
In its nucleophilic substitution reaction, aryl halide resembles
A.Vinyl chloride
B.Allyl chloride
C.Benzyl chloride
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint:We know that halides are classified as $s{p^2}{\text{C}} - {\text{X}}$ and $s{p^3}{\text{C}} - {\text{X}}$. $s{p^3}{\text{C}} - {\text{X}}$ type of halides are further classified into three types namely, alkyl halides, allylic halides and benzylic halides. $s{p^2}{\text{C}} - {\text{X}}$types of halides are classified into two types namely, vinylic and aryl halides.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s understand vinylic halide and aryl halides in detail. This is the type of halide in which the halogen atom is bonded to an $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atom of a carbon-carbon double bond.
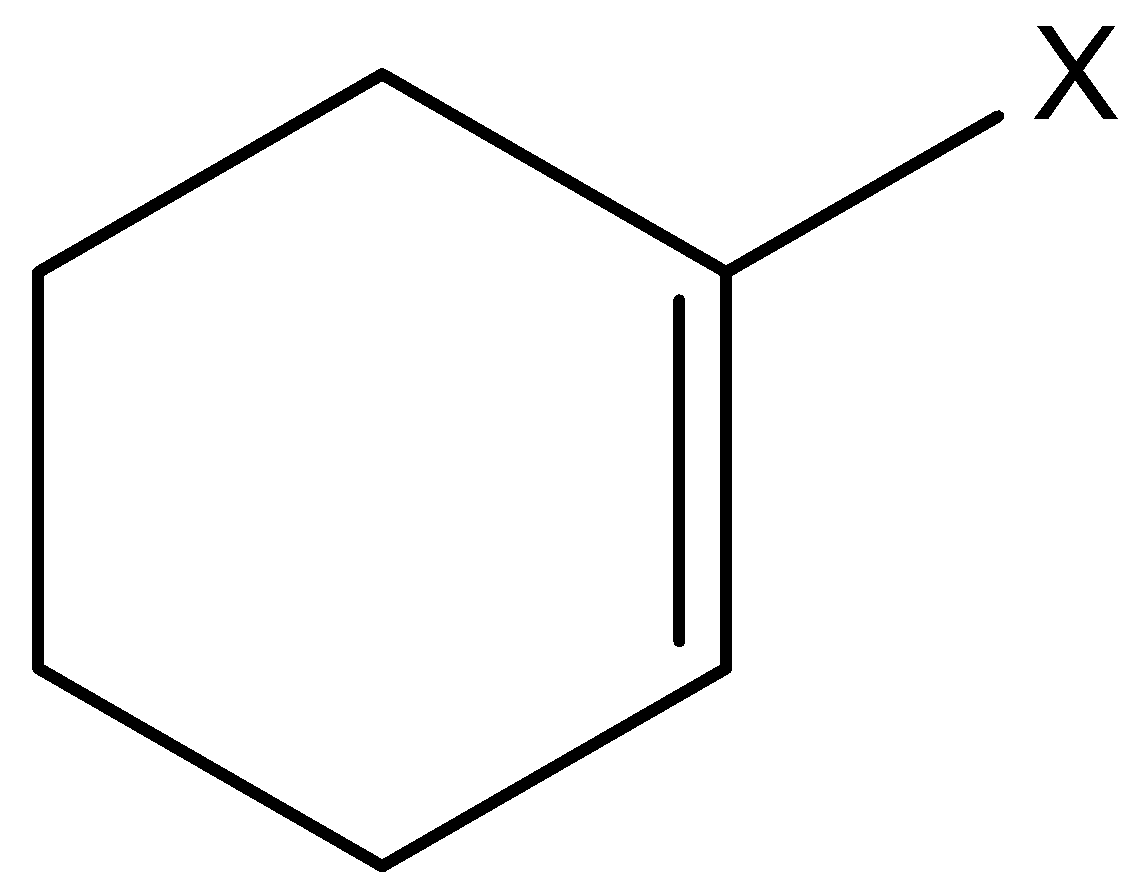
Aryl halides are the compounds in which a halogen atom is bonded to a $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atom of the aromatic ring.
