
In humans, cleavage division is
(a)Slow and synchronous
(b)Slow and asynchronous
(c)Fast and asynchronous
(d)Fast and synchronous
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: The cleavage division in humans will take at least 12 to 24 hours to complete and the cleavage division in humans is not simultaneous.
Complete answer:
-Holoblastic cleavage occurs in humans i.e. Cleavage I or meiosis I is meridional but cleavage II or meiotic II is meridional in one cell and equatorial in another (rotational cleavage). Hence it is asynchronous and slow.
-In all blastomeres stage, the first few cleavages occur simultaneously, but as the number of cells grows, simultaneity is lost, and the blastomeres differentiate independently. Embryos were categorized as asynchronous if cells were present within the embryo at various stages of the cell cycle (Interphase / Mitotic phase).
-Meridional cleavage plane: When a furrow bisects both the poles of the egg that pass through the median axis or egg center, it is called the meridional cleavage line.
Additional Information:
Characteristics of cleavage
-The cleavage parcels the cytoplasm of the egg into several cells (blastomeres) which may start on separate differentiation pathways.
-There is no growth between the divisions and the cytoplasmic ratio of the nuclear decreases about 1000 fold.
-Some of the cells lack or have very short phases of G1 and G2.
-Cytokinesis may be unequal resulting in different cell sizes.
-Holoblastic cleavage is the case where absolute cleavage furrows bisect the cells while meroblastic cleavage explains partial or incomplete development of furrows.
-Mammalian cleavage is slow, irregular, and is asynchronous. Cleavage I is meridional but cleavage II is meridional in one cell and equatorial in another (rotational cleavage). The blastomeres press together in the compaction phase at the 8 cell level.
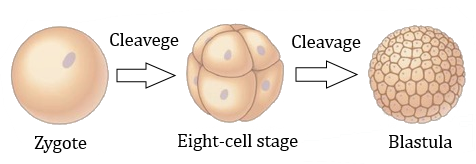
So, the correct answer is ‘slow and asynchronous’.
Note: Cleavage occurs during the zygote stage where there will be no growth of the cells, and the number of cells will increase. In the case of mitosis, the division occurs to form germ cells as well as replace the worn out and damaged cells.
Complete answer:
-Holoblastic cleavage occurs in humans i.e. Cleavage I or meiosis I is meridional but cleavage II or meiotic II is meridional in one cell and equatorial in another (rotational cleavage). Hence it is asynchronous and slow.
-In all blastomeres stage, the first few cleavages occur simultaneously, but as the number of cells grows, simultaneity is lost, and the blastomeres differentiate independently. Embryos were categorized as asynchronous if cells were present within the embryo at various stages of the cell cycle (Interphase / Mitotic phase).
-Meridional cleavage plane: When a furrow bisects both the poles of the egg that pass through the median axis or egg center, it is called the meridional cleavage line.
Additional Information:
Characteristics of cleavage
-The cleavage parcels the cytoplasm of the egg into several cells (blastomeres) which may start on separate differentiation pathways.
-There is no growth between the divisions and the cytoplasmic ratio of the nuclear decreases about 1000 fold.
-Some of the cells lack or have very short phases of G1 and G2.
-Cytokinesis may be unequal resulting in different cell sizes.
-Holoblastic cleavage is the case where absolute cleavage furrows bisect the cells while meroblastic cleavage explains partial or incomplete development of furrows.
-Mammalian cleavage is slow, irregular, and is asynchronous. Cleavage I is meridional but cleavage II is meridional in one cell and equatorial in another (rotational cleavage). The blastomeres press together in the compaction phase at the 8 cell level.

So, the correct answer is ‘slow and asynchronous’.
Note: Cleavage occurs during the zygote stage where there will be no growth of the cells, and the number of cells will increase. In the case of mitosis, the division occurs to form germ cells as well as replace the worn out and damaged cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




