
In pea, caster, and maize the number of cotyledons respectively
(a) One, two, and two
(b) Two, two and one
(c) Two, one, and two
(d) One, two, and one
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: A cotyledon is a type of embryonic leaf found in seed-bearing plants, one or more of it is likely to be the first leaves to appear from a germinating seed. Pea and castor bear the same number of cotyledons.
Complete answer:
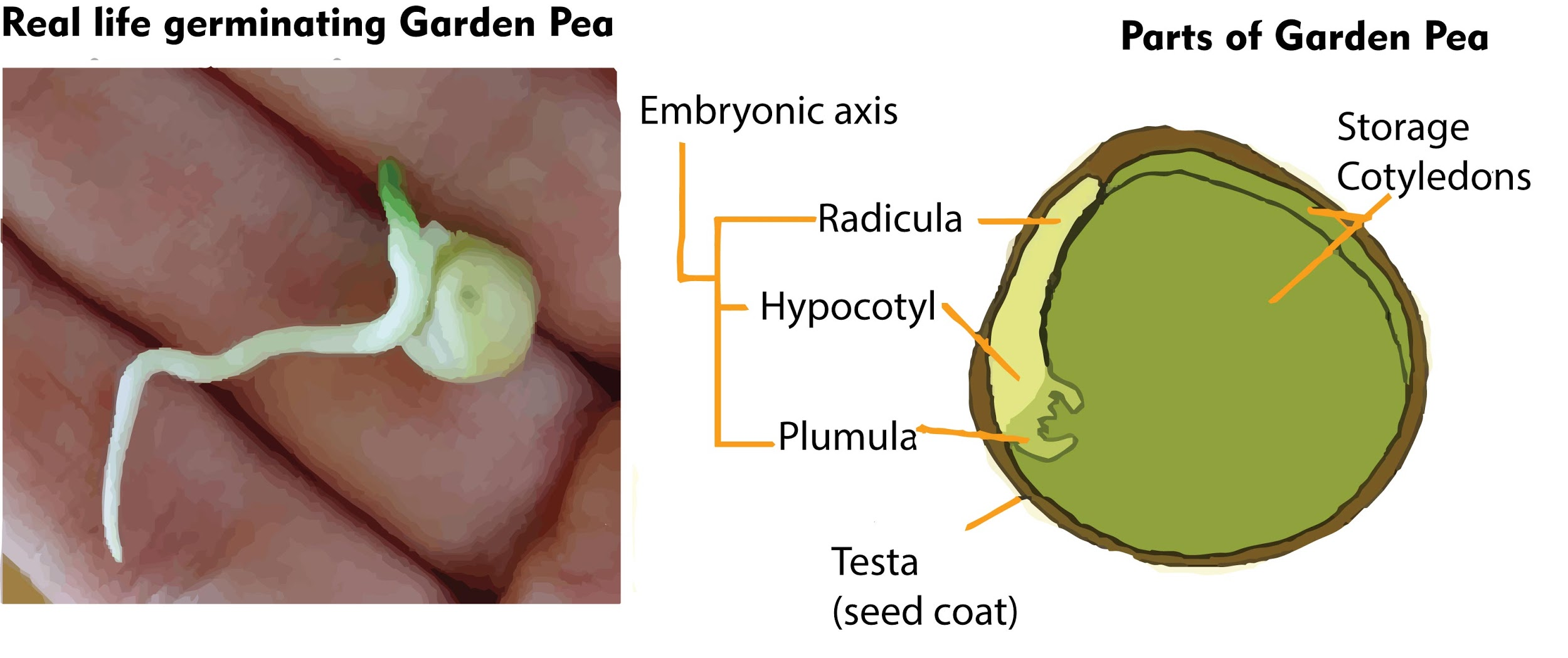
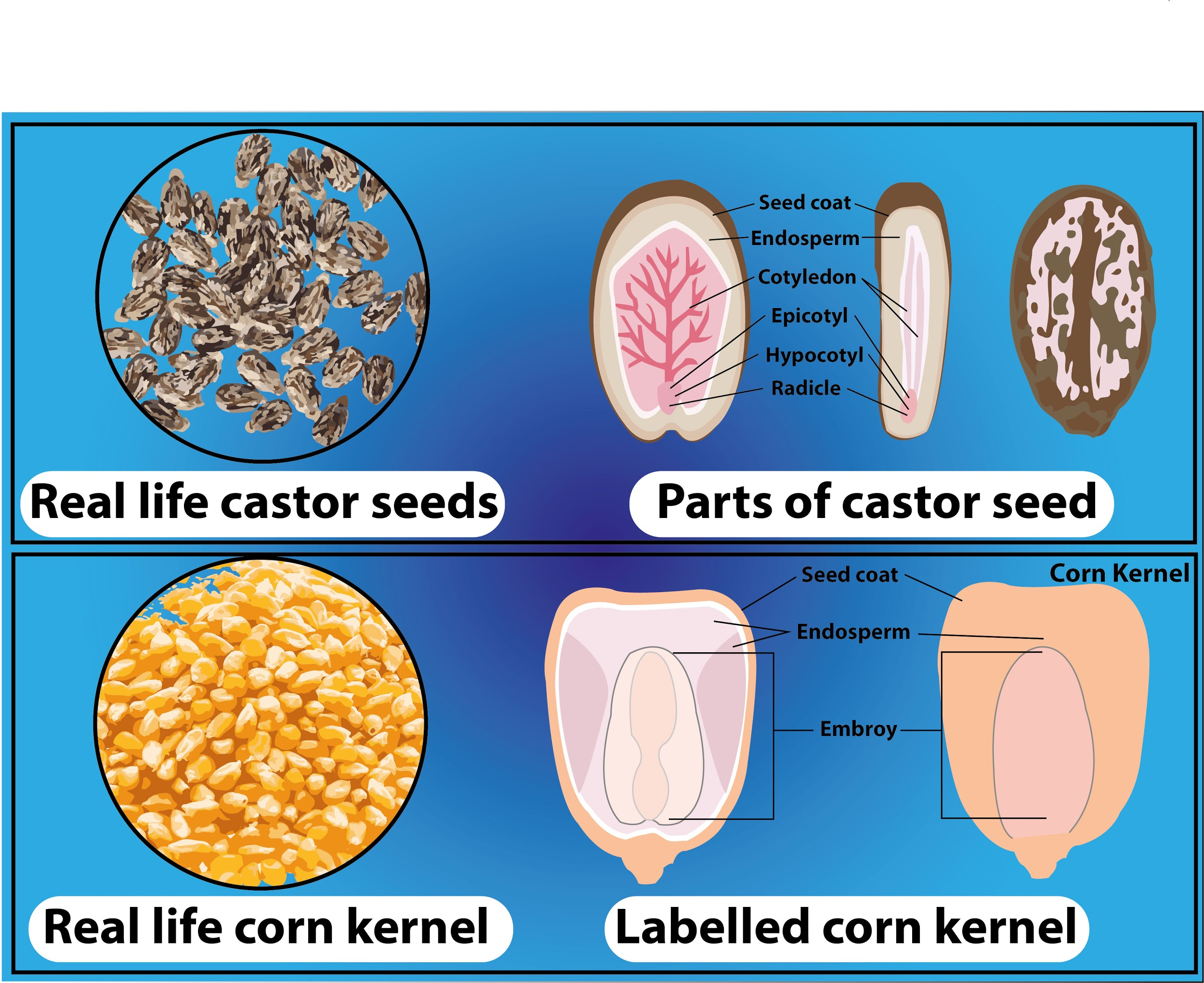
The seeds of both peas and castor are dicots while maize seeds are monocots. Within the seed of a plant, a cotyledon is a significant part of the embryo. It is defined as the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants. One or more of the cotyledons are the first to appear from a germinating seed. Based on the number of cotyledons, botanists classify flowering plants (angiosperms) into :
a) plants with one embryonic leaf, termed monocotyledonous (monocots).
b) plants with two embryonic leaves, termed dicotyledonous (dicots).
Additional Information:
-In monocots, the cotyledon is called a scutellum which is directly connected to the embryo via vascular tissues xylem and phloem. Food reserves are stored in the large endosperm. Similarly in the dicots, the two cotyledons also have vascular connections to the embryo. In endospermic dicots, for example, tomato and pepper, the food reserves are stored in the endosperm.
- In non-endospermic dicots, for example, split pea and peanuts, the triploid endosperm develops normally following double fertilization.
So, the correct answer is ‘,Two, two and one’.
Note:
-In the case of dicot seedlings with photosynthetic cotyledons, they are functionally similar to leaves. Although, true leaves and cotyledons are distinct based on their development. During embryogenesis, cotyledons are formed along with the root and shoot meristems. They are thus present in the seed before germination.