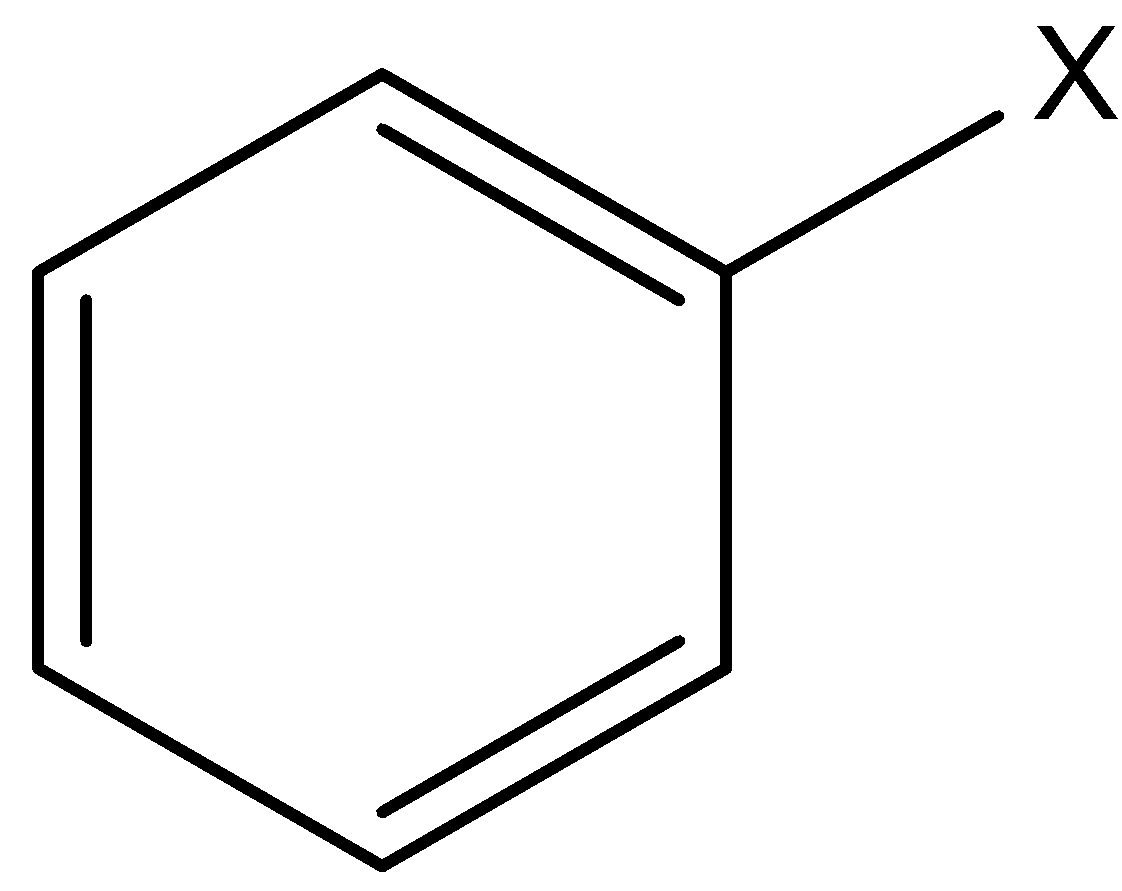
X is any halide (F, Cl, Br, I)
Now, come to the question. Here, aryl halide undergoes reaction with aqueous potassium hydroxide. The nucleophilic substitution reaction is difficult. Let’s consider chloro benzene.
