
In split genes, the coding sequences are called as
(a) Introns
(b) Operons
(c) Exons
(d) Cistrons
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: The coding sequence of an interrupted gene is split into several parts including the coding and the non-coding region.
Complete answer:
The coding regions containing actual information of the genes (exons) of most eukaryotic genes are interrupted by few to several non-coding sequences called introns which are spliced out after transcription such genes are called split genes.
Additional information:
1. The first split gene to be described in 1977 by Pierre Chambon and his colleagues was the ovalbumin genes of the chicken.
2. After the removal of introns by the process of RNA splicing the only nucleotide sequence present that is encoded by a gene is called exons.
3.The term exon refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to be the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts.
4. Introns are the interrupting sequences that do not code for any protein products.
5. The split gene theory is proposed by Periannan Senapathy. This theory requires a separate origin of all eukaryotic species.
6. Each interrupted gene or the split gene will have an exon at the beginning as well as the end.
7. The protein molecules having different active regions will have different exons to produce genetic codes in some cases.
8. Introns may also provide for increased recombination rates between exons of a gene and are significant genetic variation.
So, the correct answer is ‘Exons’.
Note: The term cistron refers to a gene and implies to its specific behavior in a cis-trans test which means that each gene is present on a specific locus on the genome. The operon is a cluster of genes that are regulated by a single promoter.
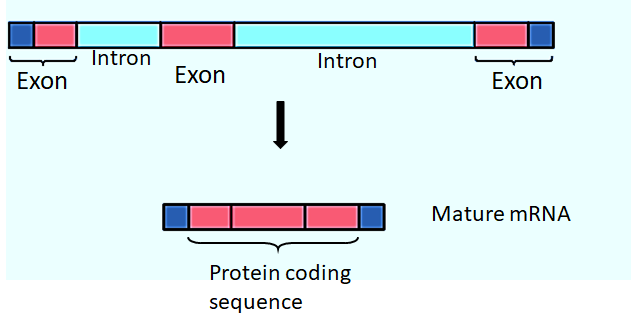
Complete answer:
The coding regions containing actual information of the genes (exons) of most eukaryotic genes are interrupted by few to several non-coding sequences called introns which are spliced out after transcription such genes are called split genes.
Additional information:
1. The first split gene to be described in 1977 by Pierre Chambon and his colleagues was the ovalbumin genes of the chicken.
2. After the removal of introns by the process of RNA splicing the only nucleotide sequence present that is encoded by a gene is called exons.
3.The term exon refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to be the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts.
4. Introns are the interrupting sequences that do not code for any protein products.
5. The split gene theory is proposed by Periannan Senapathy. This theory requires a separate origin of all eukaryotic species.
6. Each interrupted gene or the split gene will have an exon at the beginning as well as the end.
7. The protein molecules having different active regions will have different exons to produce genetic codes in some cases.
8. Introns may also provide for increased recombination rates between exons of a gene and are significant genetic variation.
So, the correct answer is ‘Exons’.
Note: The term cistron refers to a gene and implies to its specific behavior in a cis-trans test which means that each gene is present on a specific locus on the genome. The operon is a cluster of genes that are regulated by a single promoter.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




