
In \[\Delta ABC\], \[m\angle B={{90}^{\circ }}\], \[\overline{BM}\bot \overline{AC}\], \[M\in AC\]. If \[AM-CM=7\]and \[A{{B}^{2}}-B{{C}^{2}}=175\], then find AC.
Answer
609.3k+ views
Hint: The line through M divides the \[\Delta ABC\] into two right angles triangles. By using the pythagoras theorem we will write this theorem for \[\Delta AMB\] and \[\Delta BMC\]. After writing the equations by substituting the term given in the question we get the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
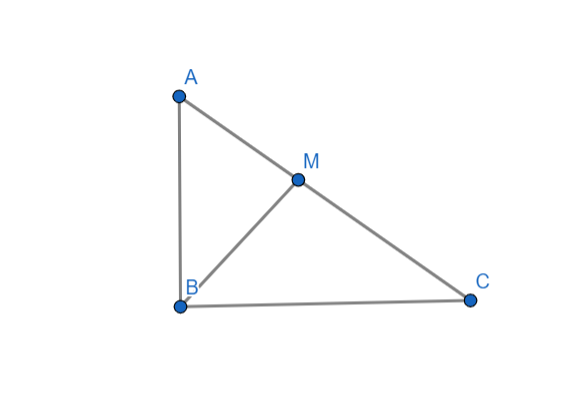
In \[\Delta AMB\]
\[A{{B}^{2}}=A{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}\] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (1)
In \[\Delta BMC\]
\[B{{C}^{2}}=C{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}\] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (2)
By doing (1) – (2) we get
\[A{{B}^{2}}\]- \[B{{C}^{2}}\]\[=A{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}\]- (\[C{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}\])
\[A{{B}^{2}}-~B{{C}^{2}}=A{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}-~C{{M}^{2}}-B{{M}^{2}}\]
By cancelling the common terms we get \[A{{B}^{2}}-~B{{C}^{2}}=A{{M}^{2}}-C{{M}^{2}}\]
\[A{{B}^{2}}-~B{{C}^{2}}=\left( AM+CM \right)\left( AM-CM \right)\]
By substituting the values given in the question we get
\[175=\left( AM+CM \right)\left( 7 \right)\]
\[\left( AM+CM \right)=\dfrac{175}{7}=25\]
\[\left( AM+CM \right)\]= AC
AC = 25.
Therefore we have found the value of AC is 25.
Note: To solve this type of problem first we have to draw the figure. Pythagoras theorem should be used for two right angled triangles. Care should be taken while solving the equation. As we got two right angled triangles we have to use Pythagoras for sure.
Complete step-by-step answer:

In \[\Delta AMB\]
\[A{{B}^{2}}=A{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}\] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (1)
In \[\Delta BMC\]
\[B{{C}^{2}}=C{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}\] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (2)
By doing (1) – (2) we get
\[A{{B}^{2}}\]- \[B{{C}^{2}}\]\[=A{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}\]- (\[C{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}\])
\[A{{B}^{2}}-~B{{C}^{2}}=A{{M}^{2}}+B{{M}^{2}}-~C{{M}^{2}}-B{{M}^{2}}\]
By cancelling the common terms we get \[A{{B}^{2}}-~B{{C}^{2}}=A{{M}^{2}}-C{{M}^{2}}\]
\[A{{B}^{2}}-~B{{C}^{2}}=\left( AM+CM \right)\left( AM-CM \right)\]
By substituting the values given in the question we get
\[175=\left( AM+CM \right)\left( 7 \right)\]
\[\left( AM+CM \right)=\dfrac{175}{7}=25\]
\[\left( AM+CM \right)\]= AC
AC = 25.
Therefore we have found the value of AC is 25.
Note: To solve this type of problem first we have to draw the figure. Pythagoras theorem should be used for two right angled triangles. Care should be taken while solving the equation. As we got two right angled triangles we have to use Pythagoras for sure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




