
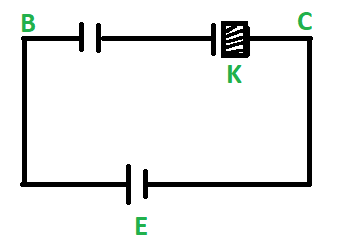
In the adjoining figure, capacitor (1) and (2) have a capacitance ‘C’ each. When the dielectric of dielectric constant K is inserted between the plates of one of the capacitor, the total charge flowing through the battery is:
$\begin{align}
& \text{A) }\dfrac{KCE}{K+1}\text{ from B to C} \\
& \\
& \text{B) }\dfrac{KCE}{K+1}\text{ from C to B} \\
& \\
& \text{C) }\dfrac{\left( K-1 \right)CE}{2\left( K+1 \right)}\text{ from B to C} \\
& \\
& \text{D) }\dfrac{\left( K-1 \right)CE}{2\left( K+1 \right)}\text{ from C to B} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The charge carrying capacity of a capacitor connected to a battery increases when a dielectric medium is introduced between the plates. Due to this, there is also an increase in the capacitance of the capacitor in which the dielectric is inserted.
Complete step by step solution:
The capacitance of two capacitors in series is given by the equation,
$\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{eqq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}$
${{C}_{eqq}}$is the equivalent capacitance produced by the two capacitors ${{\text{C}}_{1}}\text{ and }{{\text{C}}_{2}}$.
So, in our problem, both ${{\text{C}}_{1}}\text{ and }{{\text{C}}_{2}}$ are equal and the equivalent capacitance is given by,
${{C}_{eqq}}=\dfrac{C}{2}$
So the charge stored in the capacitors before the dielectric is applied is given by,
$Q=E{{C}_{eqq}}$
Where, E is the potential difference produced by the cell.
So we can write, $Q=\dfrac{EC}{2}$.
When a dielectric of dielectric constant $\text{K}$ is introduced inside one of the capacitors, the capacitance of that particular capacitor increases by a factor of $\text{K}$.
So if the dielectric is placed in capacitor 2, the capacitance of the capacitor 2 increases by, ${{C}_{2}}'=K{{C}_{2}}$.
So the effective capacitance of the two capacitors can be written as,
$\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{eqq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}'}$
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{eqq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{K{{C}_{2}}}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{eqq}}}=\dfrac{1}{C}+\dfrac{1}{KC}\text{ }\left( \because {{C}_{1}}={{C}_{2}}=C \right)\]
$\therefore {{C}_{eqq}}=\dfrac{KC}{\left( K+1 \right)}$
So the charge stored in the capacitors after the dielectric is applied is given by,
$Q'=E{{C}_{eqq}}$
$Q'=\dfrac{EKC}{\left( K+1 \right)}$
So the total charge flowing through the battery will be the difference of the charge stored when the dielectric is inserted into the capacitor and the charge stored when there is no dielectric present. Which can be represented as,
$\therefore \Delta Q=Q'-Q$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{EKC}{K+1}-\dfrac{EC}{2}$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{2EKC-EC\left( K+1 \right)}{2\left( K+1 \right)}$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{2EKC-EKC-EC}{2\left( K+1 \right)}$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{EKC-EC}{2\left( K+1 \right)}$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{\left( K-1 \right)EC}{2\left( K+1 \right)}$
The charge flowing will be opposite to the current flowing from the battery. So, in this case, it is from B to C.
Note: When a dielectric is inserted to a charged capacitor which is disconnected from the battery, the capacitance of the capacitor increases due to the lowering of potential between the capacitor plates.
The dielectric can fully enclose the region between the capacitor plates or it can occupy a small portion of the region between the plates. The capacitance varies in both cases. The variation in capacitance when a dielectric occupies only a portion of the region between the two plates depends on the width of the region occupied by the dielectric.
Complete step by step solution:
The capacitance of two capacitors in series is given by the equation,
$\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{eqq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}$
${{C}_{eqq}}$is the equivalent capacitance produced by the two capacitors ${{\text{C}}_{1}}\text{ and }{{\text{C}}_{2}}$.
So, in our problem, both ${{\text{C}}_{1}}\text{ and }{{\text{C}}_{2}}$ are equal and the equivalent capacitance is given by,
${{C}_{eqq}}=\dfrac{C}{2}$
So the charge stored in the capacitors before the dielectric is applied is given by,
$Q=E{{C}_{eqq}}$
Where, E is the potential difference produced by the cell.
So we can write, $Q=\dfrac{EC}{2}$.
When a dielectric of dielectric constant $\text{K}$ is introduced inside one of the capacitors, the capacitance of that particular capacitor increases by a factor of $\text{K}$.
So if the dielectric is placed in capacitor 2, the capacitance of the capacitor 2 increases by, ${{C}_{2}}'=K{{C}_{2}}$.
So the effective capacitance of the two capacitors can be written as,
$\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{eqq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}'}$
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{eqq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{K{{C}_{2}}}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{eqq}}}=\dfrac{1}{C}+\dfrac{1}{KC}\text{ }\left( \because {{C}_{1}}={{C}_{2}}=C \right)\]
$\therefore {{C}_{eqq}}=\dfrac{KC}{\left( K+1 \right)}$
So the charge stored in the capacitors after the dielectric is applied is given by,
$Q'=E{{C}_{eqq}}$
$Q'=\dfrac{EKC}{\left( K+1 \right)}$
So the total charge flowing through the battery will be the difference of the charge stored when the dielectric is inserted into the capacitor and the charge stored when there is no dielectric present. Which can be represented as,
$\therefore \Delta Q=Q'-Q$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{EKC}{K+1}-\dfrac{EC}{2}$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{2EKC-EC\left( K+1 \right)}{2\left( K+1 \right)}$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{2EKC-EKC-EC}{2\left( K+1 \right)}$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{EKC-EC}{2\left( K+1 \right)}$
$\Delta Q=\dfrac{\left( K-1 \right)EC}{2\left( K+1 \right)}$
The charge flowing will be opposite to the current flowing from the battery. So, in this case, it is from B to C.
Note: When a dielectric is inserted to a charged capacitor which is disconnected from the battery, the capacitance of the capacitor increases due to the lowering of potential between the capacitor plates.
The dielectric can fully enclose the region between the capacitor plates or it can occupy a small portion of the region between the plates. The capacitance varies in both cases. The variation in capacitance when a dielectric occupies only a portion of the region between the two plates depends on the width of the region occupied by the dielectric.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




