
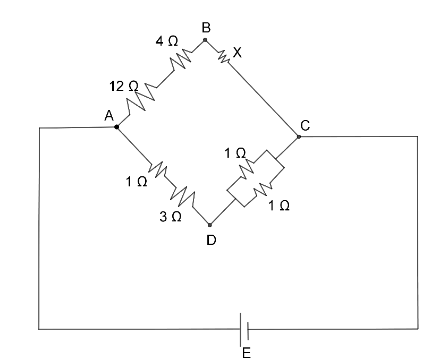
In the arrangement of resistances shown in the figure, the potential difference between $B$ and $D$ will be zero when the unknown resistance $X$ is
A. $4{\text{ }}\Omega \:$
B. ${\text{2 }}\Omega \:$
C. ${\text{3 }}\Omega \:$
D. ${\text{6 }}\Omega \:$

Answer
512.1k+ views
Hint:We will use the concept of wheatstone bridge principle. Then, we will apply the principle in the given circuit. Finally we will evaluate the numerical value of the unknown resistance.
Formulae used:
${R_{Series}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_1}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}....{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_n}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{Parallel}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{{R_3}}}{{{R_4}}}$
$\Rightarrow I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{V}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we are given a few resistors.
Let, ${R_1}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}12{\text{ }}\Omega $
${R_2}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_3}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}X{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_4}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_5}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_6}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}3{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_7}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, clearly ${R_4}$ and ${R_5}$ are parallel to each other. Thus, resistance across $CD$ is,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{CD}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_4}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_5}}}$
Substituting the values, we get
${R_{CD}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0.5{\text{ }}\Omega $
Again, resistance across $AB$ is,
${R_{AB}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_1}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_2}$
Substituting the values, we get
${R_{AB}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}16{\text{ }}\Omega $
Again, resistance across $BC$,
${R_{BC}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_3}$
Substituting the value, we get
${R_{BC}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}X{\text{ }}\Omega $
Also, resistance across $AD$,
${R_{AD}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_6}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_7}$
Substituting the values, we get
${R_{AD}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, for the potential difference across $BD$ to be zero, the ratio of the resistances across the arms of the two sides should be equal. This is known as the wheatstone bridge principle.The equation of the same is,
$\dfrac{{{R_{AB}}}}{{{R_{AD}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{{R_{BC}}}}{{{R_{CD}}}}$
Substituting the values, we get
$\dfrac{{16}}{4}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{X}{{0.5}}$
Further, we get
$X{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0.5{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}\dfrac{{16}}{4}$
After further calculation, we get
$\therefore X{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2{\text{ }}\Omega $
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:Students should remember that the wheatstone bridge principle is applicable for parallel positions. Thus, they should firstly very carefully observe the given circuit.Students often make mistakes while judging the type of connection (parallel or circuit). This makes them wrongly evaluate the net resistance. This will further make them not arrive at the correct answer. Students should keep the actual idea behind this method as that the potential difference between two points is zero only when their potentials are equal. Thus, for them to be equal the arms on either sides of the points are proportional as this will make same amount of current flowing through each will be the same
Formulae used:
${R_{Series}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_1}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}....{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_n}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{Parallel}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{{R_3}}}{{{R_4}}}$
$\Rightarrow I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{V}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we are given a few resistors.
Let, ${R_1}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}12{\text{ }}\Omega $
${R_2}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_3}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}X{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_4}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_5}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_6}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}3{\text{ }}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_7}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, clearly ${R_4}$ and ${R_5}$ are parallel to each other. Thus, resistance across $CD$ is,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{CD}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_4}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_5}}}$
Substituting the values, we get
${R_{CD}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0.5{\text{ }}\Omega $
Again, resistance across $AB$ is,
${R_{AB}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_1}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_2}$
Substituting the values, we get
${R_{AB}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}16{\text{ }}\Omega $
Again, resistance across $BC$,
${R_{BC}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_3}$
Substituting the value, we get
${R_{BC}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}X{\text{ }}\Omega $
Also, resistance across $AD$,
${R_{AD}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_6}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_7}$
Substituting the values, we get
${R_{AD}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, for the potential difference across $BD$ to be zero, the ratio of the resistances across the arms of the two sides should be equal. This is known as the wheatstone bridge principle.The equation of the same is,
$\dfrac{{{R_{AB}}}}{{{R_{AD}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{{R_{BC}}}}{{{R_{CD}}}}$
Substituting the values, we get
$\dfrac{{16}}{4}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{X}{{0.5}}$
Further, we get
$X{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0.5{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}\dfrac{{16}}{4}$
After further calculation, we get
$\therefore X{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2{\text{ }}\Omega $
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:Students should remember that the wheatstone bridge principle is applicable for parallel positions. Thus, they should firstly very carefully observe the given circuit.Students often make mistakes while judging the type of connection (parallel or circuit). This makes them wrongly evaluate the net resistance. This will further make them not arrive at the correct answer. Students should keep the actual idea behind this method as that the potential difference between two points is zero only when their potentials are equal. Thus, for them to be equal the arms on either sides of the points are proportional as this will make same amount of current flowing through each will be the same
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