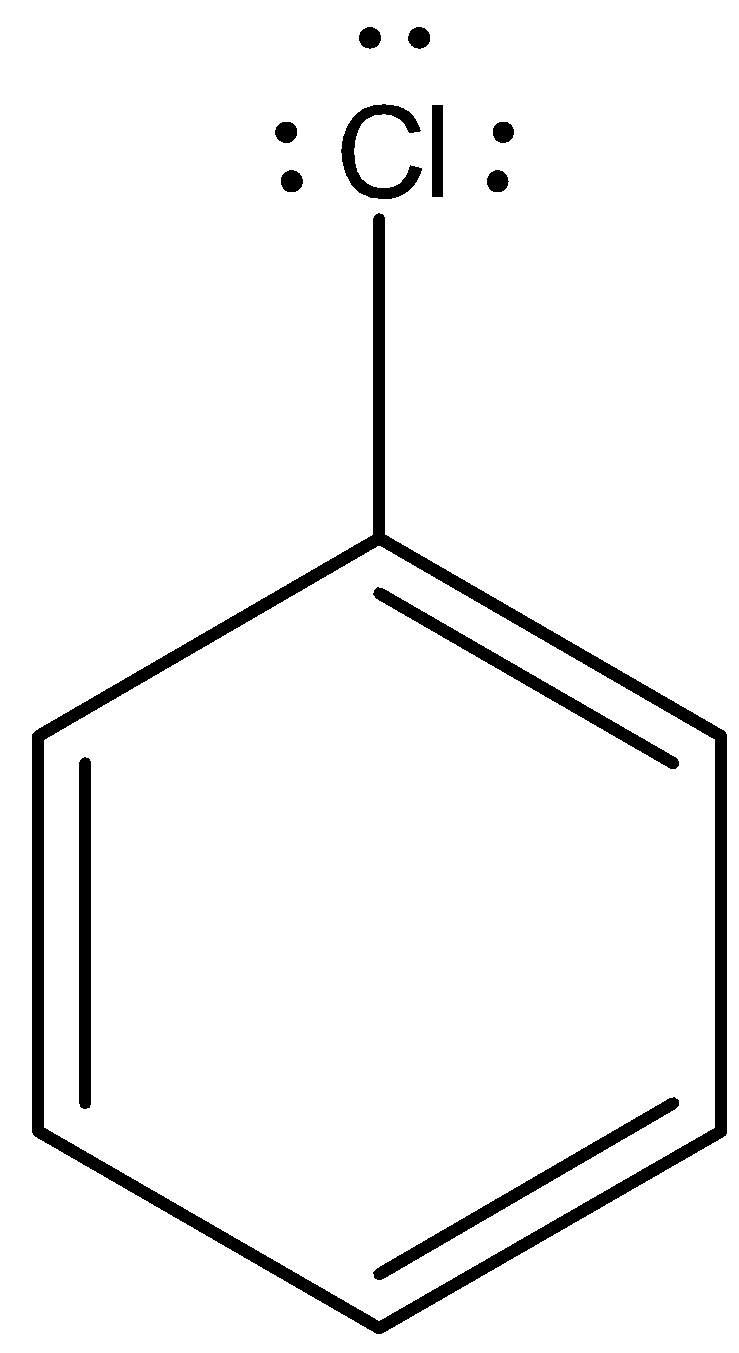
Chlorobenzene is an example of aryl halide. There are three lone pairs on the chlorine atom. The chlorine atom gives the lone pair to the neighboring carbon atom and the C-Cl bond acquires partial double bond character.
