
-In n — p — n transistor, if doping in base region is increased then collector current.
A. Remain the same
B. Increases
C. Decreases
D. None of the above
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The question is based on the concept of semiconductors .
In n-p-n transistor the collector is n-type, and the emitter is also n-type, and here the base is p-type.
Complete step by step answer:
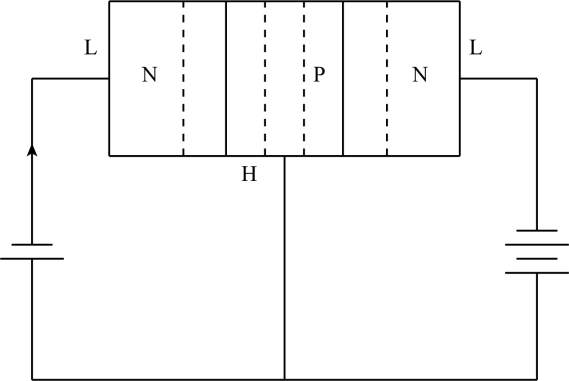
In the n-p-n transistor the depletion layer at the junction is the same for both the junction and when the doping is increased in the base region, then the number of holes gets increased in the base. The emitter and base circuit is forward biased, and the base and collector circuit is reverse biased.Because of the increase of holes in the base region, the recombination takes place very fast so that the current from emitter to collector gets decreased. In other words we can say that when we dope the base region then there is an increase of holes takes place and then the electron from emitter region recombines with the holes in the base thus th current gets reduce which is going to the collector
Due to which the current constitutes in the transistor. Such type of transistor is mostly used in the circuit because their majority charge carriers are electrons which have high mobility as compared to holes.
Note:
There are different characteristics of n-p-n and p-n-p transistors, and both depend on the n-type. P-type semiconductors.N-type is doped with pentavalent impurities, and p-type is doped with trivalent impurities. In NPN transistors, the electron moves from the emitter to collector region.The movement of electrons is the current in the transistor. This transistor is the most used device in the circuit because it constitutes the current due to election. After all, here, electrons are in the majority compared to holes.
In n-p-n transistor the collector is n-type, and the emitter is also n-type, and here the base is p-type.
Complete step by step answer:

In the n-p-n transistor the depletion layer at the junction is the same for both the junction and when the doping is increased in the base region, then the number of holes gets increased in the base. The emitter and base circuit is forward biased, and the base and collector circuit is reverse biased.Because of the increase of holes in the base region, the recombination takes place very fast so that the current from emitter to collector gets decreased. In other words we can say that when we dope the base region then there is an increase of holes takes place and then the electron from emitter region recombines with the holes in the base thus th current gets reduce which is going to the collector
Due to which the current constitutes in the transistor. Such type of transistor is mostly used in the circuit because their majority charge carriers are electrons which have high mobility as compared to holes.
Note:
There are different characteristics of n-p-n and p-n-p transistors, and both depend on the n-type. P-type semiconductors.N-type is doped with pentavalent impurities, and p-type is doped with trivalent impurities. In NPN transistors, the electron moves from the emitter to collector region.The movement of electrons is the current in the transistor. This transistor is the most used device in the circuit because it constitutes the current due to election. After all, here, electrons are in the majority compared to holes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




