
In DNA, the complementary bases are:
(A)-adenine and thymine; guanine and cytosine
(B)-adenine and thymine; guanine and uracil
(C)-adenine and guanine ;thymine and cytosine
(D)-Uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: In DNA, adenine and thymine, cytosine and guanine are bases and RNA has adenine, Uracil, cytosine and guanine. These bases are complementary to each other because the hydrogen bonds are formed between specific pairs of bases.
Complete step by step answer:
-There are two types of nucleic acids; DNA and RNA
-DNA IS deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is ribonucleic acid.
-Hydrolysis of DNA and RNA give sugar (Ribose), phosphoric acid and heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms called bases.
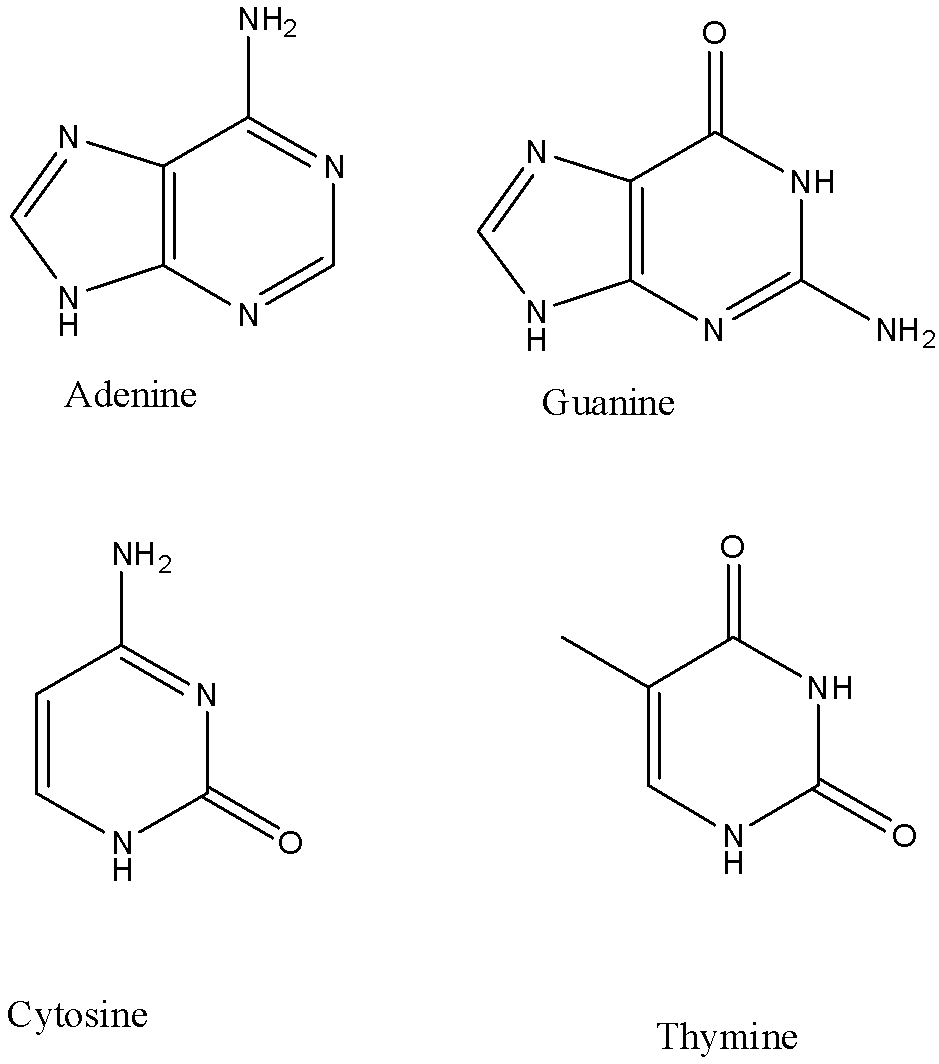
-DNA contains four bases -adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine.
-RNA contains four bases- adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil.
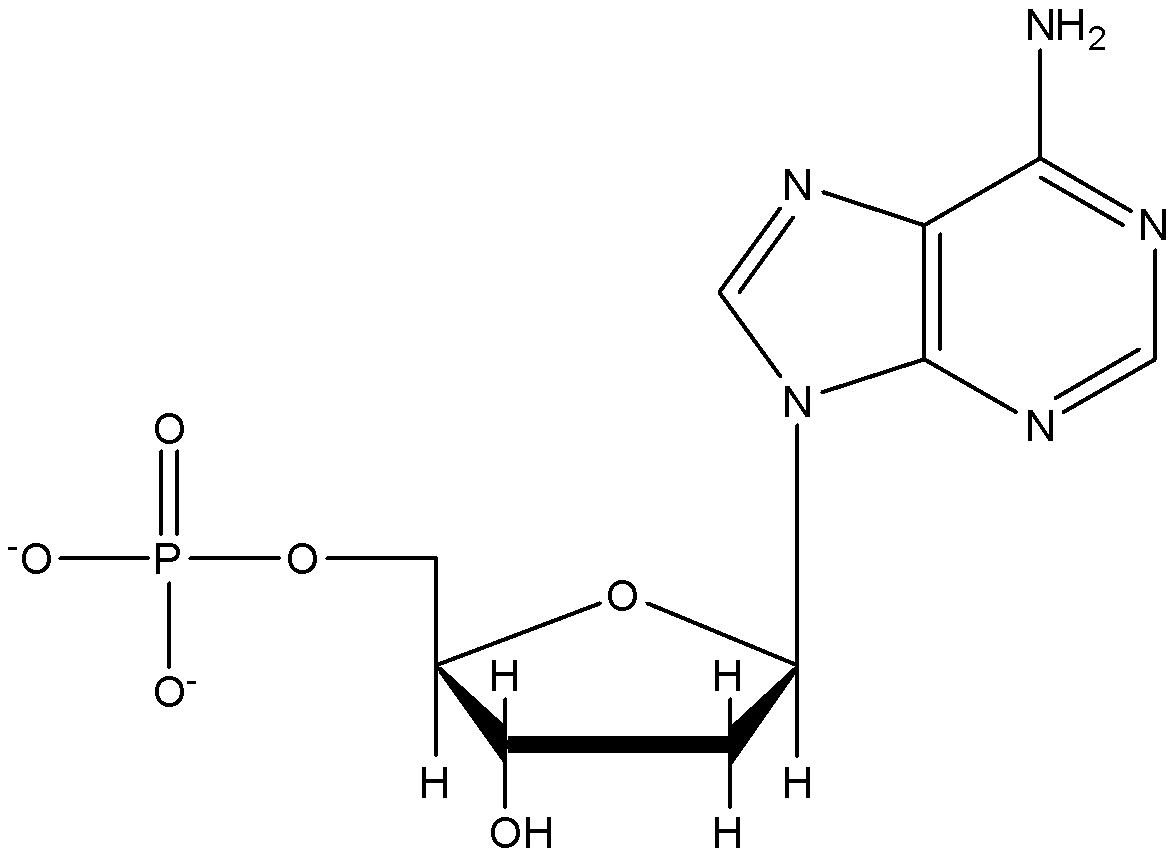
Adenine as base
-Base is attached at position 1’ position of sugar which forms nucleoside and phosphoric acid is attached at position 5’ which forms nucleotide.
-nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’ and 3’ carbon atoms of ribose sugar.