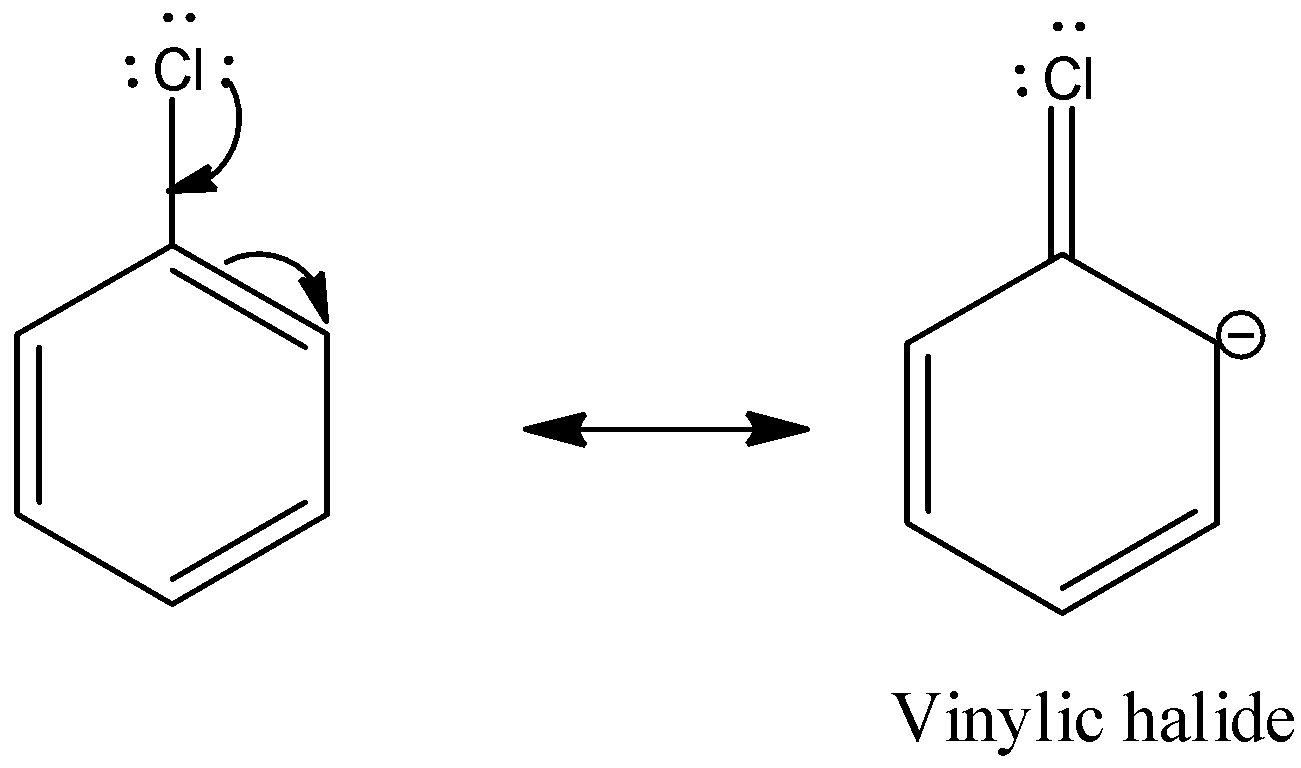
So, the substitution of nucleophiles is difficult.
