \[R\] in equation (1).
\[V = \left( {5\,\mu {\text{A}}} \right)\left( {1\,\Omega } \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = \left( {5 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}\,{\text{A}}} \right)\left( {1\,\Omega } \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\]
Hence, the potential difference across the resistor is \[5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\].
Let us now calculate the emf or potential difference across the inductor,
Substitute \[5\,{\text{mH}}\] for \[L\] and \[ - {10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] for \[\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}\] in equation (2).
\[e = \left( {5\,{\text{mH}}} \right)\left( { - {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow e = \left( {5 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{\text{H}}} \right)\left( { - {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow e = - 5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\]
Hence, the potential difference across the inductor is \[5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\].
Let us now determine the potential difference across the ends A and B of the given circuit.Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law to the given circuit.
\[{V_A} - V + \left( {15\,{\text{V}}} \right) - e = {V_B}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {V_B} - {V_A} = - V + \left( {15\,{\text{V}}} \right) - e\]
Substitute \[5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\] for \[V\] and \[5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\] for \[e\] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow {V_B} - {V_A} = - \left( {5 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}} \right) + \left( {15\,{\text{V}}} \right) - \left( { - 5 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}} \right)\]
\[ \therefore {V_B} - {V_A} = 15\,{\text{V}}\]
Hence, the required potential difference is \[15\,{\text{V}}\].
Note:The students should keep in mind that we have given the rate of decreasing the current. Hence, the value of this decreasing current rate must be used with a negative sign. Also the students should be careful while using Kirchhoff’s voltage law and use the proper signs for the difference potentials.
Formulae used:
The expression for Ohm’s law is given by
\[V = IR\] …… (1)
Here, \[V\] is the potential difference across the ends of the conductor, \[I\] is current in the conductor and \[R\] is the resistance of the conductor.
The emf \[e\] induced in a inductor is given by
\[e = L\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}\] …… (2)
Here, \[L\] is the inductance of the inductor and \[\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}\] is the rate of change of current with time.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the current in the given arrangement is \[5\,\mu {\text{A}}\] and the rate of decreases of current is \[{10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\].
\[I = 5\,\mu {\text{A}}\]
\[\Rightarrow\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}} = - {10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\]
We have asked to calculate the potential difference across the ends A and B of the given circuit.Let us first calculate the potential difference across the resistor.Substitute \[5\,\mu {\text{A}}\] for \[I\] and \[1\,\Omega \] for \[R\] in equation (1).
\[V = \left( {5\,\mu {\text{A}}} \right)\left( {1\,\Omega } \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = \left( {5 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}\,{\text{A}}} \right)\left( {1\,\Omega } \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\]
Hence, the potential difference across the resistor is \[5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\].
Let us now calculate the emf or potential difference across the inductor,
Substitute \[5\,{\text{mH}}\] for \[L\] and \[ - {10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] for \[\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}\] in equation (2).
\[e = \left( {5\,{\text{mH}}} \right)\left( { - {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow e = \left( {5 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{\text{H}}} \right)\left( { - {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{\text{A}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow e = - 5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\]
Hence, the potential difference across the inductor is \[5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\].
Let us now determine the potential difference across the ends A and B of the given circuit.Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law to the given circuit.
\[{V_A} - V + \left( {15\,{\text{V}}} \right) - e = {V_B}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {V_B} - {V_A} = - V + \left( {15\,{\text{V}}} \right) - e\]
Substitute \[5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\] for \[V\] and \[5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}\] for \[e\] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow {V_B} - {V_A} = - \left( {5 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}} \right) + \left( {15\,{\text{V}}} \right) - \left( { - 5 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}\,{\text{V}}} \right)\]
\[ \therefore {V_B} - {V_A} = 15\,{\text{V}}\]
Hence, the required potential difference is \[15\,{\text{V}}\].
Note:The students should keep in mind that we have given the rate of decreasing the current. Hence, the value of this decreasing current rate must be used with a negative sign. Also the students should be careful while using Kirchhoff’s voltage law and use the proper signs for the difference potentials.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




