
In the balance Meter Bridge, the resistance of bridge wire is $0.1\Omega /cm$. Unknown resistance X connected in the left gap and $6\Omega $ in the right gap, null point divides the wire in the ratio 2:3. Find the current drawn from the battery of 5V having negligible resistance.
A. 1A
B. 1.5A
C. 2A
D. 5A
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We have provided with balance Meter Bridge, which has null point divides wire in 2:3 ratio, hence calculate length of wires ${{l}_{1}}\text{ and }{{l}_{2}}$ which is divided into five parts apply balance condition of wheatstone network and calculate value of unknown resistance. Then use Kirchhoff’s second law to calculate the value of current flows through the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
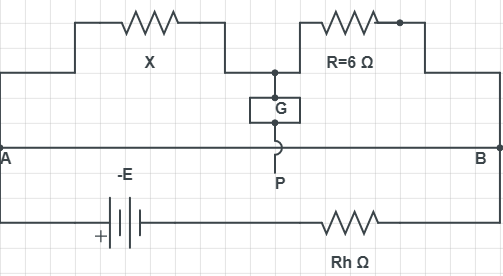
We have a Meter Bridge which balances the total resistance of bridge wire is $0.1\Omega /cm$. X is the total resistance which is connected to the left gap and R=$6\Omega $ in the right gap. Null point is dividing wire in 2:3 ratios. A battery 5V having negligible resistance is also connected to circuit. Now we need to calculate. Consider Current drawn from the 5V battery.
We know that the Meter Bridge has a resistance of $0.1\Omega /cm$ and its total length of wire is always 1m i.e., 100cm. So, resistance of wire $\left( {{R}_{W}} \right)$ is given by,
$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{W}}=0.1\times 100 \\
& {{R}_{W}}=10\Omega \\
\end{align}$
We have given wire AB is divided into 2:3 ratios. I.e. two part from A to P and tree parts from P to B. Now if we divide $10\Omega $ resistance in this wire the length of AP is given by,
${{l}_{1}}=10\times \dfrac{2}{5}=4$
(We have total five parts and ${{l}_{1}}$ are the length contains two parts out of five parts) Similarly for length PB is given by,
${{l}_{2}}=10\times \dfrac{3}{5}=6$
(We have total five parts and ${{l}_{2}}$ are the length contains three parts out of five parts)
It is given that the Meter Bridge is a balanced network or circuit and we get null points at P, we know that, in a balanced condition even though current flows in the rest of circuit, the galvanometer will not show any deflection. I.e. it shows a null point. So according to balance condition of Wheatstone network, we have,
$\dfrac{X}{R}=\dfrac{{{l}_{1}}}{{{l}_{2}}}$
Where, X= unknown resistance
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{X}{6}=\dfrac{4}{6} \\
& \therefore X=4\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Hence unknown resistance (X) is 4Ω.
Now let’s find current, we know that current drawn from 5V is given by,
$I=\dfrac{V}{{{R}_{eq}}}.......(1)$
To find equivalent resistance:
If we consider resistance across a point A and B then circuit looks like,
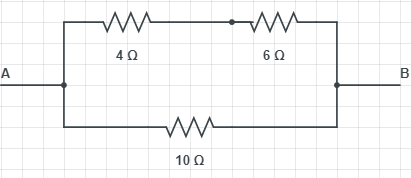
$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{1}}=4+6=10\Omega \\
& {{R}_{2}}=10\Omega \\
\end{align}$
(Since 4Ω and 6Ω are in series)
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}$
(Since ${{R}_{1}}$ And ${{R}_{2}}$ are in parallel)
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{10}=\dfrac{1}{5\Omega } \\
& {{R}_{eq}}=5\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Put value in equation (1) we get,
$I=\dfrac{5}{5}=1A$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Meter Bridge works on Wheatstone bridge network’s principle. Meter Bridge is the modification of Wheatstone’s network which is generally used to determine unknown resistance. It is also called Wheatstone's meter bridge. Since the length of wire used in this is one meter, it is called Meter Bridge.
Complete step by step answer:

We have a Meter Bridge which balances the total resistance of bridge wire is $0.1\Omega /cm$. X is the total resistance which is connected to the left gap and R=$6\Omega $ in the right gap. Null point is dividing wire in 2:3 ratios. A battery 5V having negligible resistance is also connected to circuit. Now we need to calculate. Consider Current drawn from the 5V battery.
We know that the Meter Bridge has a resistance of $0.1\Omega /cm$ and its total length of wire is always 1m i.e., 100cm. So, resistance of wire $\left( {{R}_{W}} \right)$ is given by,
$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{W}}=0.1\times 100 \\
& {{R}_{W}}=10\Omega \\
\end{align}$
We have given wire AB is divided into 2:3 ratios. I.e. two part from A to P and tree parts from P to B. Now if we divide $10\Omega $ resistance in this wire the length of AP is given by,
${{l}_{1}}=10\times \dfrac{2}{5}=4$
(We have total five parts and ${{l}_{1}}$ are the length contains two parts out of five parts) Similarly for length PB is given by,
${{l}_{2}}=10\times \dfrac{3}{5}=6$
(We have total five parts and ${{l}_{2}}$ are the length contains three parts out of five parts)
It is given that the Meter Bridge is a balanced network or circuit and we get null points at P, we know that, in a balanced condition even though current flows in the rest of circuit, the galvanometer will not show any deflection. I.e. it shows a null point. So according to balance condition of Wheatstone network, we have,
$\dfrac{X}{R}=\dfrac{{{l}_{1}}}{{{l}_{2}}}$
Where, X= unknown resistance
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{X}{6}=\dfrac{4}{6} \\
& \therefore X=4\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Hence unknown resistance (X) is 4Ω.
Now let’s find current, we know that current drawn from 5V is given by,
$I=\dfrac{V}{{{R}_{eq}}}.......(1)$
To find equivalent resistance:
If we consider resistance across a point A and B then circuit looks like,

$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{1}}=4+6=10\Omega \\
& {{R}_{2}}=10\Omega \\
\end{align}$
(Since 4Ω and 6Ω are in series)
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}$
(Since ${{R}_{1}}$ And ${{R}_{2}}$ are in parallel)
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{10}=\dfrac{1}{5\Omega } \\
& {{R}_{eq}}=5\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Put value in equation (1) we get,
$I=\dfrac{5}{5}=1A$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Meter Bridge works on Wheatstone bridge network’s principle. Meter Bridge is the modification of Wheatstone’s network which is generally used to determine unknown resistance. It is also called Wheatstone's meter bridge. Since the length of wire used in this is one meter, it is called Meter Bridge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




