
In the circuit diagram below, identical bulbs are connected in parallel. Describe and explain the effect on the brightness of the two bulbs if a third identical bulb is also attached in parallel to the two bulbs.
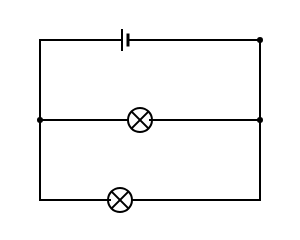

Answer
570k+ views
Hint: When appliances connected in parallel then current flowing through them is different but potential difference or voltage across them is the same. And in the case of series connection, current flowing through them is the same and potential difference is different.
Complete step by step answer:
Every electrical appliance will have rated or design values like wattage, voltage printed on it. These values give information about resistance and allowable current etc.., let $P$ and $V$ be the power and voltage rating on a bulb.
Resistance of the filament of the bulb, $R = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{P}$
If $V$ is constant then resistance of the filament is inversely proportional to the power rating on the bulb.
That is, $R \propto \dfrac{1}{P}$
For example, if we compare (100w -230v) and (60w- 230v) bulbs filament of 100w bulb will have less resistance compared to that of 60w bulb.
Allowable current in the bulb, $I = \dfrac{P}{V}$
So, here current is directly proportional to the power, if voltage is constant.
So, in the above example, a \[100W\] bulb draws more current.
Now, when two bulbs are connected in parallel, having power ${P_1}{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}{P_2}$ respectively. Current flowing through each bulb is different but potential difference across each of them is the same.
Then,
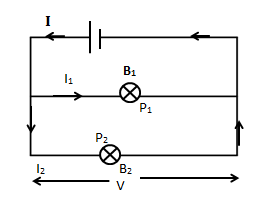
Let us consider the circuit given. In the circuit \[{B_1}\],\[{B_2}\] stands for bulbs, $I$, ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$ stands for current.
Power in the bulb 1, ${P_1} = {I_1}V$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{V} = {I_1}$………….(1)
Power in the bulb 2, ${P_2} = {I_2}V$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{P_2}}}{V} = {I_2}$………….(2)
Power equivalent in the parallel combination is given by, $I = \dfrac{{{P_{eq}}}}{V}$……………(3)
We know that, current flowing through each bulb is different,
$ \Rightarrow$ $I = {I_1} + {I_2}$
Now substitute equation (1), (2) and (3), we get
$ \Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{{{P_{eq}}}}{V} = \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{V} + \dfrac{{{P_2}}}{V}$
After simplification we get,
Total power consumed, ${P_{eq}} = {P_1} + {P_2}$
For two identical bulbs, ${P_{eq}} = P + P = 2P$
From this equation we can say, when bulbs are connected in parallel its powers will be added up. Thus brightness is more.
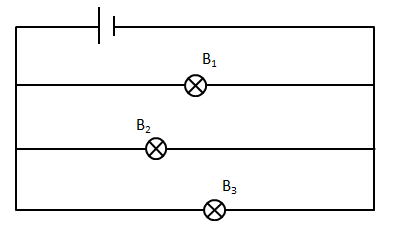
If we connect three identical bulbs in parallel then, ${P_{eq}} = P + P + P = 3P$
In a parallel combination of bulbs, the bulb of greater wattage will give more bright light and will pass greater current through it, but will have lesser resistance and same potential difference.
Thus, we can say that, when bulbs are connected in parallel, powers are added up and the brightness of the combination will increase.
Note: In parallel connection, if one bulb gets fused the other will work. The rate at which electrical work is done by the source of emf in maintaining the current in the electric circuit is called electric power.
Complete step by step answer:
Every electrical appliance will have rated or design values like wattage, voltage printed on it. These values give information about resistance and allowable current etc.., let $P$ and $V$ be the power and voltage rating on a bulb.
Resistance of the filament of the bulb, $R = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{P}$
If $V$ is constant then resistance of the filament is inversely proportional to the power rating on the bulb.
That is, $R \propto \dfrac{1}{P}$
For example, if we compare (100w -230v) and (60w- 230v) bulbs filament of 100w bulb will have less resistance compared to that of 60w bulb.
Allowable current in the bulb, $I = \dfrac{P}{V}$
So, here current is directly proportional to the power, if voltage is constant.
So, in the above example, a \[100W\] bulb draws more current.
Now, when two bulbs are connected in parallel, having power ${P_1}{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}{P_2}$ respectively. Current flowing through each bulb is different but potential difference across each of them is the same.
Then,

Let us consider the circuit given. In the circuit \[{B_1}\],\[{B_2}\] stands for bulbs, $I$, ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$ stands for current.
Power in the bulb 1, ${P_1} = {I_1}V$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{V} = {I_1}$………….(1)
Power in the bulb 2, ${P_2} = {I_2}V$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{P_2}}}{V} = {I_2}$………….(2)
Power equivalent in the parallel combination is given by, $I = \dfrac{{{P_{eq}}}}{V}$……………(3)
We know that, current flowing through each bulb is different,
$ \Rightarrow$ $I = {I_1} + {I_2}$
Now substitute equation (1), (2) and (3), we get
$ \Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{{{P_{eq}}}}{V} = \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{V} + \dfrac{{{P_2}}}{V}$
After simplification we get,
Total power consumed, ${P_{eq}} = {P_1} + {P_2}$
For two identical bulbs, ${P_{eq}} = P + P = 2P$
From this equation we can say, when bulbs are connected in parallel its powers will be added up. Thus brightness is more.

If we connect three identical bulbs in parallel then, ${P_{eq}} = P + P + P = 3P$
In a parallel combination of bulbs, the bulb of greater wattage will give more bright light and will pass greater current through it, but will have lesser resistance and same potential difference.
Thus, we can say that, when bulbs are connected in parallel, powers are added up and the brightness of the combination will increase.
Note: In parallel connection, if one bulb gets fused the other will work. The rate at which electrical work is done by the source of emf in maintaining the current in the electric circuit is called electric power.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




