
In \[Ca{{F}_{2}}\] type (fluorite structure), \[C{{a}^{2+}}\] ions from_(A)_ structure and F ions are present in all_(B)_voids. The coordination number of \[C{{a}^{2+}}\] is _(C)_ and F- is _(D)_.
(A). (B), (C) and (D) respectively are:
A. (A)- ccp; (B)- octahedral; (C)-8; (D)-4
B. (A)- bcc; (B)- tetrahedral; (C)-4; (D)-8
C. (A)- ccp; (B)- tetrahedral; (C)-8; (D)-4
D. (A)- ccp; (B)- octahedral; (C)-4; (D)-8
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Coordination number is also called Ligancy. The number of atoms, or ions that a central metal atom or ion holds as its nearest neighbors in a complex or in a coordination compound or in a crystal is called coordination number. There are two types of lattice structures, ccp and bcc.
ccp - cubic closest packing
bcc - body centered cubic lattice
Complete step by step answer:
In calcium fluoride (\[Ca{{F}_{2}}\]), the calcium ions (\[C{{a}^{2+}}\]) form the cubic closest packing (ccp) structure (let us assume as A) arrangement. The fluoride occupies all the corner positions of the cube and the center position of each face of the cube.
There are two tetrahedral positions present for each calcium ion and the fluoride ions (\[{{F}^{-}}\]) occupies all the tetrahedral sites (let us assume as B). The stoichiometry of the calcium fluoride (\[Ca{{F}_{2}}\]) is 1:2.
Every fluoride in the cube is surrounded by four calcium ions (let us assume as D). While every calcium ion is enclosed by eight fluoride atoms (C) those are located towards the corners of the cube. Then the coordination of the calcium difluoride compound is 8:4.
The structure of \[Ca{{F}_{2}}\] is as follows.
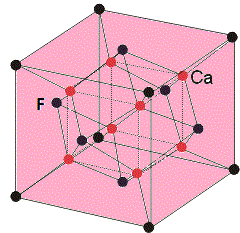
So, the correct answer is (A)- ccp; (B)- tetrahedral; (C)-8; (D)-4
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Don’t be confused with calcium fluoride (\[Ca{{F}_{2}}\]), and fluorite. Both are the same. Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride,\[Ca{{F}_{2}}\]. Calcium fluorite absorbs and neutralizes negative energy and stress.
ccp - cubic closest packing
bcc - body centered cubic lattice
Complete step by step answer:
In calcium fluoride (\[Ca{{F}_{2}}\]), the calcium ions (\[C{{a}^{2+}}\]) form the cubic closest packing (ccp) structure (let us assume as A) arrangement. The fluoride occupies all the corner positions of the cube and the center position of each face of the cube.
There are two tetrahedral positions present for each calcium ion and the fluoride ions (\[{{F}^{-}}\]) occupies all the tetrahedral sites (let us assume as B). The stoichiometry of the calcium fluoride (\[Ca{{F}_{2}}\]) is 1:2.
Every fluoride in the cube is surrounded by four calcium ions (let us assume as D). While every calcium ion is enclosed by eight fluoride atoms (C) those are located towards the corners of the cube. Then the coordination of the calcium difluoride compound is 8:4.
The structure of \[Ca{{F}_{2}}\] is as follows.

So, the correct answer is (A)- ccp; (B)- tetrahedral; (C)-8; (D)-4
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Don’t be confused with calcium fluoride (\[Ca{{F}_{2}}\]), and fluorite. Both are the same. Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride,\[Ca{{F}_{2}}\]. Calcium fluorite absorbs and neutralizes negative energy and stress.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




