
In refraction of light through a glass slab, the direction of the incident ray and the refracted ray are:
(A). Perpendicular to each other
(B). Non-parallel to each other
(C). Parallel to each other
(D). Intersecting each other
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: Understand the concept of refraction through different media. Draw a ray diagram defining the refracted ray and the emergent ray i.e. the ray which will be refracted out of the glass block according to the laws of refraction. Find the relation between the incident ray and the refracted ray from this diagram.
Complete step by step answer:
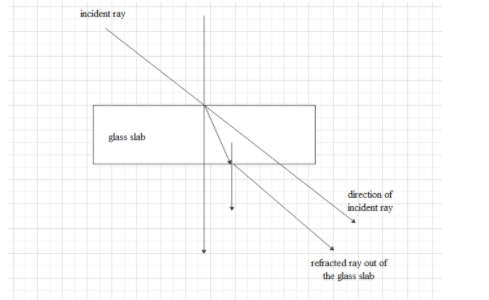
When a beam of light travels from one medium to another medium at the interface of the media a part of the light ray is reflected back to the original medium and the other part is refracted to the other medium.
The direction of propagation of an obliquely incident light that will enter the second medium will change at the interface of the two media. This phenomenon is called refraction.
The direction of the incident beam will always change at the interface of the two media. When the light ray moves from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium the light ray will change direction away from the normal. If the light ray will travel from an optically rarer medium to a optically denser medium the light ray will change direction towards the normal.
So, if a light ray will travel through a glass slab the ray will travel from a rarer medium to a denser medium. So, the refracted light ray will bend towards the normal. So, the incident ray and the refracted ray will not be parallel to each other.
But again, when the refracted ray goes out of the glass slab it will go to a rarer medium and the light ray will go away from the normal by the same amount when the refracted ray inside the glass slab bends towards the normal.
So, the incident ray and the refracted ray will always be parallel to each other.
The correct option is (C)
Note: For refraction to happen the light ray will have to incident obliquely. If the light ray will incident on the glass slab at zero angle of incidence the ray will travel without any change of direction. But for refraction to happen, the angle of incidence should be greater than zero.
Complete step by step answer:

When a beam of light travels from one medium to another medium at the interface of the media a part of the light ray is reflected back to the original medium and the other part is refracted to the other medium.
The direction of propagation of an obliquely incident light that will enter the second medium will change at the interface of the two media. This phenomenon is called refraction.
The direction of the incident beam will always change at the interface of the two media. When the light ray moves from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium the light ray will change direction away from the normal. If the light ray will travel from an optically rarer medium to a optically denser medium the light ray will change direction towards the normal.
So, if a light ray will travel through a glass slab the ray will travel from a rarer medium to a denser medium. So, the refracted light ray will bend towards the normal. So, the incident ray and the refracted ray will not be parallel to each other.
But again, when the refracted ray goes out of the glass slab it will go to a rarer medium and the light ray will go away from the normal by the same amount when the refracted ray inside the glass slab bends towards the normal.
So, the incident ray and the refracted ray will always be parallel to each other.
The correct option is (C)
Note: For refraction to happen the light ray will have to incident obliquely. If the light ray will incident on the glass slab at zero angle of incidence the ray will travel without any change of direction. But for refraction to happen, the angle of incidence should be greater than zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