-True leaves are formed after germination from the shoot apical meristem. It is also responsible for generating subsequent aerial portions of the plant.
Complete answer:
The seeds of both peas and castor are dicots while maize seeds are monocots. Within the seed of a plant, a cotyledon is a significant part of the embryo. It is defined as the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants. One or more of the cotyledons are the first to appear from a germinating seed. Based on the number of cotyledons, botanists classify flowering plants (angiosperms) into :
a) plants with one embryonic leaf, termed monocotyledonous (monocots).
b) plants with two embryonic leaves, termed dicotyledonous (dicots).
Additional Information:
-In monocots, the cotyledon is called a scutellum which is directly connected to the embryo via vascular tissues xylem and phloem. Food reserves are stored in the large endosperm. Similarly in the dicots, the two cotyledons also have vascular connections to the embryo. In endospermic dicots, for example, tomato and pepper, the food reserves are stored in the endosperm.
- In non-endospermic dicots, for example, split pea and peanuts, the triploid endosperm develops normally following double fertilization.
So, the correct answer is ‘,Two, two and one’.
Note:
-In the case of dicot seedlings with photosynthetic cotyledons, they are functionally similar to leaves. Although, true leaves and cotyledons are distinct based on their development. During embryogenesis, cotyledons are formed along with the root and shoot meristems. They are thus present in the seed before germination.
-True leaves are formed after germination from the shoot apical meristem. It is also responsible for generating subsequent aerial portions of the plant.


Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




