
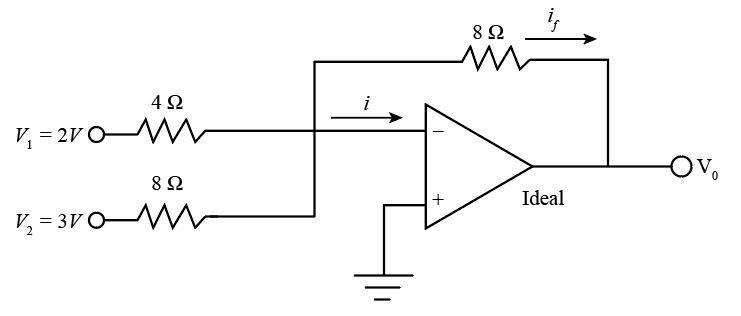
In the below figure, find the output voltage, if the op-amp is ideal
A.$ - 7\;{\rm{V}}$
B.$ - 6\;{\rm{V}}$
C.$ - 1\;{\rm{V}}$
D.$6\;{\rm{V}}$

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: To find the output voltage, we will use Ohm's law at different points of the circuit. Since the resistors are in parallel at the input terminal, we will find the current flowing through the respective resistance and then will add the current to find the final current flowing through the resistor at the output terminal. Then with the help of this final current and the resistance at the output terminal, we will find the output voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The circuit consists of three resistors ${R_1} = 4\;\Omega $ ,${R_2} = 8\;\Omega $ and ${R_f} = 8\;\Omega $ .
The voltages at the input terminal are ${V_1} = 2\;{\rm{V}}$ , ${V_2} = 3\;{\rm{V}}$ and represents the voltage at the output terminal.
We can write the expression for current flowing through resistor ${R_1}$ from the ohm’s law as
${V_1} = {i_1}{R_1}$
We rearrange the above expression as
${i_1} = \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{R_1}}}$
Similarly, we can write the expression for current flowing through resistor ${R_2}$ from the ohm’s law as
${V_2} = {i_2}{R_2}$
We rearrange the above expression as
${i_2} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}$
Since resistance ${R_1}$and ${R_2}$are parallel so the current ${i_1}$ and ${i_2}$ will add up to give the final current ${i_f}$ which can be expressed as:
${i_f} = \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}$
We will substitute $4\;\Omega $ for ${R_1}$ , $8\,\Omega $ for ${R_2}$ , $3\;{\rm{V}}$ for ${V_1}$ and $2\;{\rm{V}}$ for ${V_2}$ in the above expression.
$\begin{array}{l}
{i_f} = \dfrac{{3\;{\rm{V}}}}{{8\;\Omega }} + \dfrac{{2\;{\rm{V}}}}{{4\;\Omega }}\\
{i_f} = \left( {\dfrac{{3 + 4}}{8}} \right)\;{\rm{A}}\\
{i_f} = 0.875\;{\rm{A}}
\end{array}$
Now to find the value of ${V_o}$, we will write the relation between ${i_f}$ and ${R_f}$ from the ohm’s law and from the above figure.
${V_o} = - {i_f}{R_f}$
We will substitute $8\,\Omega $ for ${R_f}$and $0.875\;{\rm{A}}$for ${i_f}$in the above expression.
$\begin{array}{l}
{V_o} = - \left( {8\,\Omega } \right)\left( {0.875\;{\rm{A}}} \right)\\
{V_o} = - 7\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
Therefore, the output voltage in the op-amp is $ - 7\;{\rm{V}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Op-amp stands for operational amplifier. It can be categorised as a device which amplifies voltage and works with the external feedback components like resistors or capacitors from its input terminal to output terminal. This amplifier gives response only to the difference between voltages and doesn’t consider their individual values. The current at the input terminal is zero since it has high impedance.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The circuit consists of three resistors ${R_1} = 4\;\Omega $ ,${R_2} = 8\;\Omega $ and ${R_f} = 8\;\Omega $ .
The voltages at the input terminal are ${V_1} = 2\;{\rm{V}}$ , ${V_2} = 3\;{\rm{V}}$ and represents the voltage at the output terminal.
We can write the expression for current flowing through resistor ${R_1}$ from the ohm’s law as
${V_1} = {i_1}{R_1}$
We rearrange the above expression as
${i_1} = \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{R_1}}}$
Similarly, we can write the expression for current flowing through resistor ${R_2}$ from the ohm’s law as
${V_2} = {i_2}{R_2}$
We rearrange the above expression as
${i_2} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}$
Since resistance ${R_1}$and ${R_2}$are parallel so the current ${i_1}$ and ${i_2}$ will add up to give the final current ${i_f}$ which can be expressed as:
${i_f} = \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}$
We will substitute $4\;\Omega $ for ${R_1}$ , $8\,\Omega $ for ${R_2}$ , $3\;{\rm{V}}$ for ${V_1}$ and $2\;{\rm{V}}$ for ${V_2}$ in the above expression.
$\begin{array}{l}
{i_f} = \dfrac{{3\;{\rm{V}}}}{{8\;\Omega }} + \dfrac{{2\;{\rm{V}}}}{{4\;\Omega }}\\
{i_f} = \left( {\dfrac{{3 + 4}}{8}} \right)\;{\rm{A}}\\
{i_f} = 0.875\;{\rm{A}}
\end{array}$
Now to find the value of ${V_o}$, we will write the relation between ${i_f}$ and ${R_f}$ from the ohm’s law and from the above figure.
${V_o} = - {i_f}{R_f}$
We will substitute $8\,\Omega $ for ${R_f}$and $0.875\;{\rm{A}}$for ${i_f}$in the above expression.
$\begin{array}{l}
{V_o} = - \left( {8\,\Omega } \right)\left( {0.875\;{\rm{A}}} \right)\\
{V_o} = - 7\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
Therefore, the output voltage in the op-amp is $ - 7\;{\rm{V}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Op-amp stands for operational amplifier. It can be categorised as a device which amplifies voltage and works with the external feedback components like resistors or capacitors from its input terminal to output terminal. This amplifier gives response only to the difference between voltages and doesn’t consider their individual values. The current at the input terminal is zero since it has high impedance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




