
In $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ , ${\text{a = 5, b = 12 }}$ and ${\text{c = 13}}$ , how do you find the cosine of each of the angles?
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: In this question, they have given the value of sides of a triangle and asked us to find the cosine value of each of the angles. First, we should verify whether the given triangle is a right-angled triangle or not by using the hypotenuse method. And then, using the formula and properties of trigonometry, we have to find the cosine of each of the angles.
Formula used: Formula of hypotenuse (Pythagorean Theorem): ${\text{ }}{{\text{a}}^2} + {\text{ }}{{\text{b}}^2} = {{\text{c}}^2}$
Where ${\text{c}}$ is hypotenuse and ${\text{ a }}$ and ${\text{b}}$ are the other two sides of the triangle.
Property of trigonometry:
$\cos {{\theta = }}\dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
In this question, we have to find the cosine values of each angle of the triangle given.
Given that in $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ , ${\text{a = 5, b = 12 }}$ and ${\text{c = 13}}$ .
First, we will draw the triangle roughly representing the given data for more understanding.
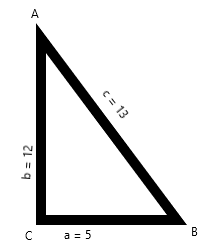
Now, we need to verify whether the given triangle is a right angle triangle or not.
We will verify that using the Pythagorean Theorem (hypotenuse method). The condition to be satisfied is, for every right-angled triangle, ${\text{ }}{{\text{a}}^2} + {\text{ }}{{\text{b}}^2} = {{\text{c}}^2}$ where ${\text{c}}$ is hypotenuse and ${\text{ a }}$ and ${\text{b}}$ are the other two sides of the triangle.
Now, applying the formula in $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$
${5^2} + {12^2} = 25 + 144$
$ = 169$
$ = {13^2}$ , which is the third side.
Therefore this $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ is a right-angled triangle.
Now, we know that
$\cos {{\theta = }}\dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
Then, $\cos {\text{ A = }}\dfrac{{\text{b}}}{{\text{c}}}$
Therefore, $\cos {\text{ A = }}\dfrac{{12}}{{13}}$
$\cos {\text{ B = }}\dfrac{{\text{a}}}{{\text{c}}}$
Therefore, $\cos {\text{ B = }}\dfrac{5}{{13}}$
$\cos {\text{ C = cos 90}}^\circ $
Therefore, $\cos {\text{ C = cos 90}}^\circ = 0$
Hence $\cos {\text{ A = }}\dfrac{{12}}{{13}}$ , $\cos {\text{ B = }}\dfrac{5}{{13}}$ and $\cos {\text{ C }} = 0$ are the required answer.
Note: Students must note that whenever such questions are raised or any question that asks us to find the values of sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant and cotangent of angles are asked, it is mandatory to find or verify whether the given triangle is a right angled triangle or not. This is an important step and carries marks.
Moreover, verifying the given triangle is right angled triangle is important because the values of sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant and cotangent can be found only in right angled triangle. Therefore, it is necessary to verify it.
Formula used: Formula of hypotenuse (Pythagorean Theorem): ${\text{ }}{{\text{a}}^2} + {\text{ }}{{\text{b}}^2} = {{\text{c}}^2}$
Where ${\text{c}}$ is hypotenuse and ${\text{ a }}$ and ${\text{b}}$ are the other two sides of the triangle.
Property of trigonometry:
$\cos {{\theta = }}\dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
In this question, we have to find the cosine values of each angle of the triangle given.
Given that in $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ , ${\text{a = 5, b = 12 }}$ and ${\text{c = 13}}$ .
First, we will draw the triangle roughly representing the given data for more understanding.

Now, we need to verify whether the given triangle is a right angle triangle or not.
We will verify that using the Pythagorean Theorem (hypotenuse method). The condition to be satisfied is, for every right-angled triangle, ${\text{ }}{{\text{a}}^2} + {\text{ }}{{\text{b}}^2} = {{\text{c}}^2}$ where ${\text{c}}$ is hypotenuse and ${\text{ a }}$ and ${\text{b}}$ are the other two sides of the triangle.
Now, applying the formula in $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$
${5^2} + {12^2} = 25 + 144$
$ = 169$
$ = {13^2}$ , which is the third side.
Therefore this $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ is a right-angled triangle.
Now, we know that
$\cos {{\theta = }}\dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
Then, $\cos {\text{ A = }}\dfrac{{\text{b}}}{{\text{c}}}$
Therefore, $\cos {\text{ A = }}\dfrac{{12}}{{13}}$
$\cos {\text{ B = }}\dfrac{{\text{a}}}{{\text{c}}}$
Therefore, $\cos {\text{ B = }}\dfrac{5}{{13}}$
$\cos {\text{ C = cos 90}}^\circ $
Therefore, $\cos {\text{ C = cos 90}}^\circ = 0$
Hence $\cos {\text{ A = }}\dfrac{{12}}{{13}}$ , $\cos {\text{ B = }}\dfrac{5}{{13}}$ and $\cos {\text{ C }} = 0$ are the required answer.
Note: Students must note that whenever such questions are raised or any question that asks us to find the values of sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant and cotangent of angles are asked, it is mandatory to find or verify whether the given triangle is a right angled triangle or not. This is an important step and carries marks.
Moreover, verifying the given triangle is right angled triangle is important because the values of sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant and cotangent can be found only in right angled triangle. Therefore, it is necessary to verify it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




