
In process $ 2 $ , energy dissipated across the resistance $ {E_D} $ is
$ \left( A \right){E_D} = 3\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2} \right) \\
\left( B \right){E_D} = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2 \\
\left( C \right){E_D} = 3C{V_0}^2 \\
\left( D \right){E_D} = \dfrac{1}{3}\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2} \right) \\ $

Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we need to analyze the two processes as given in the question, then, the dissipation energy of the charged capacitor $ {E_D} $ is calculated by subtracting the voltage change from the work done for charging the capacitor, the difference gives us the correct value of $ {E_D} $ .
Formula used: The formula for the dissipation energy of a charged capacitor is:
$ {E_D} = {W_b} - \Delta V $
Where, work done is given by
$ {W_b} = \dfrac{{C{V_0}}}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{3} + \dfrac{{2{V_0}}}{3} + {V_0}} \right) $
And voltage change by
$ \Delta V = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2 $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
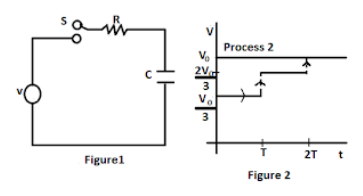
Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure $ 1 $
In the process $ 2 $ ,as we can see in the figure $ 2 $ the voltage is first decreased to one third of the voltage $ {V_0} $ , i.e. $ \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{3} $ and kept at that value for time $ T > > RC $ , then the voltage is increased to twice this voltage , i.e. $ \dfrac{{2{V_0}}}{3} $ and again kept at the same for time $ T > > RC $ . Then, this process is repeated again and the voltage is increased to the value $ {V_0} $ .
Now the dissipation energy for the capacitor is $ {E_D} $ and its value is calculated as
$ {E_D} = {W_b} - \Delta V \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = \dfrac{{C{V_0}}}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{3} + \dfrac{{2{V_0}}}{3} + {V_0}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2 \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = \dfrac{{C{V_0}}}{3}\left( {2{V_0}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2 = \dfrac{{C{V_0}^2}}{6} \\ $
This is the same energy value as given in the option $ \left( D \right){E_D} = \dfrac{1}{3}\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2} \right) $ , hence, $ \left( D \right) $ is correct. $ {V_0} $
Note :
In the Process $ 1 $ , as we can see in the circuit, the switch S is closed here at $ t = 0 $ and the capacitor has the full charge with the voltage. For the time, $ T > > RC $ , the capacitor continues to charge . Across the resistance $ R $ , the dissipation that occurs is $ {E_D} $ . The energy stored in the fully charged capacitor is finally $ {E_C} $ .
Formula used: The formula for the dissipation energy of a charged capacitor is:
$ {E_D} = {W_b} - \Delta V $
Where, work done is given by
$ {W_b} = \dfrac{{C{V_0}}}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{3} + \dfrac{{2{V_0}}}{3} + {V_0}} \right) $
And voltage change by
$ \Delta V = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2 $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure $ 1 $
In the process $ 2 $ ,as we can see in the figure $ 2 $ the voltage is first decreased to one third of the voltage $ {V_0} $ , i.e. $ \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{3} $ and kept at that value for time $ T > > RC $ , then the voltage is increased to twice this voltage , i.e. $ \dfrac{{2{V_0}}}{3} $ and again kept at the same for time $ T > > RC $ . Then, this process is repeated again and the voltage is increased to the value $ {V_0} $ .
Now the dissipation energy for the capacitor is $ {E_D} $ and its value is calculated as
$ {E_D} = {W_b} - \Delta V \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = \dfrac{{C{V_0}}}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{3} + \dfrac{{2{V_0}}}{3} + {V_0}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2 \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = \dfrac{{C{V_0}}}{3}\left( {2{V_0}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2 = \dfrac{{C{V_0}^2}}{6} \\ $
This is the same energy value as given in the option $ \left( D \right){E_D} = \dfrac{1}{3}\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}C{V_0}^2} \right) $ , hence, $ \left( D \right) $ is correct. $ {V_0} $
Note :
In the Process $ 1 $ , as we can see in the circuit, the switch S is closed here at $ t = 0 $ and the capacitor has the full charge with the voltage. For the time, $ T > > RC $ , the capacitor continues to charge . Across the resistance $ R $ , the dissipation that occurs is $ {E_D} $ . The energy stored in the fully charged capacitor is finally $ {E_C} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