So, we find that any aryl halides in nucleophilic substitution reaction resembles the vinylic halide.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
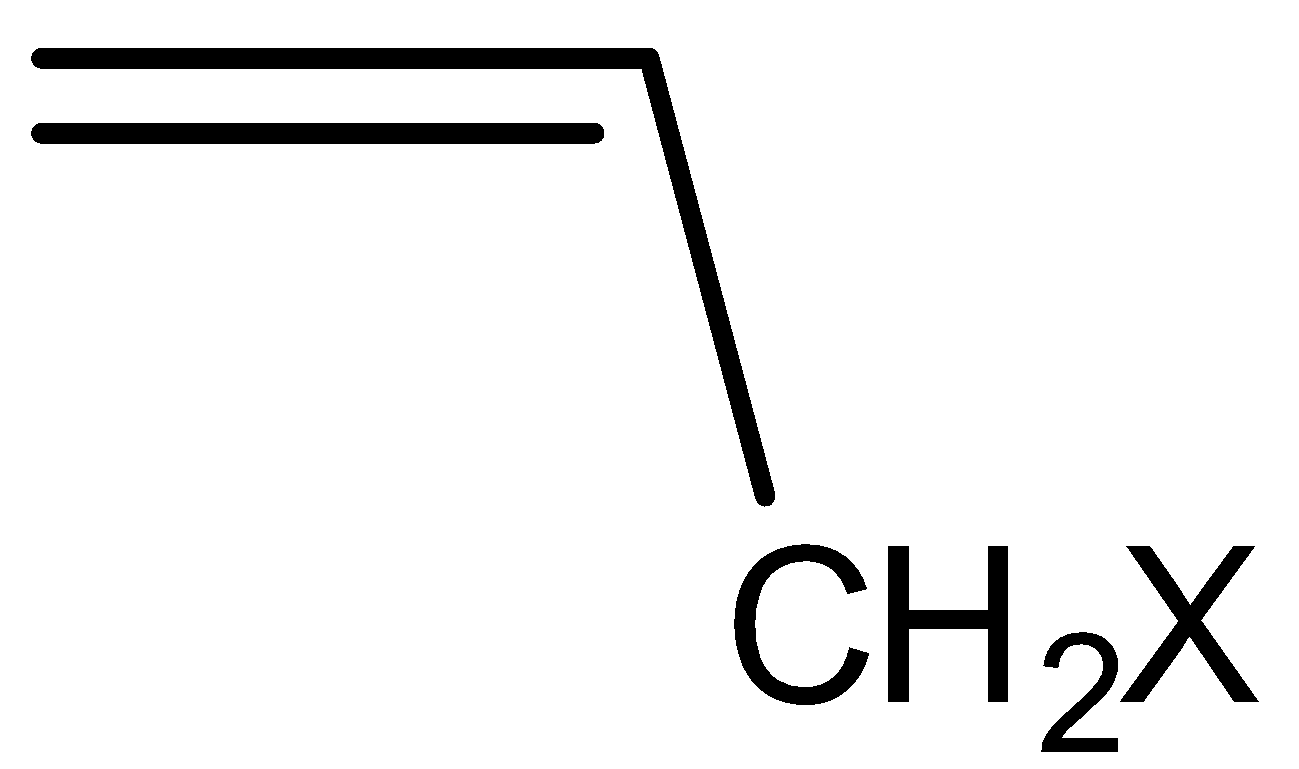
On the basis of $s{p^3}{\text{C}} - {\text{X}}$ type of carbon halogen bond, alkyl halides are classified into three types alkyl halide, allylic halide and benzylic halides. Alkyl halides are those in which an alkyl group is bonded to a halogen group (ex methyl chloride). Allylic halides are those halides in which a halogen atom is bonded to an $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atom next to carbon-carbon double bond.
Example:
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s understand vinylic halide and aryl halides in detail. This is the type of halide in which the halogen atom is bonded to an $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atom of a carbon-carbon double bond.

Aryl halides are the compounds in which a halogen atom is bonded to a $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atom of the aromatic ring.

X is any halide (F, Cl, Br, I)
Now, come to the question. Here, aryl halide undergoes reaction with aqueous potassium hydroxide. The nucleophilic substitution reaction is difficult. Let’s consider chloro benzene.

Chlorobenzene is an example of aryl halide. There are three lone pairs on the chlorine atom. The chlorine atom gives the lone pair to the neighboring carbon atom and the C-Cl bond acquires partial double bond character.

So, the substitution of nucleophiles is difficult.
So, we find that any aryl halides in nucleophilic substitution reaction resembles the vinylic halide.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
On the basis of $s{p^3}{\text{C}} - {\text{X}}$ type of carbon halogen bond, alkyl halides are classified into three types alkyl halide, allylic halide and benzylic halides. Alkyl halides are those in which an alkyl group is bonded to a halogen group (ex methyl chloride). Allylic halides are those halides in which a halogen atom is bonded to an $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atom next to carbon-carbon double bond.
Example:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




