
In man, Schizont stages of Plasmodium vivax are found in
A. Erythrocytes only
B. Erythrocytes and liver cells
C. Liver cell only
D. Erythrocytes liver cells and spleen
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: Plasmodium vivax, which is related to the public health burden, is the major cause of malaria. While improved malaria control efforts have effectively reduced the incidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in many areas, in regions where both parasites coexist, there has been a consistent increase in the percentage of malaria due to P. vivax.
Complete answer:There are two hosts involved in the malaria life cycle. During the blood meal, a female Anopheles which is infected with malaria inoculates sporozoites into the human host bloodstream.
The sporozoites infect the liver cells and then these cells will mature to schizonts which will then mature and give rise to merozoites. P. vivax and P. ovale a dormant stage which is hypnozoites they can persist in the liver and will cause relapse by invading the bloodstream.
Exo erythrocytic schizogony after replication in the liver the parasites will undergo sexual replication in the erythrocytes which are now called erythrocytic schizogony. Now merozoites will infect red blood cells. Trophozoites will mature to schizonts in the ring stage which will mature and give merozoites. Some of the parasitic cells differentiate into the sexual erythrocyte stage.
Blood stage parasitic cells are responsible for the clinical manifestation of the disease. The male and female gametocytes are ingested by an Anopheles mosquito during a blood meal. The mosquito’s multiplication is known as the sporogonic cycle.
Hence the correct answer is option B, Erythrocytes, and liver cells.
Below is the picture of the Plasmodium life cycle.
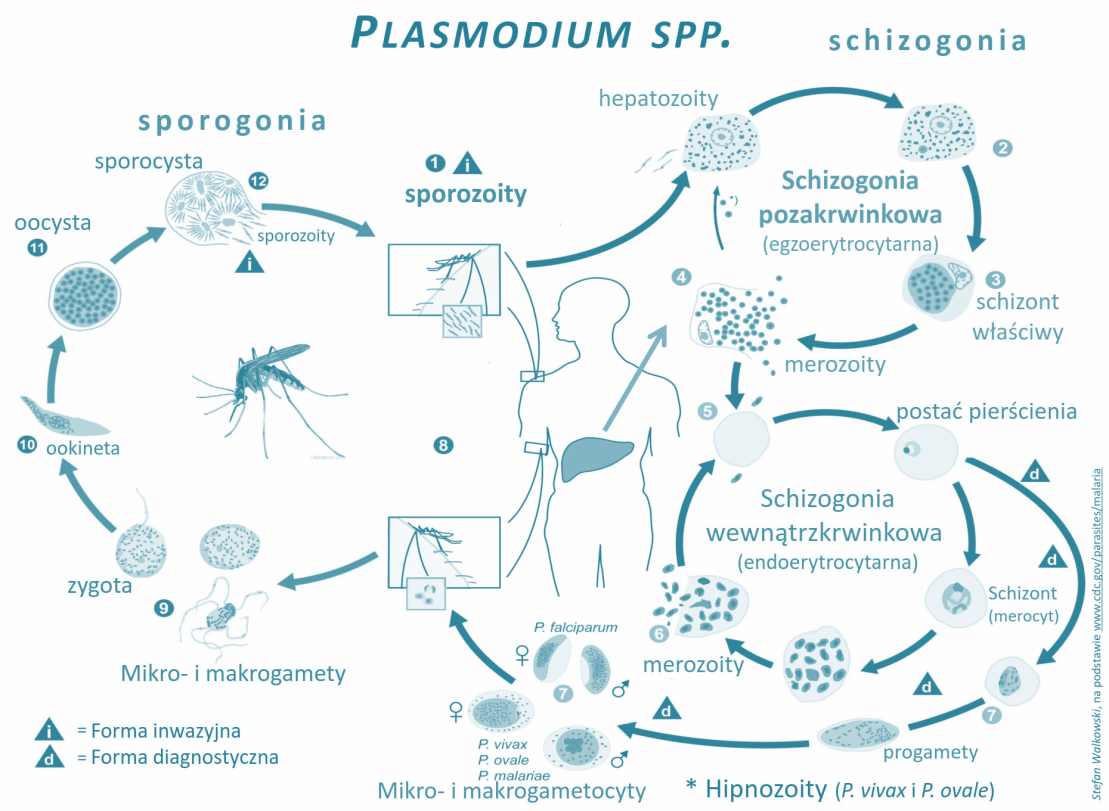
Note: Plasmodium vivax is very large and can fill up the entire red blood cell with 10 to 24 merozoites, each of the cells having distinct chromatin and cytoplasm. They are also present in the liver. Their cell size and shape can vary from the more compact Plasmodium Malariae and Plasmodium ovale schizonts.
Complete answer:There are two hosts involved in the malaria life cycle. During the blood meal, a female Anopheles which is infected with malaria inoculates sporozoites into the human host bloodstream.
The sporozoites infect the liver cells and then these cells will mature to schizonts which will then mature and give rise to merozoites. P. vivax and P. ovale a dormant stage which is hypnozoites they can persist in the liver and will cause relapse by invading the bloodstream.
Exo erythrocytic schizogony after replication in the liver the parasites will undergo sexual replication in the erythrocytes which are now called erythrocytic schizogony. Now merozoites will infect red blood cells. Trophozoites will mature to schizonts in the ring stage which will mature and give merozoites. Some of the parasitic cells differentiate into the sexual erythrocyte stage.
Blood stage parasitic cells are responsible for the clinical manifestation of the disease. The male and female gametocytes are ingested by an Anopheles mosquito during a blood meal. The mosquito’s multiplication is known as the sporogonic cycle.
Hence the correct answer is option B, Erythrocytes, and liver cells.
Below is the picture of the Plasmodium life cycle.

Note: Plasmodium vivax is very large and can fill up the entire red blood cell with 10 to 24 merozoites, each of the cells having distinct chromatin and cytoplasm. They are also present in the liver. Their cell size and shape can vary from the more compact Plasmodium Malariae and Plasmodium ovale schizonts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




