
In the below reaction, the reactivity of alcohols is;
$ROH + HX \to RX + {H_2}O$ ;
A) \[Tertiary{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}secondary{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}primary\]
B) \[Tertiary{\text{ }} < {\text{ }}secondary{\text{ }} < {\text{ }}primary\]
C) \[Tertiary{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}primary{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}secondary\]
D) \[Secondary{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}primary{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}tertiary\]
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Alcohols are compounds in which a hydroxyl (– OH) group is attached to saturated carbon atom.
General Formula: $R - OH$
Monohydric alcohols are classified as primary (1°) secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°), depending upon whether the –OH group is attached to a primary, a secondary, or a tertiary carbon.
Complete step by step answer:Alcohols are reactive compounds. They are attacked by polar or ionic reagents. This is because:
The C–O and O–H bonds of the alcohols are polar since oxygen is highly electronegative.
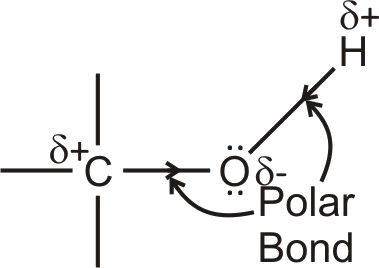
They oxygen atoms of alcohols is an electron-rich centre because it has two unshared pairs of electrons
Alcohols react with hydrogen (\[HX\]) to form the corresponding alkyl halides
Eg; $C{H_3}C{H_2}OH + HBr \to C{H_3}C{H_2}Br + {H_2}O$
In general, tertiary alcohols react rapidly with hydrogen halides; secondary alcohols react somewhat slower; and primary alcohols, even more slowly.
The reaction is acid catalyzed. Alcohols react with the strongly acidic hydrogen halides \[HCl,{\text{ }}HBr\] , and {\text{ }}HI\], but they do not react with non acidic \[NaCl,{\text{ }}NaBr,{\text{ }}or{\text{ }}NaI\] . Primary and secondary alcohols can be converted to alkyl chlorides and bromides by allowing them to react with a mixture of a sodium halide and sulfuric acid:
The order of reactivity of alcohols is \[3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ \] methyl.
So,Option “A” is correct.
Note: The order of reactivity of hydrogen halides\[is{\text{ }}HI{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}HBr{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}HCl\] . \[HCl\] reacts only in the presence of a catalyst anhydrous\[(ZnC{l_2})\] .No catalyst is required in the case of \[HBr{\text{ }}or{\text{ }}HI\].
Primary alcohols react with hydrogen halides by an \[{S_N}1\] mechanism.
General Formula: $R - OH$
Monohydric alcohols are classified as primary (1°) secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°), depending upon whether the –OH group is attached to a primary, a secondary, or a tertiary carbon.
Complete step by step answer:Alcohols are reactive compounds. They are attacked by polar or ionic reagents. This is because:
The C–O and O–H bonds of the alcohols are polar since oxygen is highly electronegative.

They oxygen atoms of alcohols is an electron-rich centre because it has two unshared pairs of electrons
Alcohols react with hydrogen (\[HX\]) to form the corresponding alkyl halides
Eg; $C{H_3}C{H_2}OH + HBr \to C{H_3}C{H_2}Br + {H_2}O$
In general, tertiary alcohols react rapidly with hydrogen halides; secondary alcohols react somewhat slower; and primary alcohols, even more slowly.
The reaction is acid catalyzed. Alcohols react with the strongly acidic hydrogen halides \[HCl,{\text{ }}HBr\] , and {\text{ }}HI\], but they do not react with non acidic \[NaCl,{\text{ }}NaBr,{\text{ }}or{\text{ }}NaI\] . Primary and secondary alcohols can be converted to alkyl chlorides and bromides by allowing them to react with a mixture of a sodium halide and sulfuric acid:
The order of reactivity of alcohols is \[3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ \] methyl.
So,Option “A” is correct.
Note: The order of reactivity of hydrogen halides\[is{\text{ }}HI{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}HBr{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}HCl\] . \[HCl\] reacts only in the presence of a catalyst anhydrous\[(ZnC{l_2})\] .No catalyst is required in the case of \[HBr{\text{ }}or{\text{ }}HI\].
Primary alcohols react with hydrogen halides by an \[{S_N}1\] mechanism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




