
In germanium crystal, the forbidden energy gap in joule is:
A. $1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}$
B. Zero
C. $1.12 \times {10^{ - 19}}$
D. $1.76 \times {10^{ - 19}}$
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: whenever we speak about conductivity of a substance let it be an insulator or conductor or semiconductor we consider energy levels of charge carriers. There are two bands one is valence band and the other is conduction band. Forbidden energy gap is the energy barrier between these two bands
Formula used:
$1eV = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}J$
Complete answer:
The energy variation between lower valence band and upper conduction band is called the forbidden energy gap of a semiconductor. In between this energy gap in case of intrinsic semiconductor no electron exists. Now with increase in temperature thermal energy of an electron in valence band increases and reaches the conduction band and this charge carrier conducts electricity. But in the case of conductors, charge carriers which conduct electricity exist already.
When temperature of the conductor is increased both atoms and free electrons gain thermal energy and start vibrating vigorously with higher amplitudes.
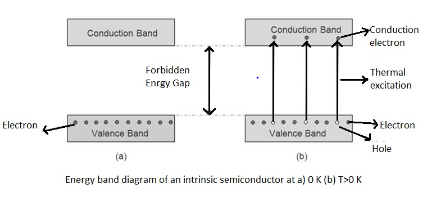
Forbidden energy gaps in semiconductors would be nearly 1eV.
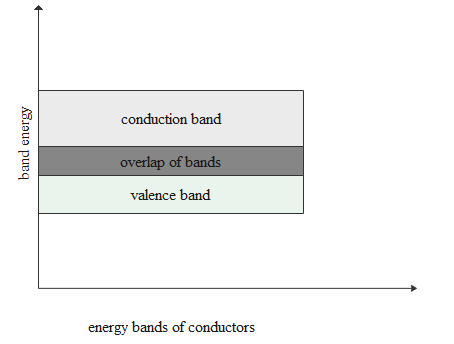
In case of conductors both conduction and valence bands get overlapped.
Due to increase in temperature number of collisions increases and rate at which collision occurs also increases.
When this rate gets increased it becomes obstruction to flow of electrons in that conductor. This slows down electron flow which means current flow is decreased because current is nothing but rate of flow of free charge carriers. Current flow reduced means resistance is increased.
Forbidden energy gap for germanium crystals is 0.7 electron volts.
$1eV = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}J$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow 0.7eV = 0.7 \times 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}J \cr
& \Rightarrow 0.7eV = 1.12 \times {10^{ - 19}}J \cr} $
Hence option C will be the answer.
Note: Since germanium is in intrinsic form there is the forbidden energy gap and conductivity will be low. If it’s temperature is increased then the gap decreases. If it is doped with trivalent or pentavalent impurity then it will be converted to the p-type or n-type extrinsic semiconductor.
Formula used:
$1eV = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}J$
Complete answer:
The energy variation between lower valence band and upper conduction band is called the forbidden energy gap of a semiconductor. In between this energy gap in case of intrinsic semiconductor no electron exists. Now with increase in temperature thermal energy of an electron in valence band increases and reaches the conduction band and this charge carrier conducts electricity. But in the case of conductors, charge carriers which conduct electricity exist already.
When temperature of the conductor is increased both atoms and free electrons gain thermal energy and start vibrating vigorously with higher amplitudes.

Forbidden energy gaps in semiconductors would be nearly 1eV.

In case of conductors both conduction and valence bands get overlapped.
Due to increase in temperature number of collisions increases and rate at which collision occurs also increases.
When this rate gets increased it becomes obstruction to flow of electrons in that conductor. This slows down electron flow which means current flow is decreased because current is nothing but rate of flow of free charge carriers. Current flow reduced means resistance is increased.
Forbidden energy gap for germanium crystals is 0.7 electron volts.
$1eV = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}J$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow 0.7eV = 0.7 \times 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}J \cr
& \Rightarrow 0.7eV = 1.12 \times {10^{ - 19}}J \cr} $
Hence option C will be the answer.
Note: Since germanium is in intrinsic form there is the forbidden energy gap and conductivity will be low. If it’s temperature is increased then the gap decreases. If it is doped with trivalent or pentavalent impurity then it will be converted to the p-type or n-type extrinsic semiconductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