-primary structure of DNA contains sequences of nucleotides in the chain of nucleic acid.
-In secondary structure, two strands of nucleic acids are wound around each other to give double helix structure
-Two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds.
-These bases are complementary to each other because the hydrogen bonds are formed between specific pairs of bases.
-Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine and cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds.
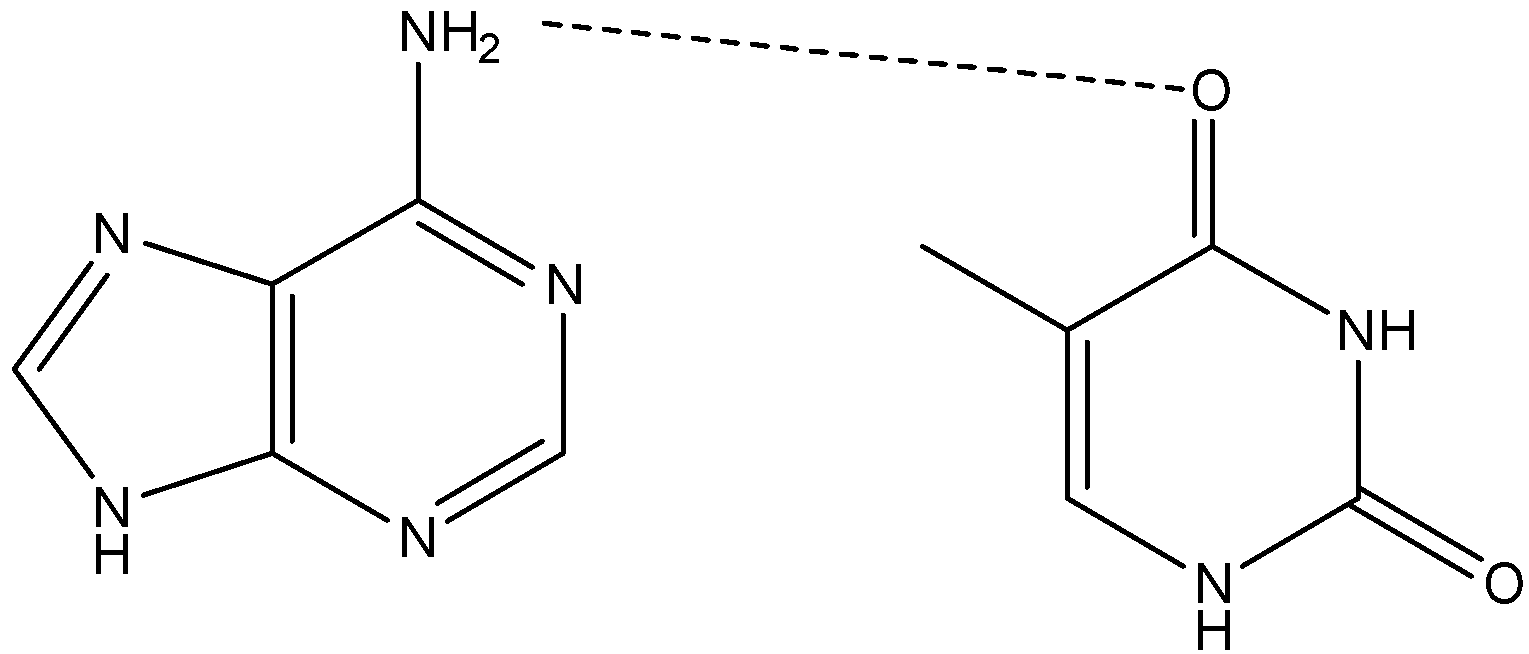
Note: Adenine always pairs with thymine as they both have OH and NH groups, which can form hydrogen bridges , whereas with other bases it is unfavorable as they are each other’s way. Adenine always pairs with thymine because they form two hydrogen bonds. Guanine and cytosine form three hydrogen bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
-There are two types of nucleic acids; DNA and RNA
-DNA IS deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is ribonucleic acid.
-Hydrolysis of DNA and RNA give sugar (Ribose), phosphoric acid and heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms called bases.
-DNA contains four bases -adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine.
-RNA contains four bases- adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil.

Adenine as base

-Base is attached at position 1’ position of sugar which forms nucleoside and phosphoric acid is attached at position 5’ which forms nucleotide.
-nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’ and 3’ carbon atoms of ribose sugar.

-primary structure of DNA contains sequences of nucleotides in the chain of nucleic acid.
-In secondary structure, two strands of nucleic acids are wound around each other to give double helix structure
-Two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds.
-These bases are complementary to each other because the hydrogen bonds are formed between specific pairs of bases.
-Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine and cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds.

Note: Adenine always pairs with thymine as they both have OH and NH groups, which can form hydrogen bridges , whereas with other bases it is unfavorable as they are each other’s way. Adenine always pairs with thymine because they form two hydrogen bonds. Guanine and cytosine form three hydrogen bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




