
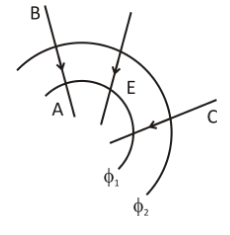
In moving from A to B along an electric field line, the electric field does $6.4 \times {10^{ - 19}}\,J$ of work on an electron. If ${\phi _1}$, ${\phi _2}$ are equipotential surfaces, then the potential difference $\left( {{V_C} - {V_A}} \right)$ is
A. $ - 4V$
B. $4V$
C. Zero
D. $64V$

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint:First let us see what an equipotential surface is: Any surface on which the potential is constant is called an equipotential surface. In other words, the potential distance between any two points on an equipotential surface is zero. Here we have to use the formula for work done in an equipotential surface to get the answer.
Complete step by step solution:
The work done in moving a charge on an equipotential surface between two points is zero. If a point charge is transferred from point ${V_A}$ to ${V_B}$ on an equipotential surface, the work performed in transferring the charge is given by the equipotential surface as:
$W = {q_ \circ }\left( {{V_A} - {V_B}} \right)$
Since, ${V_A} - {V_B}$ is equal to zero, the total work done is $W = 0$.
Given, Work done, $W = 6.4 \times {10^{ - 19}}\,J$
Charge, ${q_ \circ } = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}\,C$
We know that,
$
W = {q_ \circ }\left( {{V_c} - {V_A}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {V_C} - {V_A} = \dfrac{W}{{{q_ \circ }}} \\
\Rightarrow {V_C} - {V_A} = \dfrac{{6.4 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}{{1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}} \\
\therefore{V_C} - {V_A} = 4V \\
$
Hence, option B is the answer.
Additional information:
-Equipotential surface properties
-The electric field is still perpendicular to the potential surface of the equipment.
-Two potentially identical surfaces will never collide.
-Equipotential surfaces are concentric spherical shells with a point charge.
-Equipotential surfaces are planes normal to the x-axis with a uniform electric field.
-From high potential to low potential, the position of the equipotential surface.
Note:Here we have to remember the formula of work done for equipotential surfaces properly. Also, we should properly put the values of the work done and charge otherwise the answer would be wrong. If the points are all at the same electric potential in an electric field, so they are known as the equipotential points. It is known as an equipotential line if these points are connected by a line or a curve. It is called an equipotential surface if those points lie on a surface. In addition, it is known as an equipotential volume if these points are spread throughout a room or a volume.
Complete step by step solution:
The work done in moving a charge on an equipotential surface between two points is zero. If a point charge is transferred from point ${V_A}$ to ${V_B}$ on an equipotential surface, the work performed in transferring the charge is given by the equipotential surface as:
$W = {q_ \circ }\left( {{V_A} - {V_B}} \right)$
Since, ${V_A} - {V_B}$ is equal to zero, the total work done is $W = 0$.
Given, Work done, $W = 6.4 \times {10^{ - 19}}\,J$
Charge, ${q_ \circ } = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}\,C$
We know that,
$
W = {q_ \circ }\left( {{V_c} - {V_A}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {V_C} - {V_A} = \dfrac{W}{{{q_ \circ }}} \\
\Rightarrow {V_C} - {V_A} = \dfrac{{6.4 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}{{1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}} \\
\therefore{V_C} - {V_A} = 4V \\
$
Hence, option B is the answer.
Additional information:
-Equipotential surface properties
-The electric field is still perpendicular to the potential surface of the equipment.
-Two potentially identical surfaces will never collide.
-Equipotential surfaces are concentric spherical shells with a point charge.
-Equipotential surfaces are planes normal to the x-axis with a uniform electric field.
-From high potential to low potential, the position of the equipotential surface.
Note:Here we have to remember the formula of work done for equipotential surfaces properly. Also, we should properly put the values of the work done and charge otherwise the answer would be wrong. If the points are all at the same electric potential in an electric field, so they are known as the equipotential points. It is known as an equipotential line if these points are connected by a line or a curve. It is called an equipotential surface if those points lie on a surface. In addition, it is known as an equipotential volume if these points are spread throughout a room or a volume.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




